Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Cardiol. Sep 26, 2015; 7(9): 511-524
Published online Sep 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i9.511
Published online Sep 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i9.511
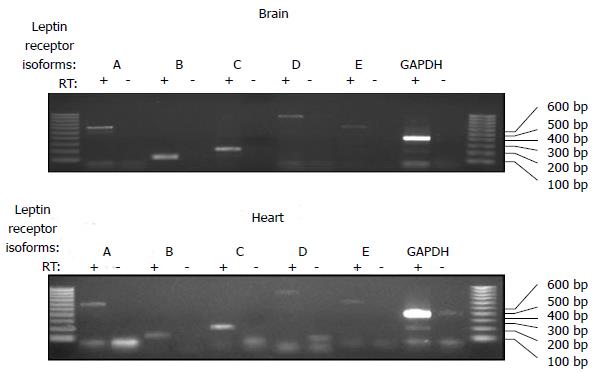
Figure 1 Comparison of leptin receptor isoforms in the mouse brain and heart.
RNA was isolated from the brain and heart and reverse transcribed into cDNA. Polymerase chain reaction was then performed using primers specific for each mouse isoform of the leptin receptor as previously described[12]. All 5 of the leptin receptor isoforms were detected in the mouse heart as well as the brain.
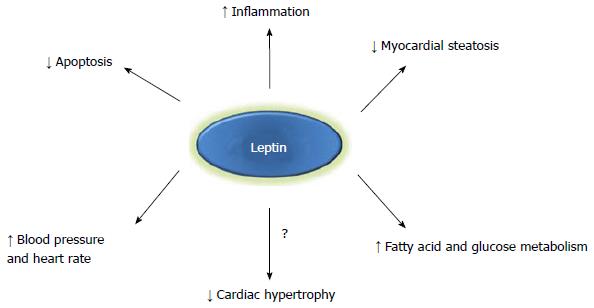
Figure 2 Potential mechanisms by which leptin may mediate cardiac function.
Leptin may exert cardioprotective or maladaptive effects through hemodynamic factors such as increased heart rate and blood pressure, metabolic changes including augmented fatty acid or glucose utilization, reduced cardiac apoptosis, or structural cardiac changes such reduced cardiac lipid accumulation and possibly attenuated myocardial hypertrophy. Increased inflammation may be beneficial in some cardiac conditions (i.e., post-myocardial infarction) depending on the timing and extent of the inflammatory response.
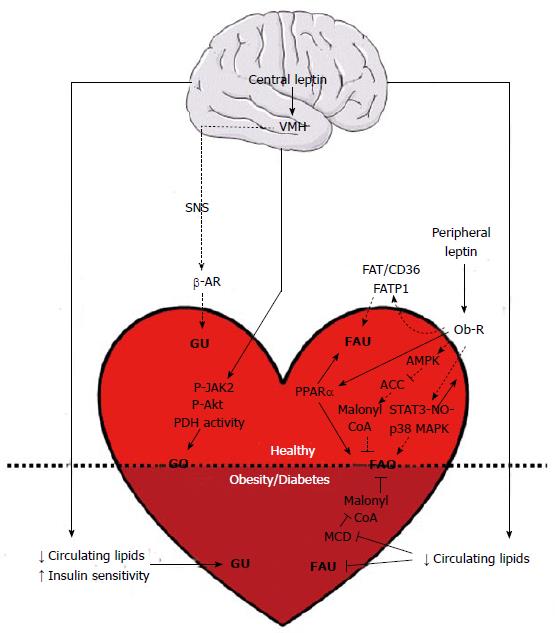
Figure 3 Cardiometabolic effects of leptin in health and obesity.
Triangular and flat arrowheads represent stimulatory and inhibitory effects on the designed targets, respectively. Dotted lines indicate acute leptin effects (appearing between less than an hour and several hours of treatment), while plain lines represent chronic leptin effects (reported after several days or weeks of treatment). ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; β-AR: Beta-adrenergic receptor; FAO: Fatty acid oxidation; FAT/CD36: Fatty acid translocase/cluster of differentiation 36; FATP1: Fatty acid transport protein 1; FAU: Fatty acid uptake; GO: Glucose oxidation; GU: Glucose uptake; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCD: Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase; NO: Nitric oxide; Ob-R: Leptin receptor; P-Akt: Phosphorylated Akt kinase; PDH: Pyruvate dehydrogenase; P-JAK2: Phosphorylated Janus kinase 2; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; SNS: Sympathetic nervous system; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; VMH: Ventromedial hypothalamus. Horizontal black line demarcates differences between the healthy heart and the heart in obesity/diabetes.
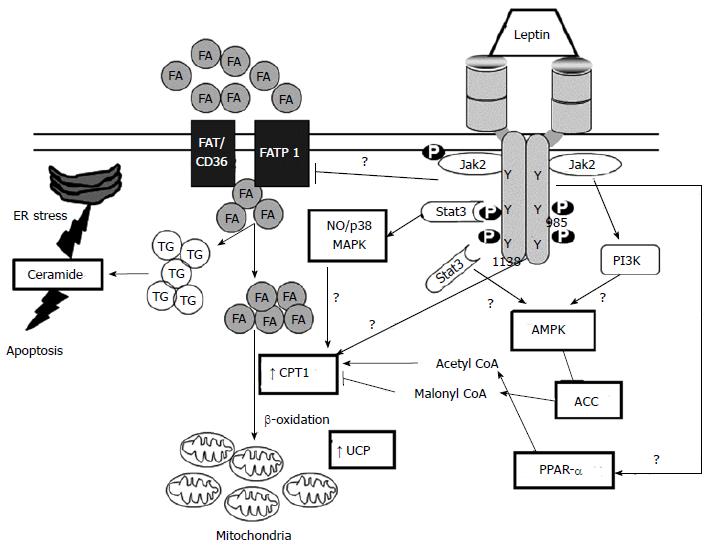
Figure 4 Leptin and cardiac lipotoxicity.
Triangular and flat arrowheads represent stimulatory and inhibitory effects on the designed targets, respectively. Heavier lines represent proposed actions of leptin. ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; CPT-1: Carnitine palmityl transferase-1; ER: Endoplasmatic reticulum; FA: Fatty acids; FAT/CD36: Fatty acid translocase/cluster of differentiation 36; FATP1: Fatty acid transport protein 1; NO: Nitric oxide; P-JAK2: Phosphorylated Janus kinase 2; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TG: Triglycerides; UCP: Uncoupling protein.
- Citation: Hall ME, Harmancey R, Stec DE. Lean heart: Role of leptin in cardiac hypertrophy and metabolism. World J Cardiol 2015; 7(9): 511-524
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v7/i9/511.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v7.i9.511