Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Jun 26, 2012; 4(6): 218-220
Published online Jun 26, 2012. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v4.i6.218
Published online Jun 26, 2012. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v4.i6.218
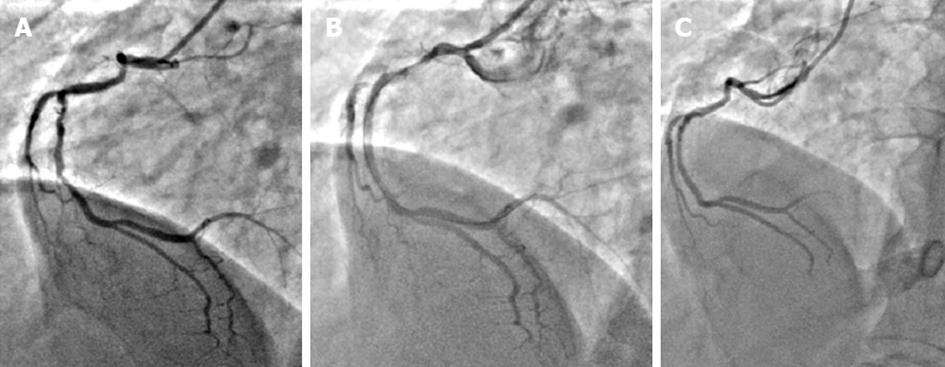
Figure 1 Right coronary angiogram in left anterior oblique 30° view.
A: Mid right coronary angiogram (RCA) shows 70% diffuse stenosis; B: Mid RCA shows no luminal narrowing after stenting; C: Patent mid RCA stent at 2 years of follow up.
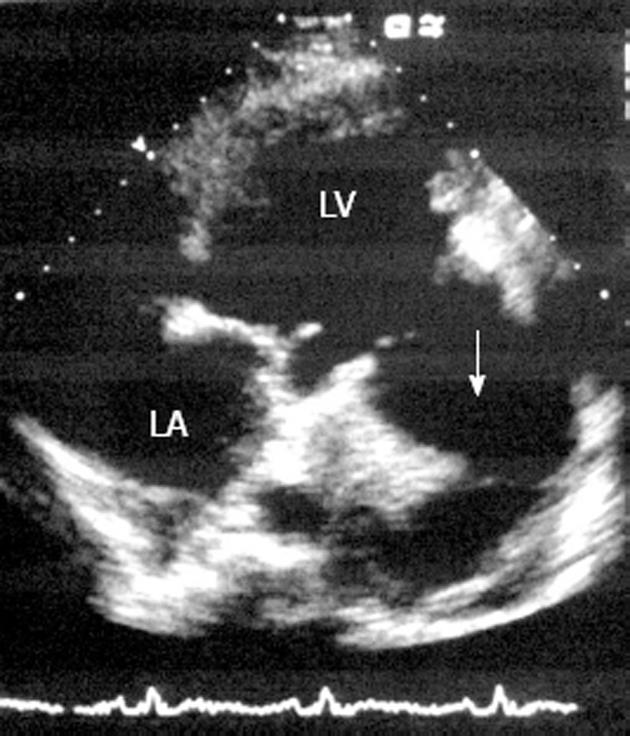
Figure 2 Echocardiography in apical 4-chamber view shows a large sub-mitral pseudoaneurysm (white arrow) containing a thrombus.
LV: Left ventricular; LA: Left atrial.
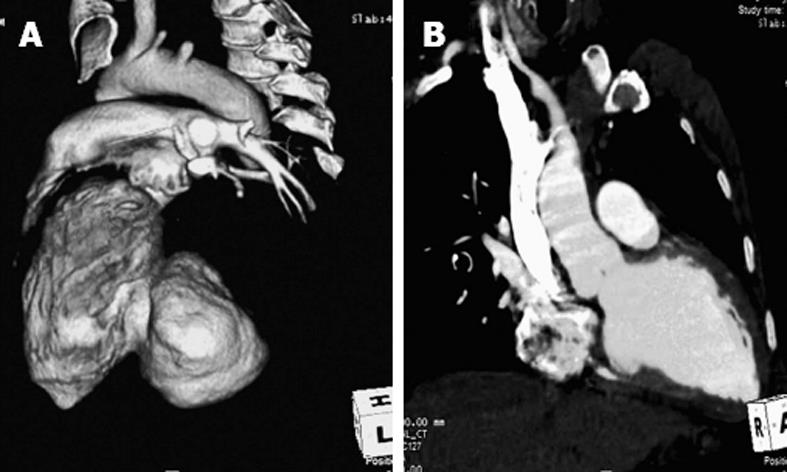
Figure 3 Computed tomography image of the heart.
A: Volume-rendered image shows a large pseudoaneurysm arising from the postero-lateral wall of the left ventricle; B: Postoperative reconstructed oblique coronal image shows opacified left ventricular cavity without a pseudoaneurysm.
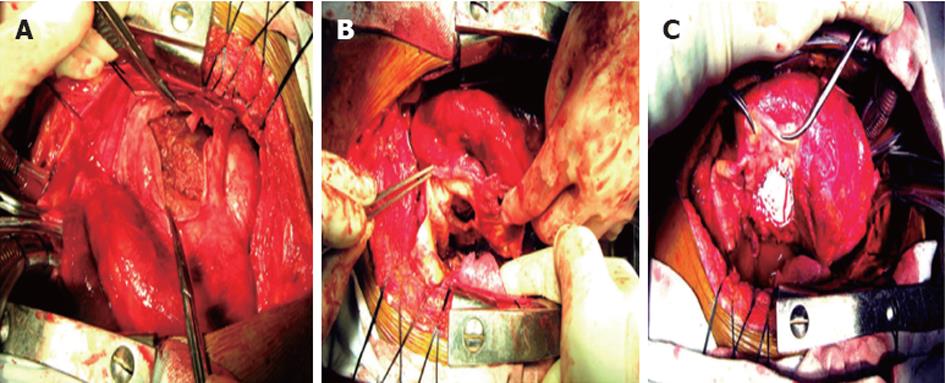
Figure 4 Operative photograph of the pseudoaneurysm.
A: Incised pseudoaneurysm sac showing a thrombus in the cavity; B: A circular connection 40 mm in size between the true left ventricular cavity and pseudoaneurysm sac; C: Polytetrafluoroethylene patch repair of the pseudoaneurysm.
- Citation: Vijayvergiya R, Pattam J, Rana SS, Singh JD, Puri GD, Singhal M. Giant left ventricular pseudoaneurysm presenting with hemoptysis. World J Cardiol 2012; 4(6): 218-220
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v4/i6/218.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v4.i6.218