Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. Aug 26, 2014; 6(8): 874-877
Published online Aug 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i8.874
Published online Aug 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i8.874
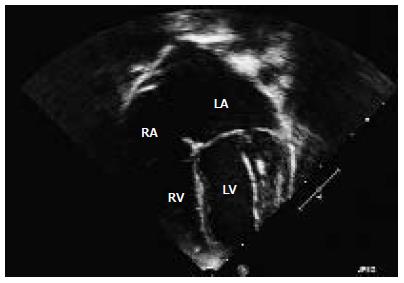
Figure 1 Four-chamber echocardiographic images illustrating echogenic left papillary muscle and chordae apparatus.
LV: Left ventricle; LA: Left atrium; RA: Right atrium; RV: Right ventricle.
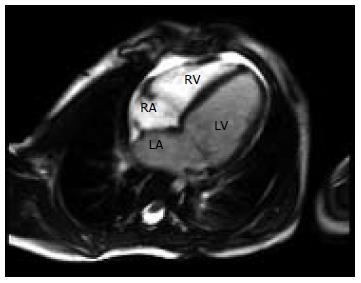
Figure 2 Four-chamber cardiac magnetic resonance cine imaging demonstrating a dilated left atrium and left ventricle.
LV: Left ventricle; LA: Left atrium; RA: Right atrium; RV: Right ventricle.
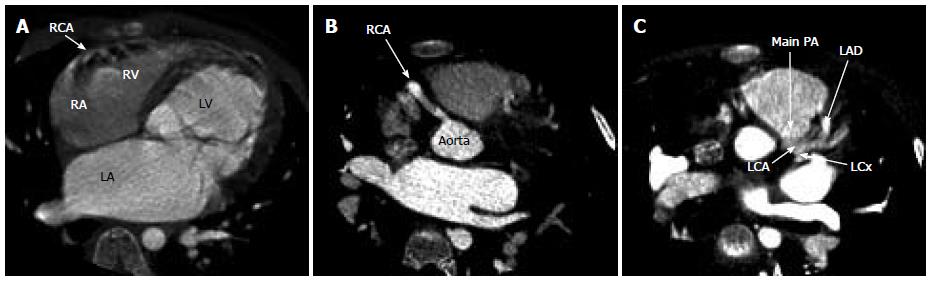
Figure 3 Computed tomographic angiography.
A: Computed tomographic angiography demonstrating extensive collateral vessels from the right coronary artery as well as a dilated left ventricle; B: Computed tomographic angiography showing dilated right coronary artery; C: Computed tomographic angiography illustrating the left anterior descending artery communicating with the main pulmonary artery. LV: Left ventricle; LA: Left atrium; RA: Right atrium; RV: Right ventricle; RCA: Right coronary artery; LAD: Left anterior descending artery; LCA: Left coronary artery; LCx: Left circumflex artery; PA: Pulmonary artery.
- Citation: Lam JC, Giuffre M, Myers KA. Late intervention in an asymptomatic pediatric patient with anomalous left coronary artery. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(8): 874-877
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i8/874.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i8.874