Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Cardiol. Dec 26, 2014; 6(12): 1234-1244
Published online Dec 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i12.1234
Published online Dec 26, 2014. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v6.i12.1234
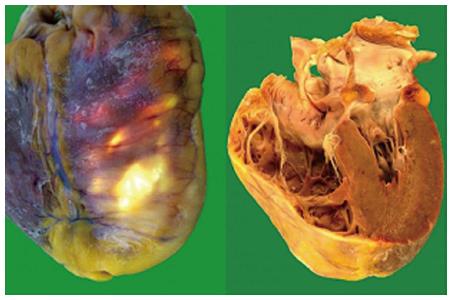
Figure 1 Gross anatomic specimens in a patient affected by arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy who died suddenly.
Severe right ventricular enlargement and wall atrophy and fatty replacement are evident.
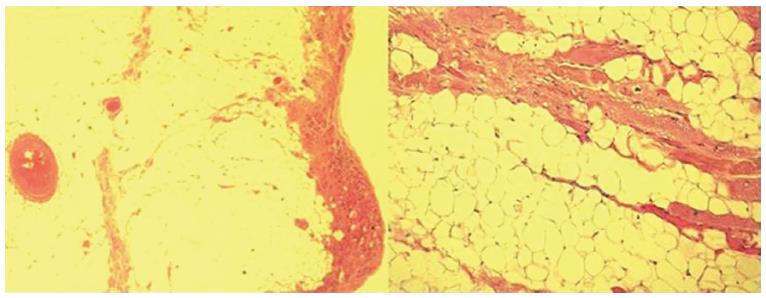
Figure 2 Histologic specimens of a case with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy that show severe right ventricular fibro-fatty replacement and loss and degeneration of myocytes (Hematoxylin Eosin × 2.
5, × 10).
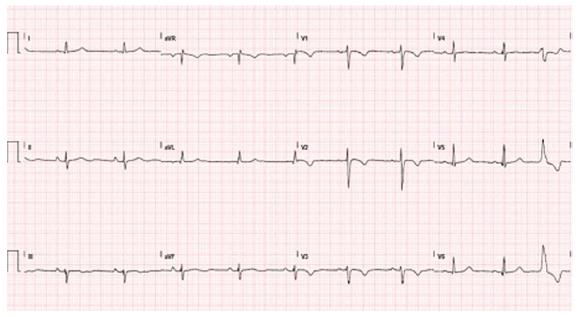
Figure 3 Typical electrocardiogram in a patient with classical arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy.
Negative T waves in anterior precordial leads are present. A ventricular premature beat with left bundle branch block morphology is also observed.
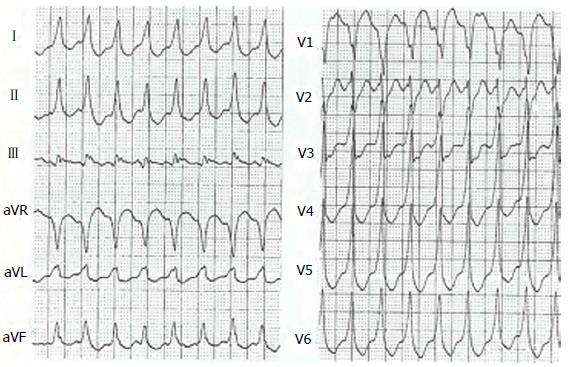
Figure 4 Ventricular tachycardia with left bundle branch block pattern in a patient with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy.
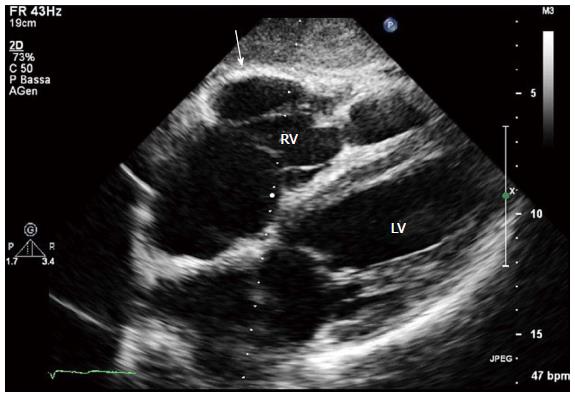
Figure 5 Two-dimensional echocardiogram, 4 chamber subcostal view, end diastolic frame, in an arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy patient.
RV wall aneurysm at subtricuspid basal level is evident (arrow). LV: Left ventricle; RV: Right ventricle.
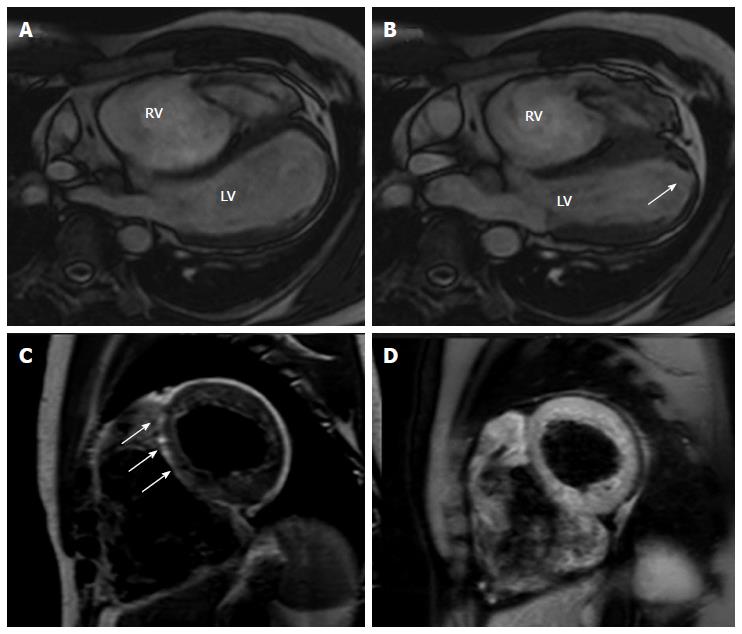
Figure 6 Cardiac magnetic resonance images of an arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy patient with mild left ventricular involvement.
A, B: End-diastolic and end-systolic frames, off-axis 4 chamber view. Note the multiple bulging segments at right ventricular (RV) free wall. An apical hypokinesia of the left ventricle (LV) is also seen (arrow); C, D: Short axis T1-weighted dark blood imaging without (C) and with fat saturation (D) in the same patient with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Note the hyperintense area in the interventricular (IV) septum in T1-weighted image (arrows) and corresponding hypointensity at T1-weighted dark blood imaging with fat-saturation indicating fatty infiltration in the IV septum.
- Citation: Pinamonti B, Brun F, Mestroni L, Sinagra G. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: From genetics to diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. World J Cardiol 2014; 6(12): 1234-1244
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v6/i12/1234.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v6.i12.1234