Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Cardiol. Dec 26, 2015; 7(12): 843-860
Published online Dec 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.843
Published online Dec 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.843
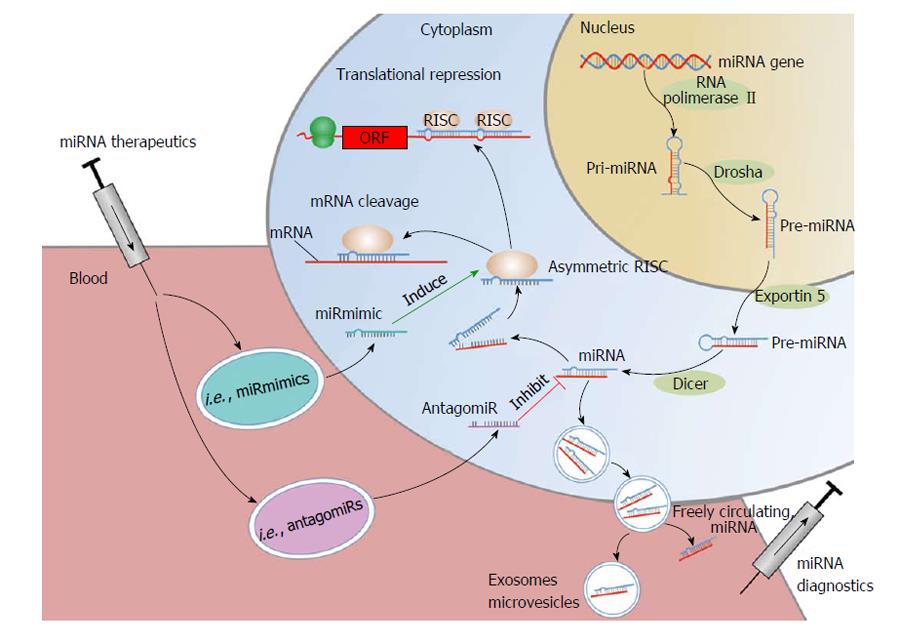
Figure 1 microRNA synthesis and mode of function.
Pri-miRNAs are generated in the nucleus by RNA polymerase II. The endonuclease “Drosha” catalyzes the transformation of pri-miRNA into pre-miRNA, which is transported into the cytoplasm by Exportin 5. Subsequently, the mature miRNA is generated by the endonuclease “Dicer”. The mature miRNA is incorporated into the RISC complex; in this form leading to degradation of target mRNAs and/or inhibition of translation. Mature miRNAs can be released into the circulation, incorporated into vesicles such as MVB, exosomes, microvesicles or as freely circulating miRNAs. miRNA therapeutics such as miRmimics and antagomirs can be administered directly into the blood flow or applied by oral uptake. Antagomirs specifically bind to and silence endogenous miRNAs, leading to reduced RISC activation and mRNA degradation. miRmimics specifically bind to target mRNAs to increase their degradation. mRNA: Messenger RNA; miRNA: microRNA; ORF: Open reading frame; RISC: RNA-induced silencing complex; MVB: Multivescular bodies.
- Citation: Schulte C, Westermann D, Blankenberg S, Zeller T. Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating microRNAs in heart failure with preserved and reduced ejection fraction. World J Cardiol 2015; 7(12): 843-860
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v7/i12/843.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v7.i12.843