Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Jul 21, 2010; 2(7): 198-204
Published online Jul 21, 2010. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v2.i7.198
Published online Jul 21, 2010. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v2.i7.198
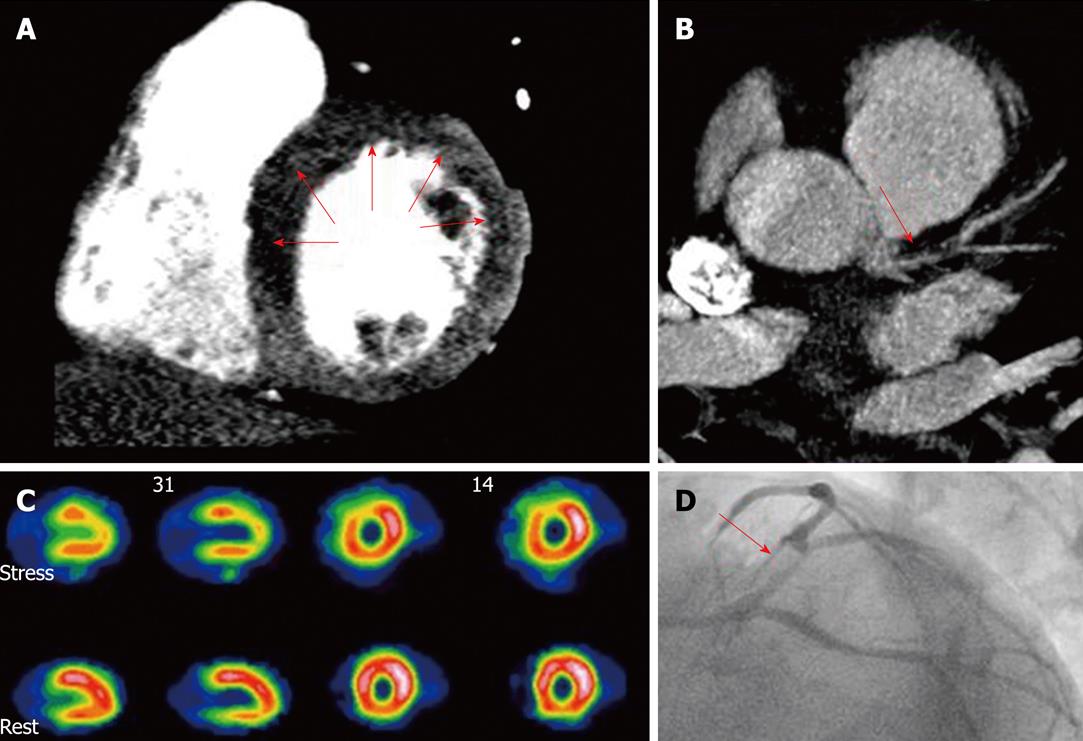
Figure 1 Combined assessment of myocardial perfusion at pharmacological (adenosine) stress and coronary angiography within a single-session cardiac computed tomography.
Cardiac computed tomography (CT) (panels A and B) showed diminished perfusion of the left ventricle anterior and septal wall (A, arrows) and a significant lesion at the proximal left anterior descending artery (B, arrow), findings confirmed by single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) (C) and invasive coronary angiography (D, arrow). A: CT perfusion (stress); B: Coronary CT angiography; C: SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging; D: Invasive angiography. With permission of Blankstein et al[21], J Am Coll Cardiol 2009; 54: 1072-1084.
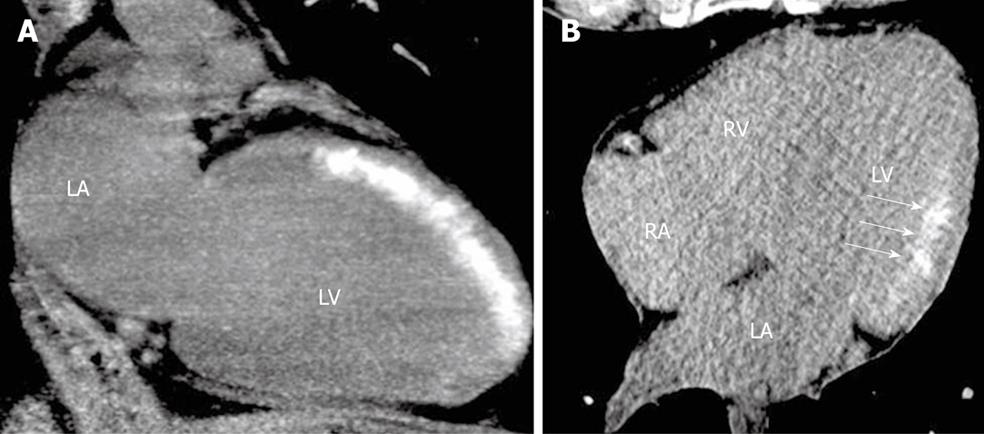
Figure 2 Early assessment of myocardial viability immediately after primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with anterior (A) and inferolateral (B) ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction.
Delayed enhancement of iodinated contrast administrated during percutaneous coronary intervention is observed using non-contrast enhanced cardiac computed tomography, without heart rate control and using a low dose-saving protocol. Discrimination between transmural (A) and subendocardial (B, arrows) extent of the irreversible myocardial damage (delayed enhancement) can be achieved using this technique. LA: Left atrium; LV: Left ventricle; RA: Right atrium; RV: Right ventricle.
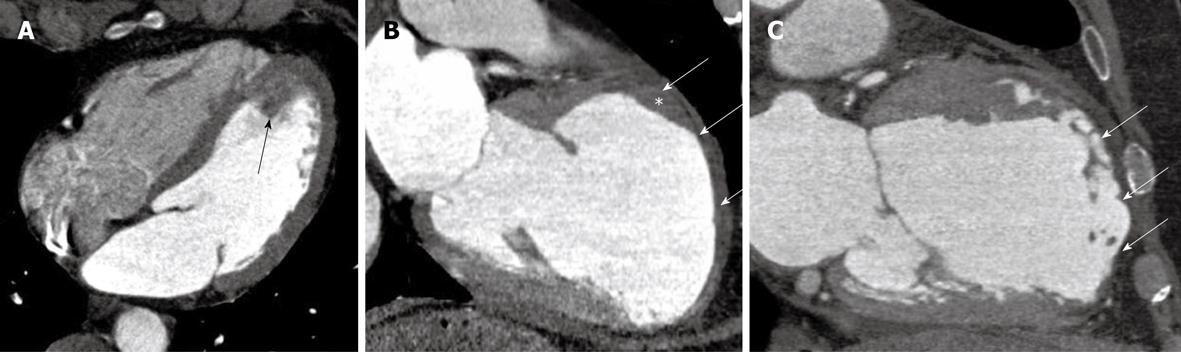
Figure 3 Acute and chronic sequelae of myocardial infarction.
A: A four-chamber view of a patient with acute chest pain and an occluded mid left descending coronary artery. A fresh, mobile, pedunculated thrombus is observed at the left ventricular apex (arrow); B: A two chamber view of a patient with recent onset heart failure and history of previous myocardial infarction. A left ventricle aneurysm is detected at the anterior wall, with significant wall thinning, pericardial effusion (arrows) and a fixed thrombus (*); C: An anterior wall chronic myocardial infarction, with significant wall thinning and lipomatous metaplasia (arrows).
- Citation: Rodríguez-Granillo GA, Ingino CA, Lylyk P. Myocardial perfusion imaging and infarct characterization using multidetector cardiac computed tomography. World J Cardiol 2010; 2(7): 198-204
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v2/i7/198.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v2.i7.198