Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2014; 6(7): 653-662
Published online Jul 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i7.653
Published online Jul 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i7.653
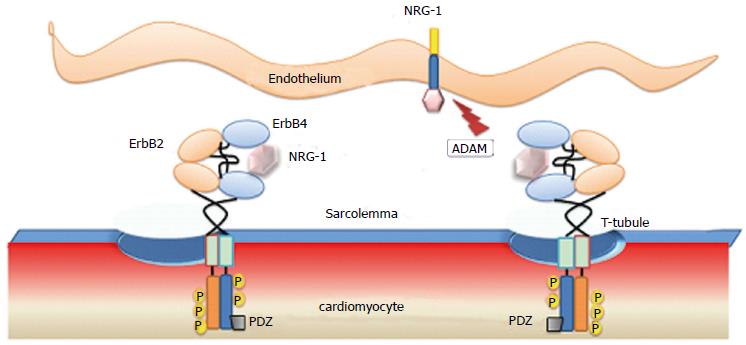
Figure 1 Endothelium-Cardiac muscle interactions through paracrine neuregulin-1 signaling.
Secreted neuregulin-1 from endothelial cells binds to erbB4 inducing auto- and trans-phosphorylation of ErbB2/ErbB4 heterodimers, expressed in cardiomyocytes. NRG-1: Neuregulin-1; PDZ: Postsynaptic density 95, disc large and zona occludens-1 homologous protein domain; ADAM: A desintegrin and metallopeptidase; P: Phosphorylated tyrosine.
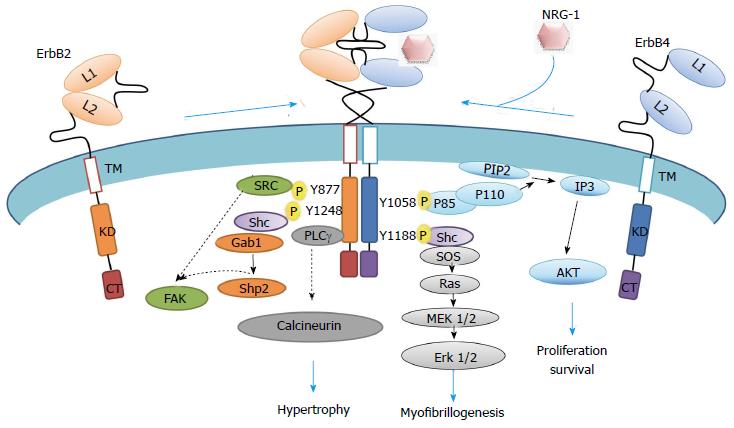
Figure 2 Representation of neuregulin-1-erbB2/erbB4 intracellular signaling cascade.
Schematic representation of active ErbB2/ErbB4 heterodimers through phosphorylation, which phosphosites are docking sites for intracellular molecules involved in pathways that modulate myocyte biology. Specific non-phosphorylated residues interact to PDZ domain proteins. CT: Cytoplasmic tail; KD: Kinase domain; L: Ligand binding site; TM: Transmembrane domain; NRG-1: Neuregulin-1; PIP2: Phosphoinositol-2-phosphate; SOS: Son of sevenless; IP3: Inositol triphosphate; AKT: Thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1, a serine/threonine protein kinase; MEK: Mitogen activated kinase erk kinase; Shc: Src homology domain containing transforming protein; Shp: Protein tyrosine phosphatase; FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; Gab: Binding protein of growth factor bound protein Grb2; P: Phosphorylated tyrosine residues.
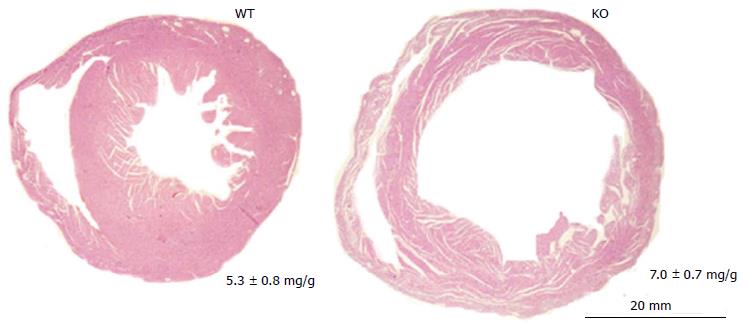
Figure 3 Ventricular specific erbB4-knockout leads to adult dilated cardiomyopathy.
Representative image of transverse ventricular sections stained with hematoxilin-eosin. Camber dilation is overt in mouse erbB4-KO hearts in the adulthood. WT: Wild type; KO: Knock-out.
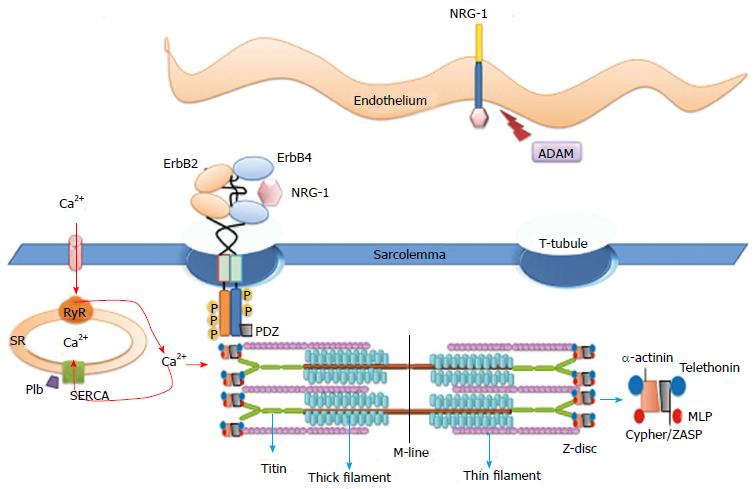
Figure 4 Functional interaction of molecules placed at the T-tubules.
The ErbB2 and ErbB4 proteins are localized to the T-tubules. This compartment of the sarcolemma provides specific sites for functional interactions with molecules at the sarcoplasmic reticulum and at the myofibril Z-band. Molecular interactions at the T-tubules and at the intercalated discs provide the electric-contractile coupling of the myocardium. Scheme of the sarcomeric units of thin and thick filaments are anchored by titin and actin at the Z-band viaα-actinin scaffold protein complex. Muscle LIM domain protein (MLP), telethonin (T-cap) and PDZ and LIM domain protein (ZASP). PDZ: Postsynaptic density 95, disc large and zonula occludens-1; ADAM: A desintegrin and metallopeptidase; SERCA: Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase; Plb: Phospholamban; RyR: Ryanodine receptor; SR: Sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- Citation: Vasti C, Hertig CM. Neuregulin-1/erbB activities with focus on the susceptibility of the heart to anthracyclines. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(7): 653-662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i7/653.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i7.653