Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Cardiol. Dec 26, 2016; 8(12): 689-694
Published online Dec 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i12.689
Published online Dec 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i12.689
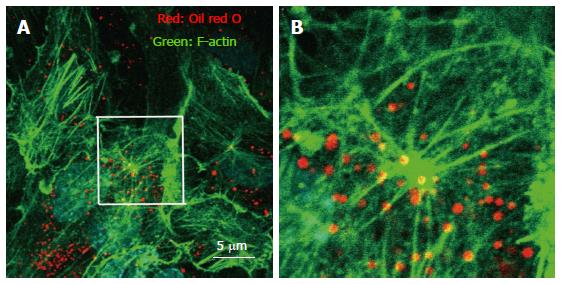
Figure 1 Immunohistochemistry of actin, and visualization of vesicle structures after free cholesterol loading and angiotensin II in cultured human aortic endothelial cells.
The cells were loaded by cholesterol-saturated methyl-b-cyclodextrin (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) (Chol/MBCD) and angiotensin II (Wako, Tokyo, Japan) (200 nmol/L). Following treatment, cell were fixed, and stained using Alexa 546-conjugated phalloidin (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) for visualization of F-actin and oil red O for visualization of vesicle structure. Oil red O-positive vesicles formed, and moved along the F-actin filament in the setting of actin remodeling induced by angiotensin II. B is a magnified view of the white square in A.
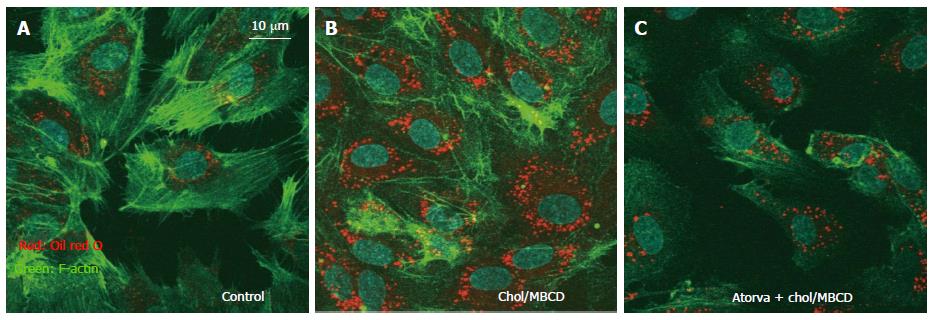
Figure 2 Immunohistochemistry of actin and visualization of vesicle structures after free cholesterol loading and atorvastatin pretreatment in cultured human aortic endothelial cells.
The cells were loaded by cholesterol-saturated methyl-b-cyclodextrin (Chol/MBCD) with and without atorvastatin (10 μmol/L) pretreatment. Atorvastatin (Pfizer, New York, NY) pretreatment (C) significantly suppressed formation of vesicles induced by free cholesterol loading, as shown by oil red O as compared with Chol/MBCD loading alone (B); A: Control.
- Citation: Amiya E. Interaction of hyperlipidemia and reactive oxygen species: Insights from the lipid-raft platform. World J Cardiol 2016; 8(12): 689-694
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v8/i12/689.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v8.i12.689