Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2014; 6(6): 393-404
Published online Jun 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i6.393
Published online Jun 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i6.393
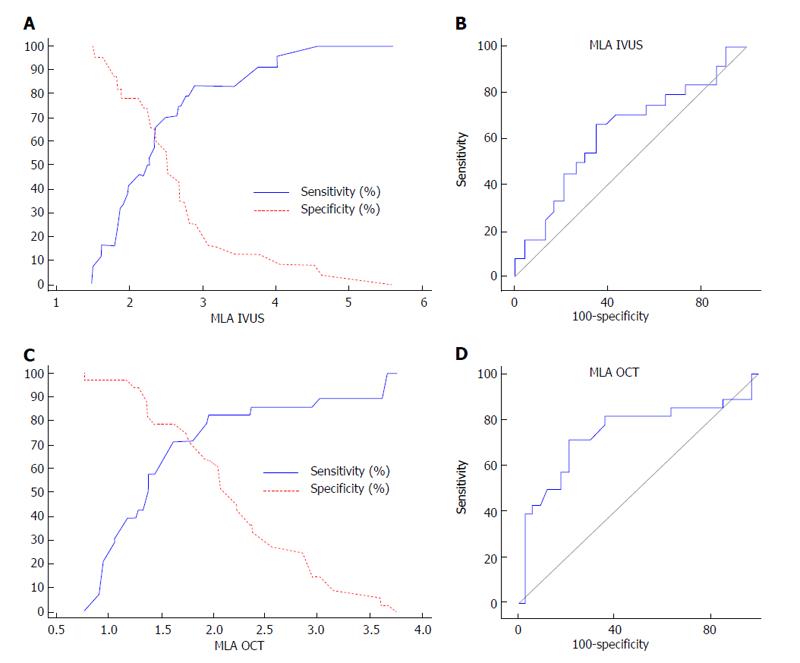
Figure 1 Intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography derived minimum lumen area and fractional flow reserve.
A: Sensitivity and specificity curve for IVUS-derived MLA to predict FFR ≤ 0.80; B: Receiver-operating characteristic curve for IVUS-derived MLA to predict FFR ≤ 0.80; C: Sensitivity and specificity curve for OCT-derived MLA to predict FFR ≤ 0.80; D: Receiver-operating characteristic curve for OCT-derived MLA to predict FFR ≤ 0.80[19]. MLA: Minimum lumen area; IVUS: Intravascular ultrasound; OCT: Optical coherence tomography; FFR: Fractional flow reserve.
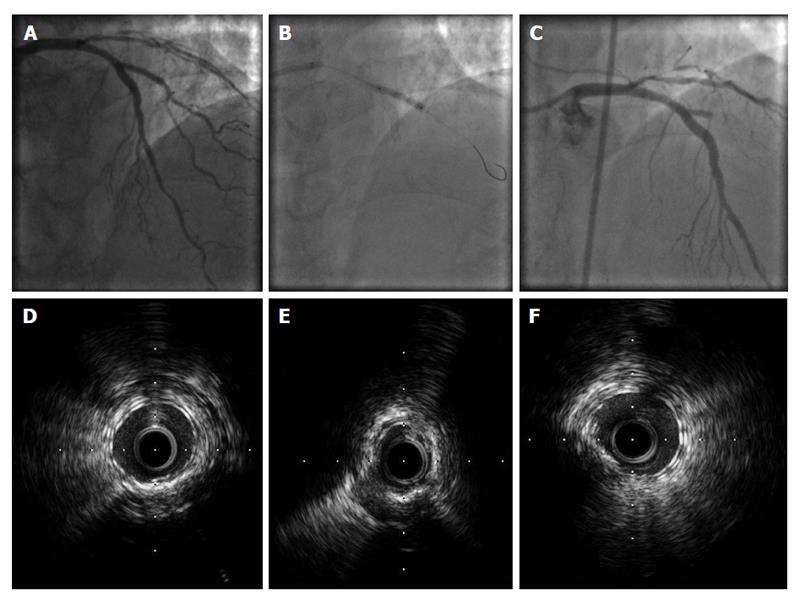
Figure 2 Intravascular ultrasound findings in patient with stent failure.
A: Left anterior descending-Diagonal bifurcation treated with everolimus-eluting stent implantation in the left anterior descending and bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting scaffold implantation (T-stenting) in the diagonal branch; B: Post-dilatation with a noncompliant balloon in the diagonal branch; C: Four days later, the patient presented with acute myocardial infarction and stent thrombosis in the diagonal branch; D-E: Post-intervention IVUS showed stent underexpansion in the mid part of the diagonal branch (E) with good stent expansion at the proximal part (D) and at the distal part (F) of the diagonal branch. IVUS: Intravascular ultrasound.
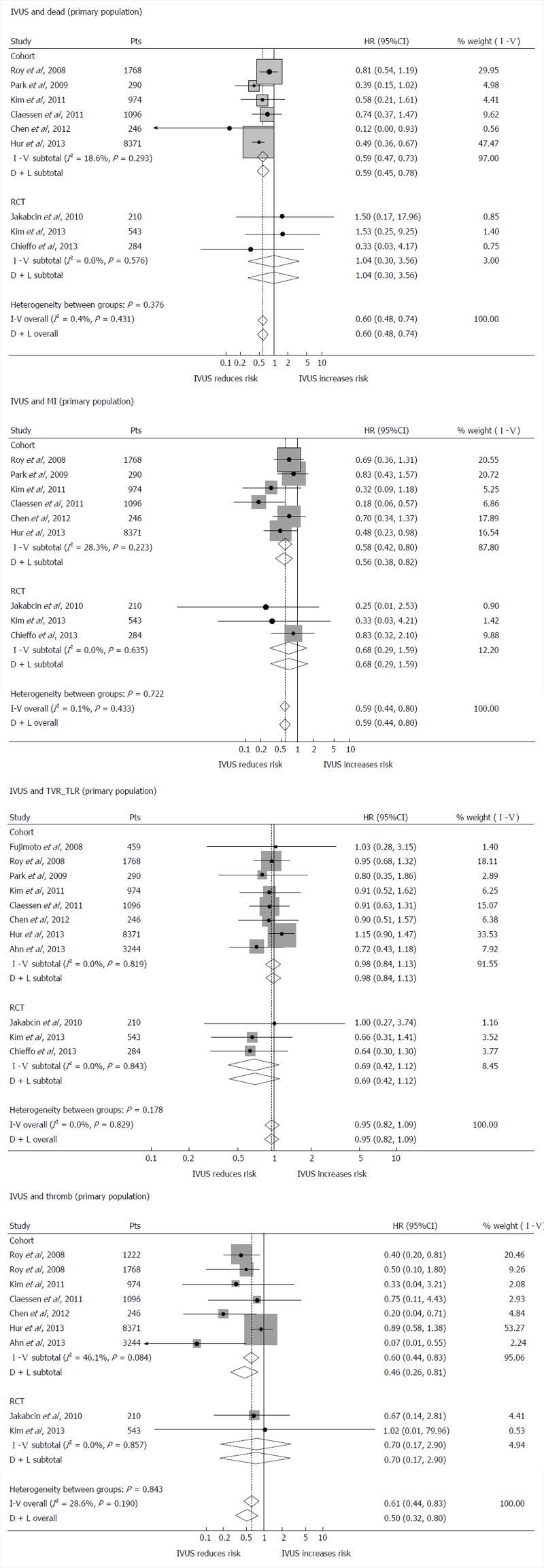
Figure 3 Impact of intravascular ultrasound vs angiography guidance of percutaneous coronary intervention on clinical outcomes.
A Forrest plot of the secondary endpoints [i.e., death, myocardial infarction (MI), target vessel and lesion revascularization (TVR_TLR), thrombosis]. Diamonds represent the meta-analytic estimates and 95%CI. Adapted from [37]. IVUS: Intravascular ultrasound.
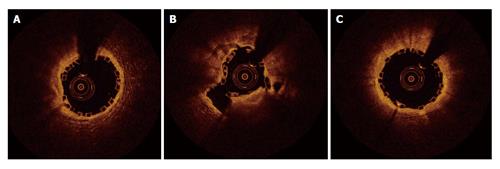
Figure 4 Optical coherence tomography findings in patient with stent underexpansion.
A-C: Post-intervention OCT of the diagonal branch after bioabsorbable scaffold implantation in a patient who presented 4 d later with stent thrombosis and acute myocardial infarction. OCT showed stent underexpansion of the mid part of the diagonal branch (B) with good stent expansion at the proximal (A) and distal (C) part of the diagonal branch. OCT: Optical coherence tomography.
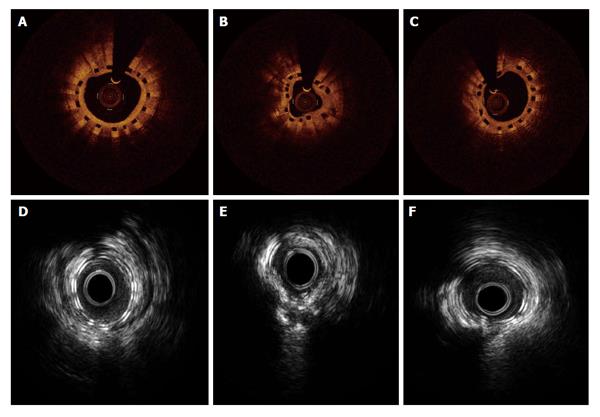
Figure 5 Intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography findings 1 yr after bioabsorbable stent implantation.
A-C: The OCT findings 12 mo after bioabsorbable scaffold implantation showed complete strut coverage; D-E: IVUS also shows uncovered struts in the same patient. IVUS: Intravascular ultrasound; OCT: Optical coherence tomography.
- Citation: Jegere S, Narbute I, Erglis A. Use of intravascular imaging in managing coronary artery disease. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(6): 393-404
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i6/393.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i6.393