Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Cardiol. Oct 26, 2016; 8(10): 559-565
Published online Oct 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i10.559
Published online Oct 26, 2016. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v8.i10.559
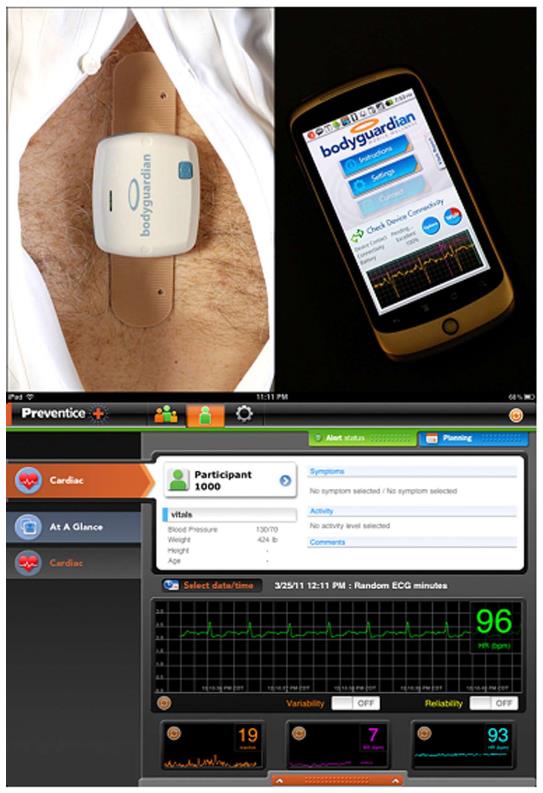
Figure 1 Remote monitoring system.
Top left: The rechargeable module is attached to the adhesive SnapStrip. The SnapStrip is positioned vertically over the sternum. Top right: The cellphone serves as (1) a wireless communication hub with the cloud and (2) as a user interface. Bottom: Recorded physiologic data including ECG and heart rate are presented on an iPAD for analysis and review. ECG: Electrocardiograph.
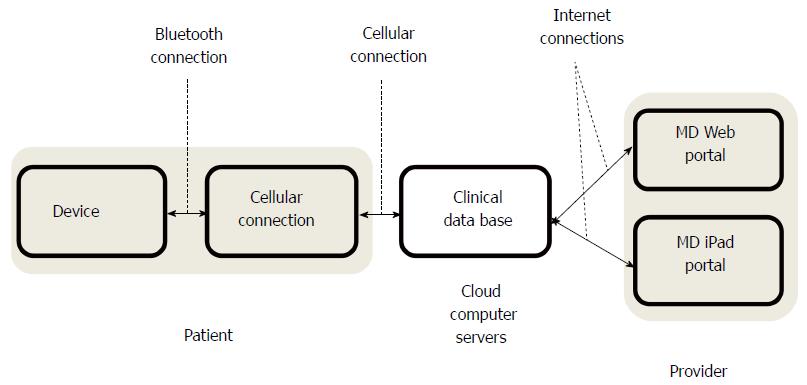
Figure 2 Remote monitoring system architecture.
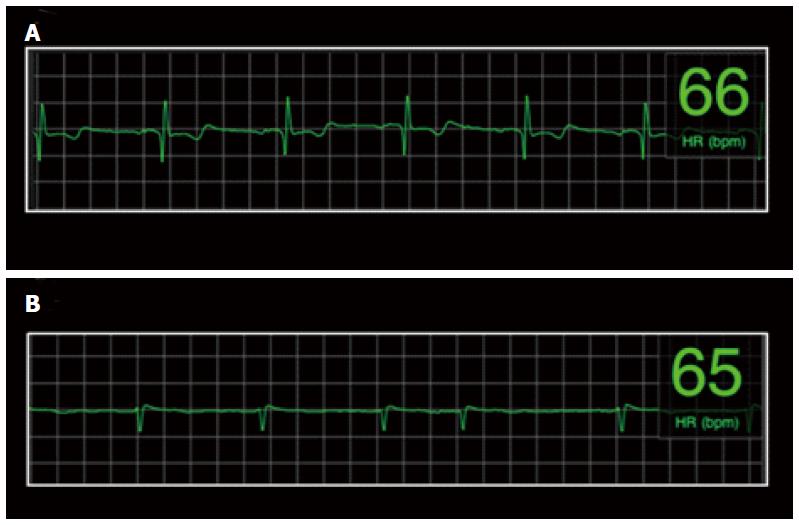
Figure 3 Representative examples of electrocardiograph strips.
A: This strip demonstrates sinus rhythm. All 4 raters scored this strip as having high quality (score 3); B: This strip demonstrates atrial fibrillation. Although the raters quality score ranged from 1 through 3, the irregularly irregular RR interval and absence of discernible P waves present in this Electrocardiograph signal is diagnostic for atrial fibrillation.
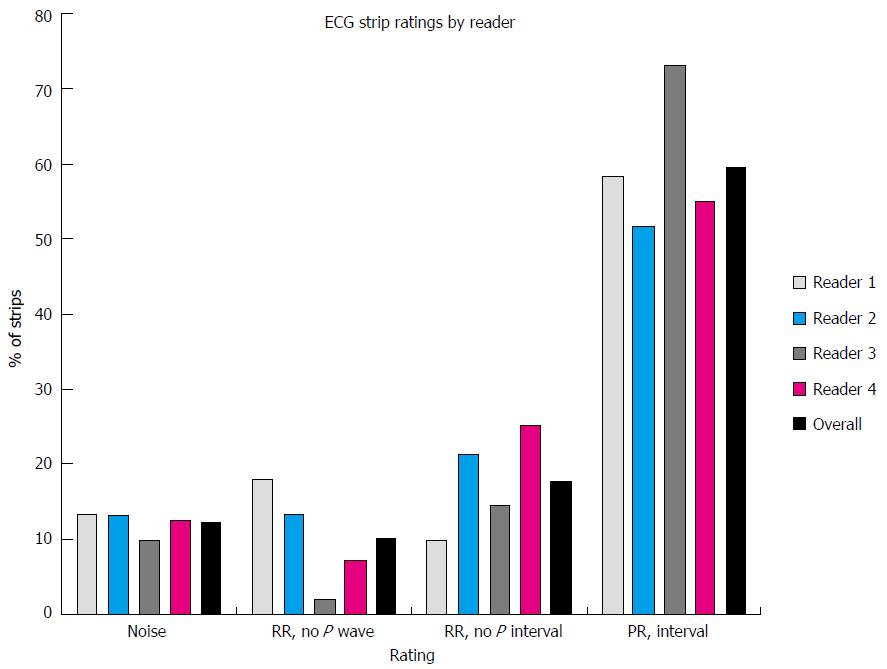
Figure 4 Electrocardiograph strip ratings by reader.
Average combined and individual assessments of electrocardiograph quality based on 4 independent experienced raters. The vertical axis represents the percentage of strips rated within each category for each reader. ECG: Electrocardiograph.
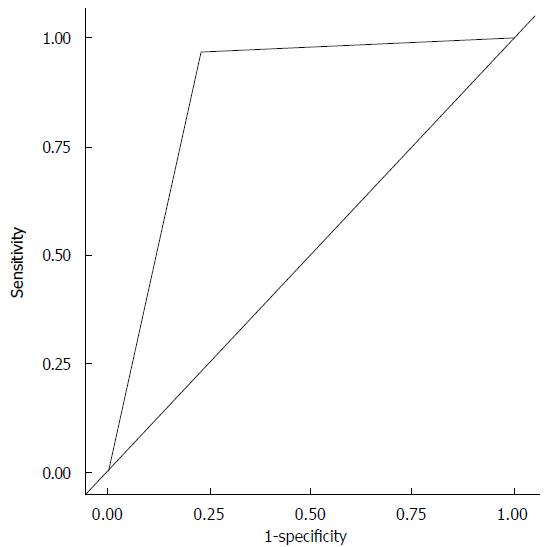
Figure 5 Receiver operator characteristic curve for atrial fibrillation using heart rate variability ≥ 7.
- Citation: Bruce CJ, Ladewig DJ, Somers VK, Bennet KE, Burrichter S, Scott CG, Olson LJ, Friedman PA. Remote electrocardiograph monitoring using a novel adhesive strip sensor: A pilot study. World J Cardiol 2016; 8(10): 559-565
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v8/i10/559.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v8.i10.559