Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2015; 7(6): 306-310
Published online Jun 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i6.306
Published online Jun 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i6.306
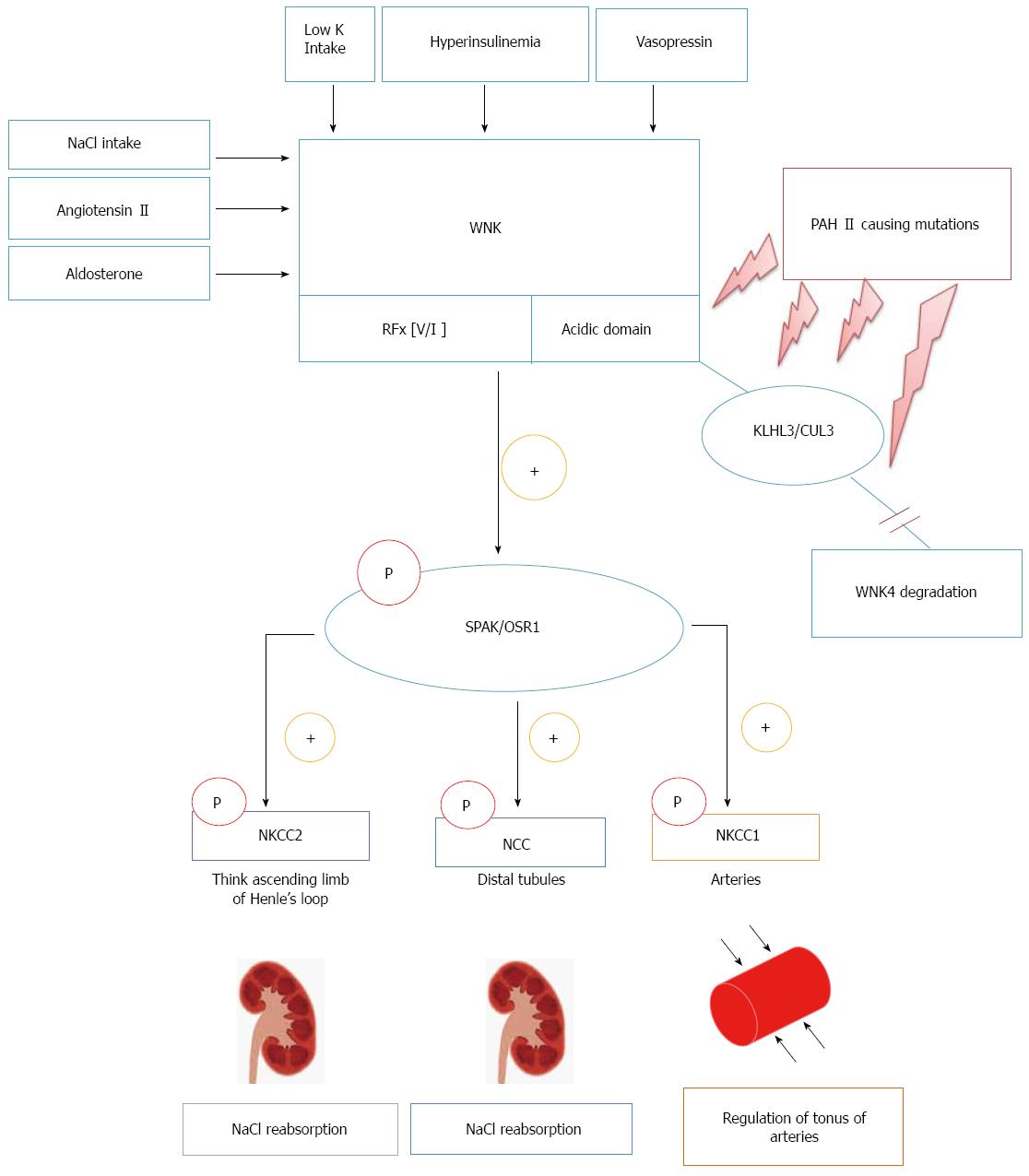
Figure 1 Potential mechanisms of With-no-lysine (K) - SPS1-related proline/alanine-rich kinase/oxidative stress-responsive kinase 1 - Na-Cl co-transporter/Na+-K+-2Cl (-) cotransporter to contribute to hypertension.
Several regulators of the activation of WNK cascade, such as KLHL3/CUL3, low potassium intake, hyperinsulinemia and some hormones (angiotensin II, aldosterone and vasopressin) may act on the kidneys or aortic tissues. SPAK and OSR1 are activated via phosphorylation by upstream WNK kinases using docking site in the RFX (V/I). As a result, SPAK/OSR1 may regulate cation-chloride-coupled cotransporters in kidneys, tonus of aortic tissues, and blood pressure. PAH II causing mutations in acidic domain of WNK4, KLHL3 and Cullin 3 activate SPAK/OSR1-NCC signaling by decreasing WNK4 degradation and accumulation of WNK4. KLHL3: Kelch kinase protein-3; CUL3: Cullin3; PAH II: Pseudohypoaldosteronism type II; WNK: With-no-lysine (K); SPAK: SPS1-related proline/alanine-rich kinase; NCC: Na-Cl co-transporter; NKCC: Na+-K+-2Cl (-) cotransporter; OSR1: Oxidative stress-responsive kinase 1.
- Citation: Lin GM, Liu PY, Wu CF, Wang WB, Han CL. Perspective of future drugs targeting sterile 20/SPS1-related proline/alanine-rich kinase for blood pressure control. World J Cardiol 2015; 7(6): 306-310
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v7/i6/306.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v7.i6.306