Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Oct 26, 2012; 4(10): 288-295
Published online Oct 26, 2012. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v4.i10.288
Published online Oct 26, 2012. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v4.i10.288
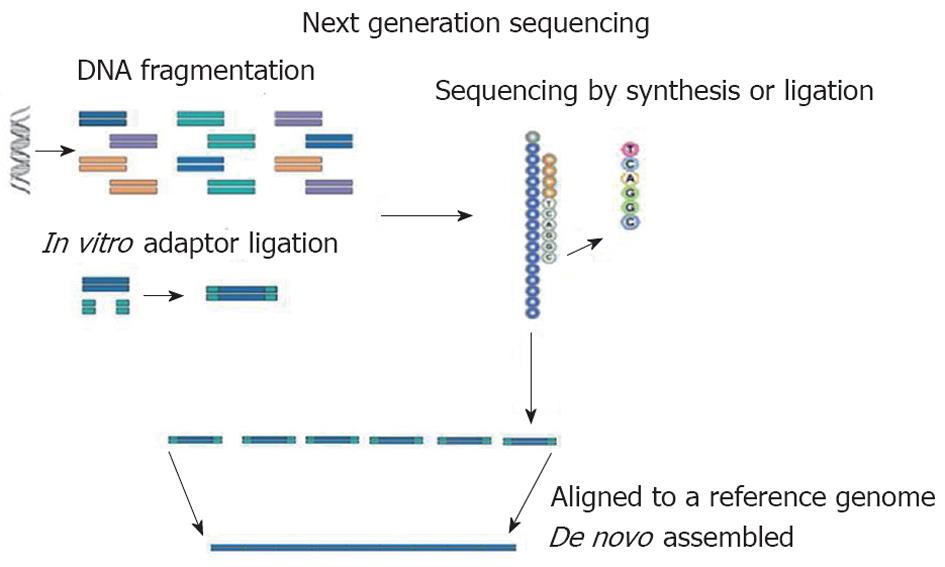
Figure 1 Basic principles of next generation sequencing.
A whole genome or a targeted region of the genome are randomly digested into small fragments and then sequenced. The sequence obtained is subsequently aligned to a reference genome or de novo assembled.
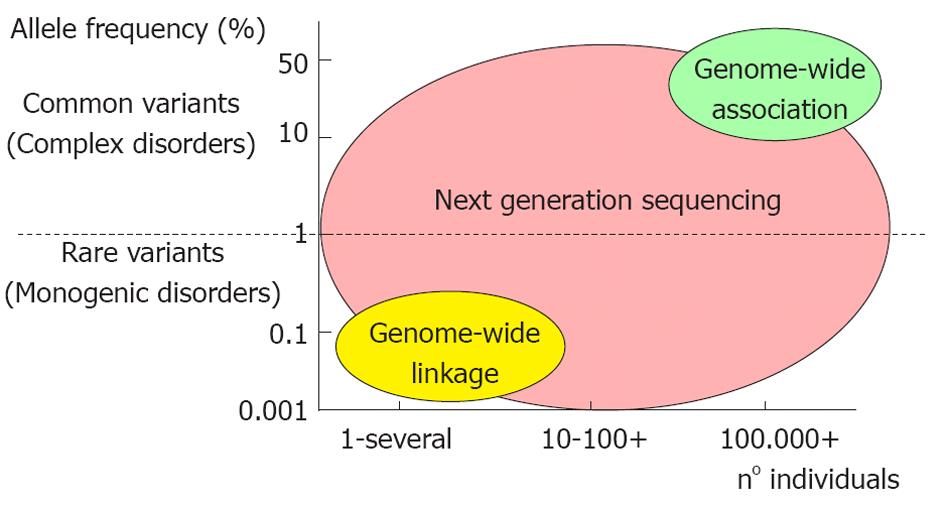
Figure 2 Genetic contribution to monogenic and multigenic cardiovascular diseases and their study approach.
The monogenic diseases are caused by a rare mutation in a specific gene and are very rare (< 10 individuals). In the complex diseases, many common genetic variants occur and have a major frequency in the population (> 100 000). The study approach for monogenic diseases is a genome wide linkage study in which one single mutation is identified. Conversely, for complex diseases the genome wide association study is very important to identify a series of common variants contributing to the etiology of the disease. Target re-sequencing by next generation sequencing is an approach which permits the study of both monogenic and complex diseases.
- Citation: Faita F, Vecoli C, Foffa I, Andreassi MG. Next generation sequencing in cardiovascular diseases. World J Cardiol 2012; 4(10): 288-295
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v4/i10/288.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v4.i10.288