Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2010; 2(4): 104-106
Published online Apr 26, 2010. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v2.i4.104
Published online Apr 26, 2010. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v2.i4.104
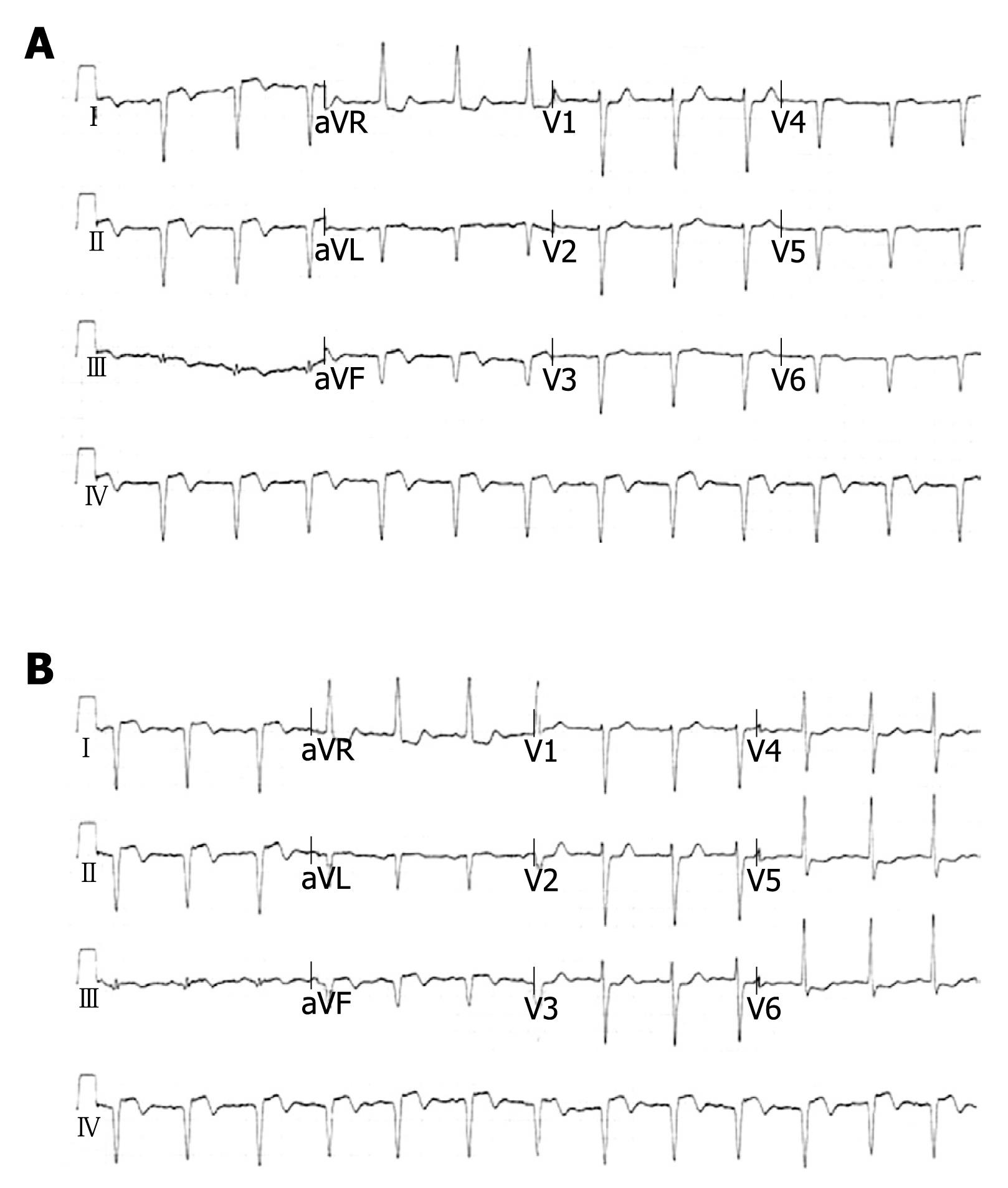
Figure 1 ECG findings in dextrocardia.
A: ECG of standard limb and chest leads suggestive of dextrocardia and inferior wall myocardial infarction; B: ECG of standard limb leads and right sided chest leads suggestive of dextrocardia.
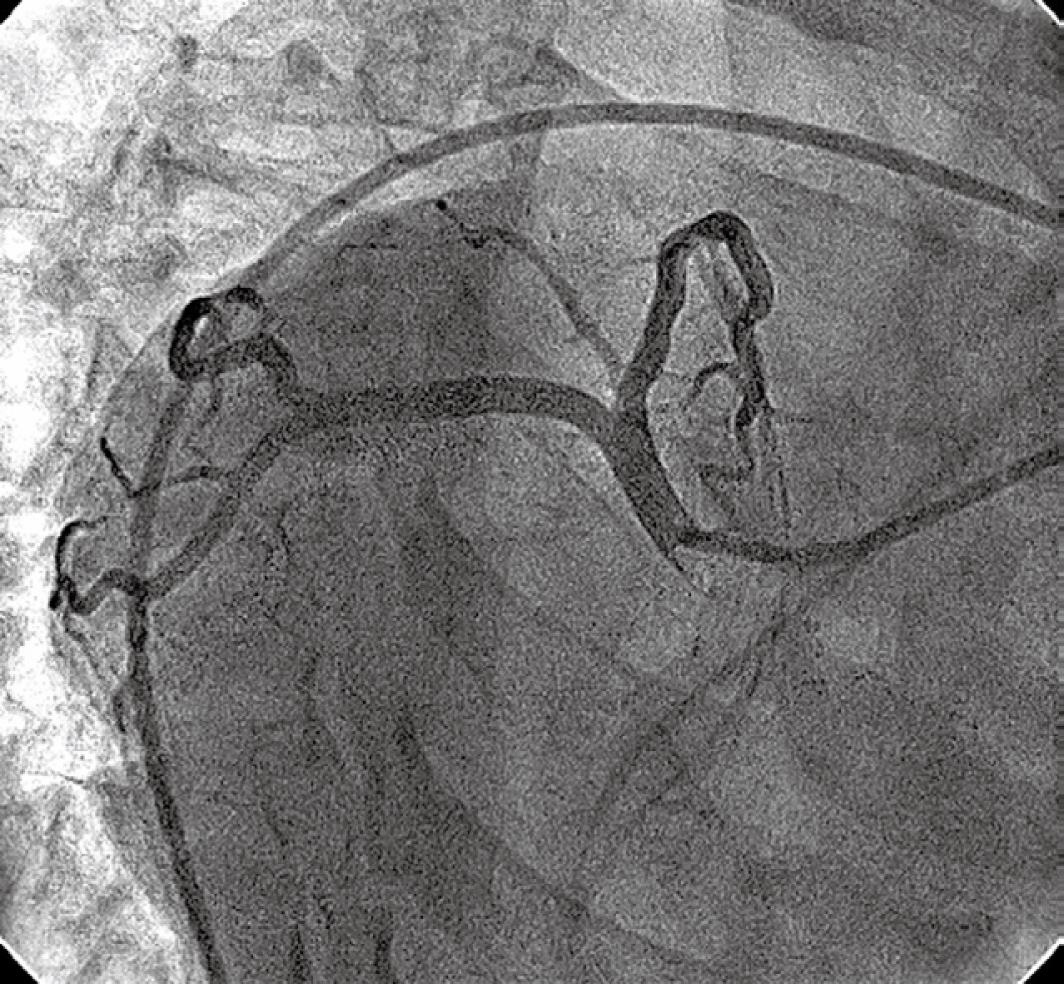
Figure 2 Left coronary angiogram with a JL4, 6F catheter in a RAO 45°, caudal 20° view showing a normal left main artery and its branches.
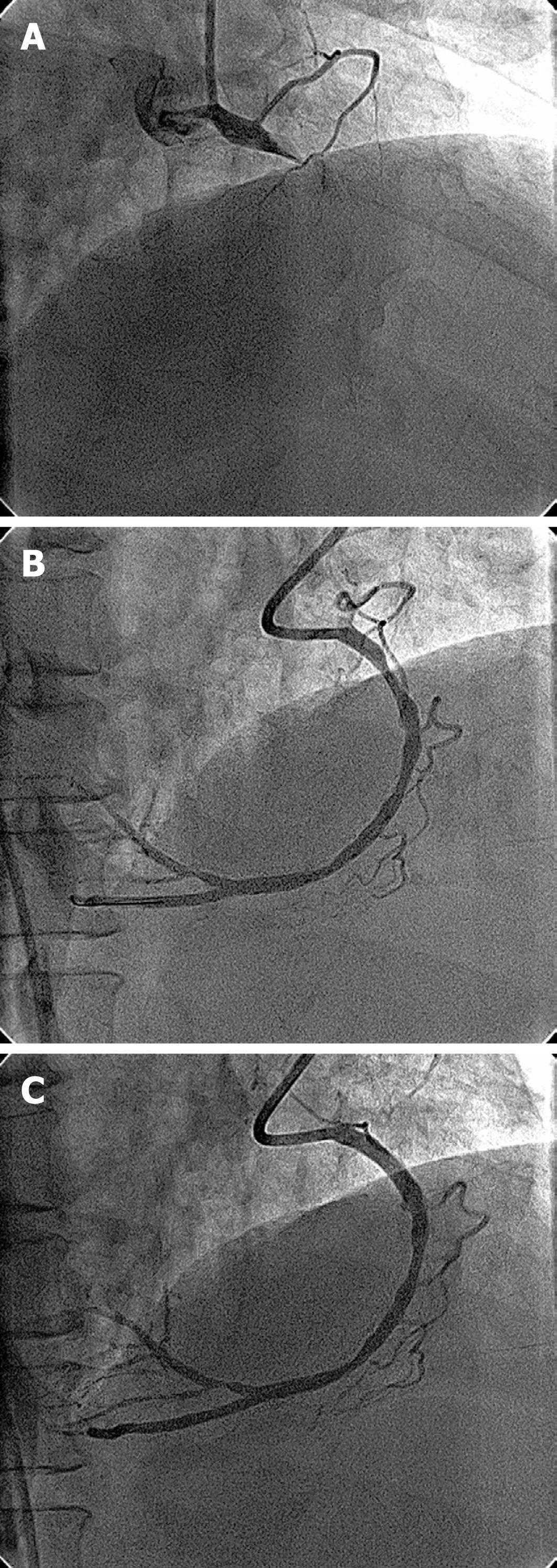
Figure 3 Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) of right coronary artery (RCA) in dextrocardia.
A: The diagnostic angiogram with a JR 4, 6F catheter in a RAO 40°, cranial 20° view showing total cutoff of the proximal RCA; B: The RCA in a RAO 40°, cranial 20° view showing a proximal lesion following balloon angioplasty; C: The RCA in a RAO 40°, cranial 20° view following stenting showing TIMI-3 flow.
- Citation: Vijayvergiya R, Grover A. Percutaneous coronary intervention for acute myocardial infarction in a patient with dextrocardia. World J Cardiol 2010; 2(4): 104-106
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v2/i4/104.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v2.i4.104