Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Cardiol. Oct 26, 2010; 2(10): 344-356
Published online Oct 26, 2010. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v2.i10.344
Published online Oct 26, 2010. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v2.i10.344
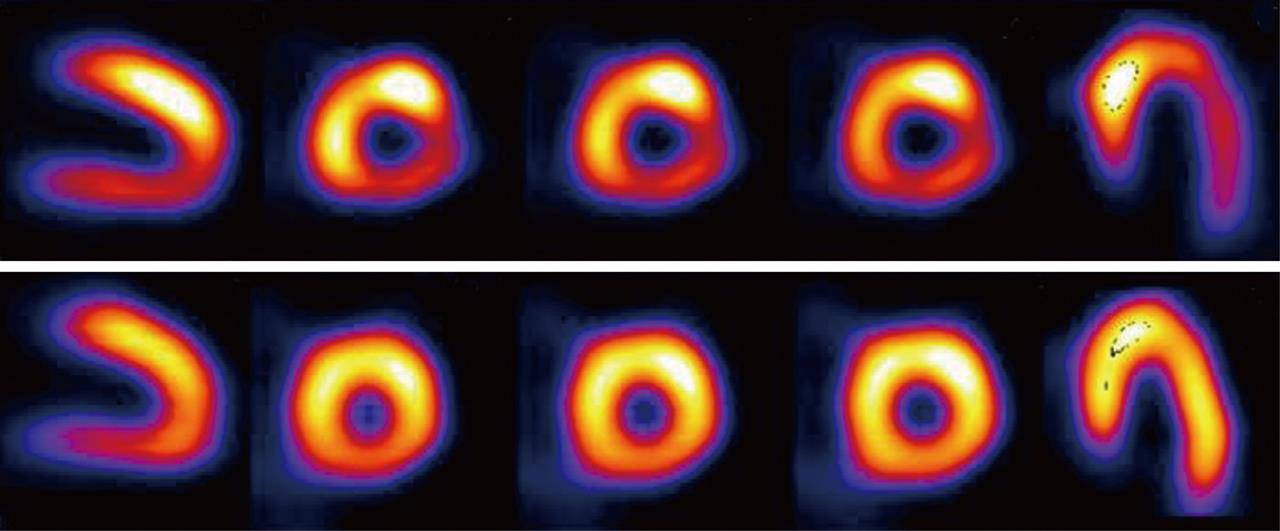
Figure 1 Single photon emission computed tomography image of exercise 201Tl scintigraphy in a 70-year-old man.
The stress image (upper panel) shows decreased perfusion in the infero-lateral region. There is a redistribution of the tracer in the rest image (lower panel), which indicates exercise-induced myocardial ischemia in the infero-lateral region of the left ventricle.
Figure 2 Post-stress left ventricular dysfunction detected by quantitative gated single positron emission computed tomography analysis.
Transient ischemic dilatation was observed in a patient with multi-vessel disease. ESV: End-systolic volume; EDV: End-diastolic volume; EF: Ejection fraction.
Figure 3 A patient with heart failure had 123I-MIBG imaging and was treated with β-blockers.
After treatment, 123I-MIBG H/M ratio and washout rate (WR) were improved.
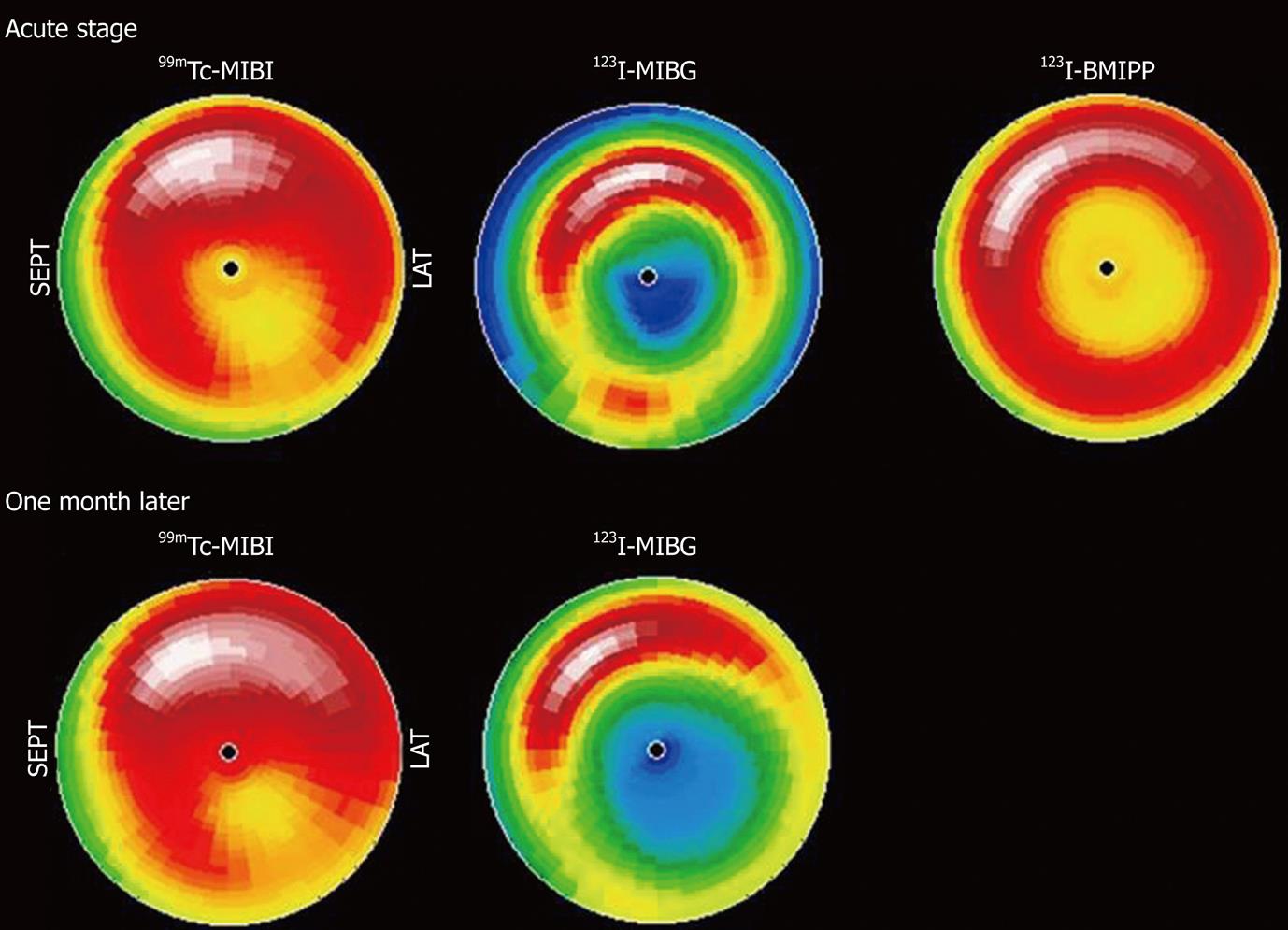
Figure 4 Scintigraphic features of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy are depicted.
Bull’s eye maps of 99mTc-sestamibi (MIBI), 123I-MIBG and 123I-β-methyl-p-iodophenyl-pentadecanoic acid (BMIPP) are shown. Both 123I-MIBG and 123I-BMIPP images show reduced uptake in the apical segment of the myocardium, which are typical features of the disease.
Figure 5 Fusion image reveals that the ischemic area in the basal antero-lateral region shown by single photon emission computed tomography image is perfused by small vessels or has no corresponding artery assessed as imaging artifacts.
Thus, the fusion image has increased diagnostic confidence for the detection of the culprit lesion in patients with coronary artery bypass grafting.
- Citation: Matsuo S, Nakajima K, Kinuya S. Clinical use of nuclear cardiology in the assessment of heart failure. World J Cardiol 2010; 2(10): 344-356
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v2/i10/344.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v2.i10.344