Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Cardiol. Oct 26, 2015; 7(10): 609-620
Published online Oct 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i10.609
Published online Oct 26, 2015. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v7.i10.609
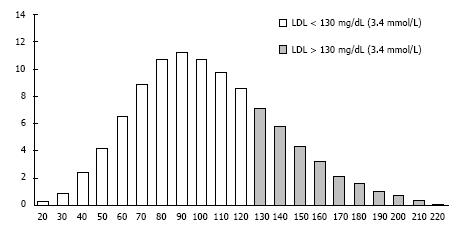
Figure 1 Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels on admission in patients with acute coronary syndrome[74].
LDL: Low-density lipoprotein.
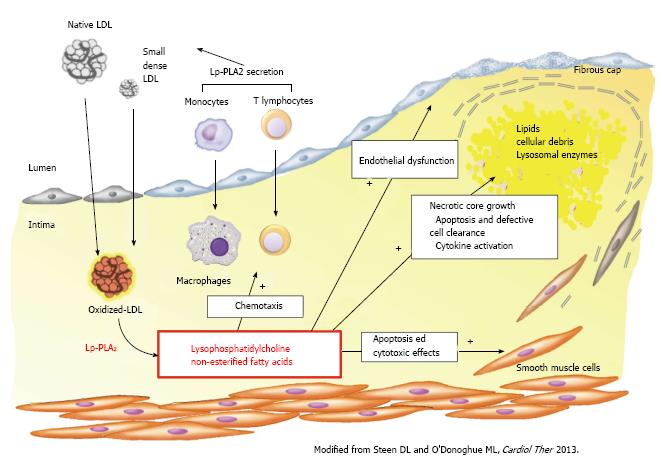
Figure 2 Pathogenic role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in atherosclerosis development.
LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; Lp-PLA2: Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2.
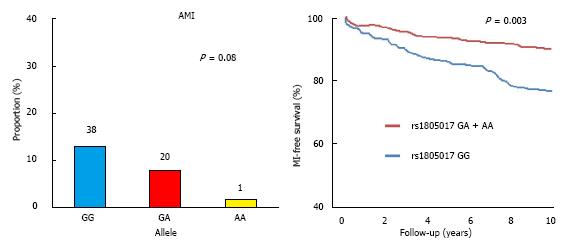
Figure 3 Increased number of acute myocardial infarction depending on the variant gene Arg92His.
A: The patients with variant gene GG (Arg92) have a greater number of infarcts compared to the other two variants; B: The Kaplan-Meyer curve shows a lower survival free from acute myocardial infarction in patients with variant GG (Arg92). AMI: Acute myocardial infarction.
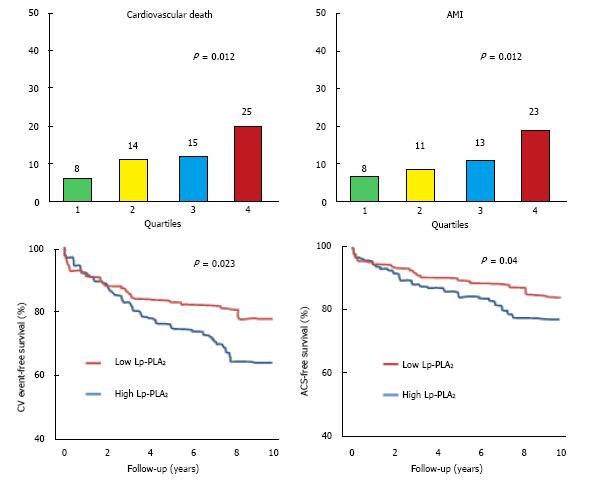
Figure 4 The Kaplan-Meyer curves underline a greater survival free from cardiovascular events (death, acute myocardial infarction) in patients with lower lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity.
ACS: Acute coronary syndrome; CV: Cardiovascular.
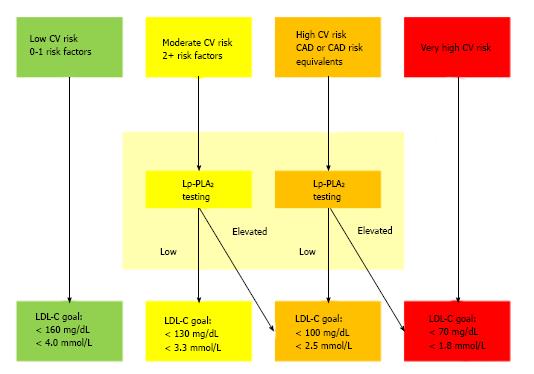
Figure 5 Relevance of measuring of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity for risk stratification in adult patients with moderate cardiovascular risk (> 2 risk factors) or higher[80].
Lp-PLA2: Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2; LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; CAD: Coronary artery disease; CV: Cardiovascular.
- Citation: Maiolino G, Bisogni V, Rossitto G, Rossi GP. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 prognostic role in atherosclerotic complications. World J Cardiol 2015; 7(10): 609-620
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v7/i10/609.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v7.i10.609