Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. Sep 26, 2014; 6(9): 968-984
Published online Sep 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i9.968
Published online Sep 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i9.968
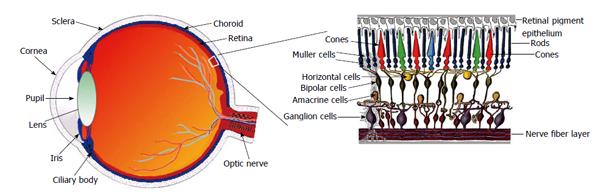
Figure 1 A drawing of a section through the human eye with a schematic enlargement of the retina [Helga Kolb from AMER Sci (2003)].
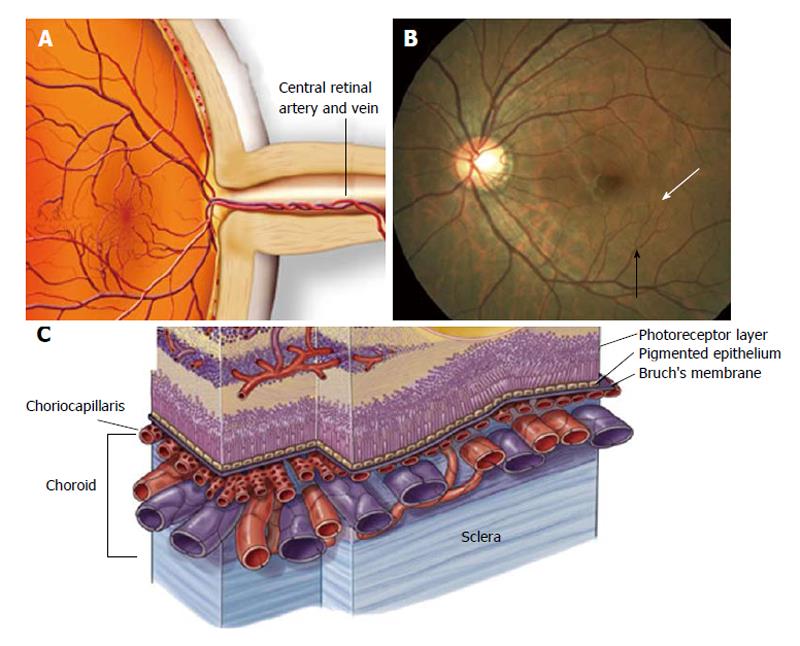
Figure 2 Anatomy of ocular circulation.
A: Central retinal artery and vein respectively; B: Arteriole (black arrowhead); capillaries (white arrowhead); C: Choroidal vasculature (Anand-Apte, Hollyfield, Academic Press, Elsevier Books, 2009; 9-15).
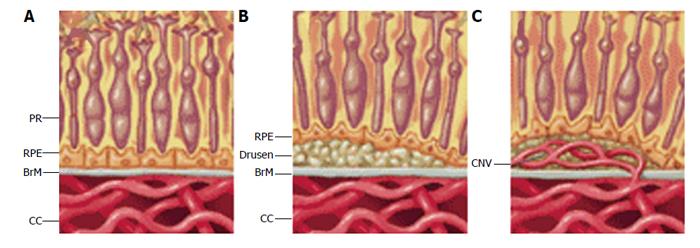
Figure 3 The pathologic changes to the retina and choroidal blood vessels typical of dry and early wet age-related macular degeneration respectively.
A: Control; B: Early age-related macular degeneration (AMD); C: Wet AMD. PR: Photoreceptors; RPE: Retinal pigment epithelium; BrM: Brusch’s membrane; CC: Choriocapillaries; CNV: Choroidal neovascularization (provided by the OcuCure Therapeutics’ website).
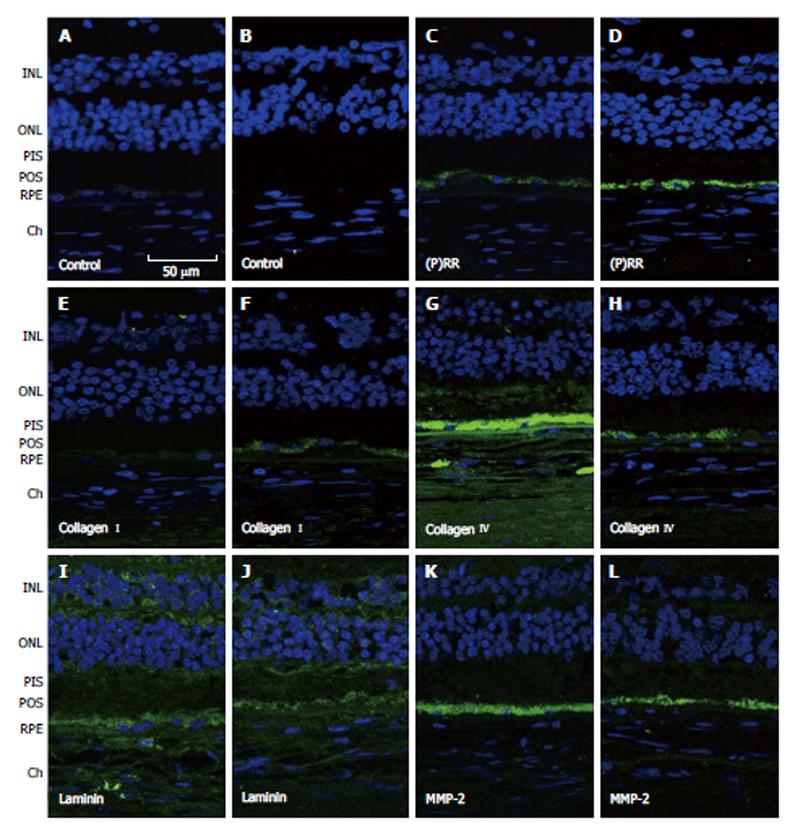
Figure 4 Representative immunofluorescent double staining of prorenin receptor, collagen types I and IV, laminin and matrix metalloproteinase-2 (green) and nuclei (bleu) in retina sections from human donor eyes with no known eye disease (B, D, F, H, J and L), and human donor eyes with dry age-related macular degeneration and hypertension (A, C, E, G, I and K)[121].
Negative controls were generated by omission of the primary antibody (A and B). Sections were analyzed by using confocal microscopy (original magnification, × 40). INL: Inner sections were analyzed with a confocal microscope at a magnification of × 40. INL: Inner nuclear layer; ONL: Outer nuclear layer; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinase; PIS: Photoreceptor inner segments; POS: Photoreceptor outer segments; RPE: Retinal pigment epithelium; Ch: Choroid.
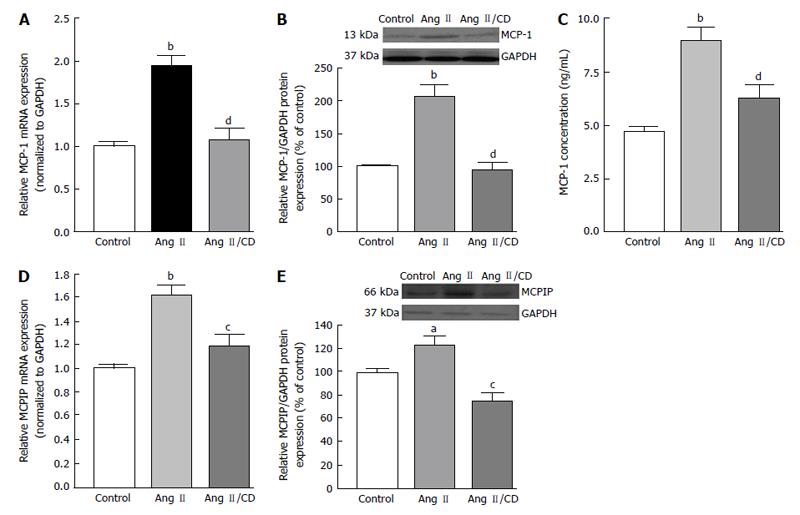
Figure 5 Hypertension-induced Angiotensin II up-regulated monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 induced protein expression through AT1R activation in retinal pigmented epithelium-choroid[140].
C57BL 6 mice were treated with saline (1), Ang II (2), and Ang II in combination with candesartan (10 mg/kg per day) (3). Blood pressure was recorded before and after treatment. After 30 d of treatment, animals were sacrificed and eyes enucleated and collected for microdisection of retinal pigmented epithelium-choroid. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and MCP-1 induced protein (MCPIP) proteins were analyzed by real-time PCR and Western blot. MCP-1 and MCPIP mRNA expression by real-time PCR (A and D), protein expression by Western blot (B and E), and MCP-1 protein secretion by ELISA (C). GAPDH was used as control. Data are expressed as mean ± SE (n = 3). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs Ang II-treated animals. CD: Candesartan. Ang: Angiotensin; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; GAPDH: Glyceraldegyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; ELISA: Enzyme-linked immuno assay.
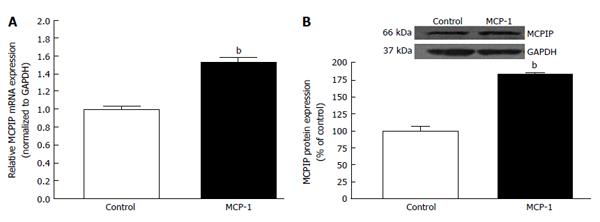
Figure 6 Monocyte chemoattractant protein up-regulates monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 induced protein expression in ARPE-19 cells[140].
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) increases MCP-1 induced protein (MCPIP) mRNA (A) and MCPIP protein expression (B) in human retinal pigment epithelium cells. The maintenance medium was deprived of phenol red for 2 d. Medium FBS content was then brought down from 10% to 1% for 1 d. Subsequently, cells were treated with with 50 pg/mL MCP-1 for 24 h in a medium supplemented with 0.1% FBS. Cell homogenates were collected to assess MCPIP expression by real-time PCR and Western blot. GAPDH was used as control. Data are mean ± SE (n = 4). bP < 0.01 vs control cells; FBS: Medium with fetal bovine serum; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
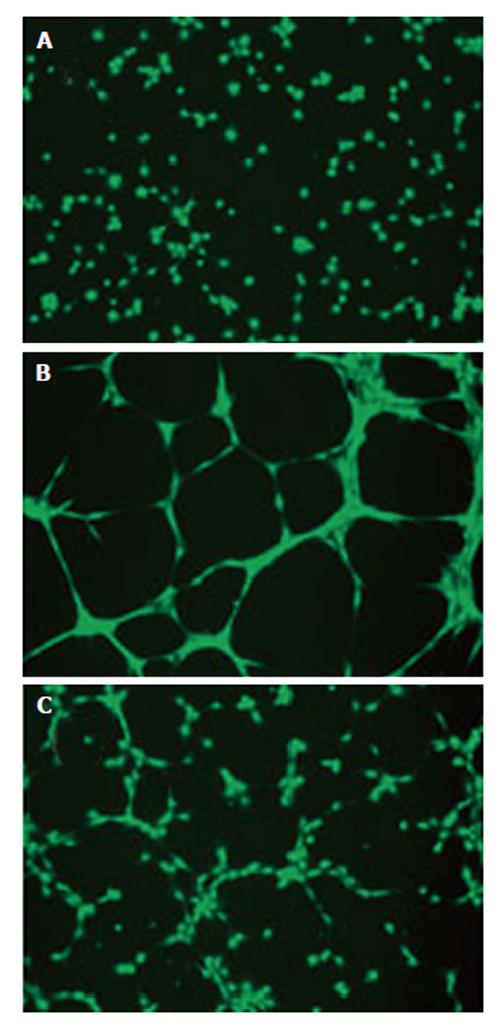
Figure 7 Conditioned medium collected from human ARPE-19 cells exposed to Ang II promotes tube formation in choroidal microvascular endothelial through AT1 activation[140].
Cells were exposed to: (1) Ang II alone; or (2) Ang II in combination with candesartan for 24 h, supernatants were collected after treatment and human choroidal microvascular endothelial (cECs) were treated with the supernatants for 24 h. Thereafter, cells were trypsinized and then seeded (42000 cells/cm2) on a 24-well polystyrene plate coated with Geltrex™ (50 μL/cm2) according to the manufacturer’s protocol followed by incubation in EBM medium for 24 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2. At 16 h post-seeding, 2 μg/mL of Calcein, AM (Invitrogen, Cat # C3099), was added directly to the culture well and allowed to incubate for 20 min (37 °C, 5% CO2). Cells were visualized using a fluorescence microscope. A: Control; B: cECs exposed to conditioned medium from Ang II-treated ARPE-19 cells; C: cECs treated with medium collected from treated retinal pigment epithelium cells. EBM: Endothelial cell basal; AM: Acetoxymethyl.
- Citation: Marin Garcia PJ, Marin-Castaño ME. Angiotensin II-related hypertension and eye diseases. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(9): 968-984
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i9/968.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i9.968