Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Jul 26, 2025; 17(7): 107751
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.107751
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.107751
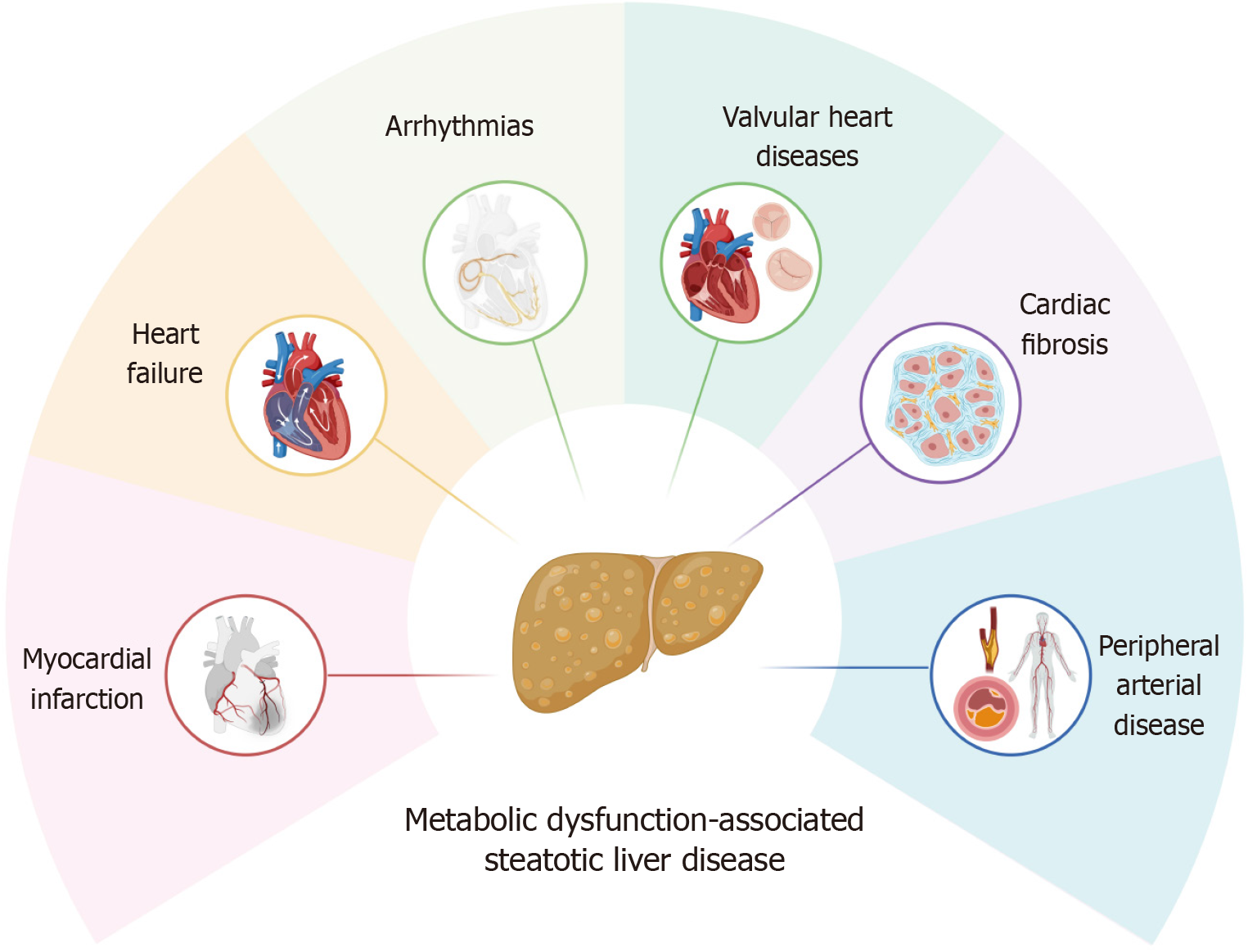
Figure 1
Cardiovascular complications associated with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
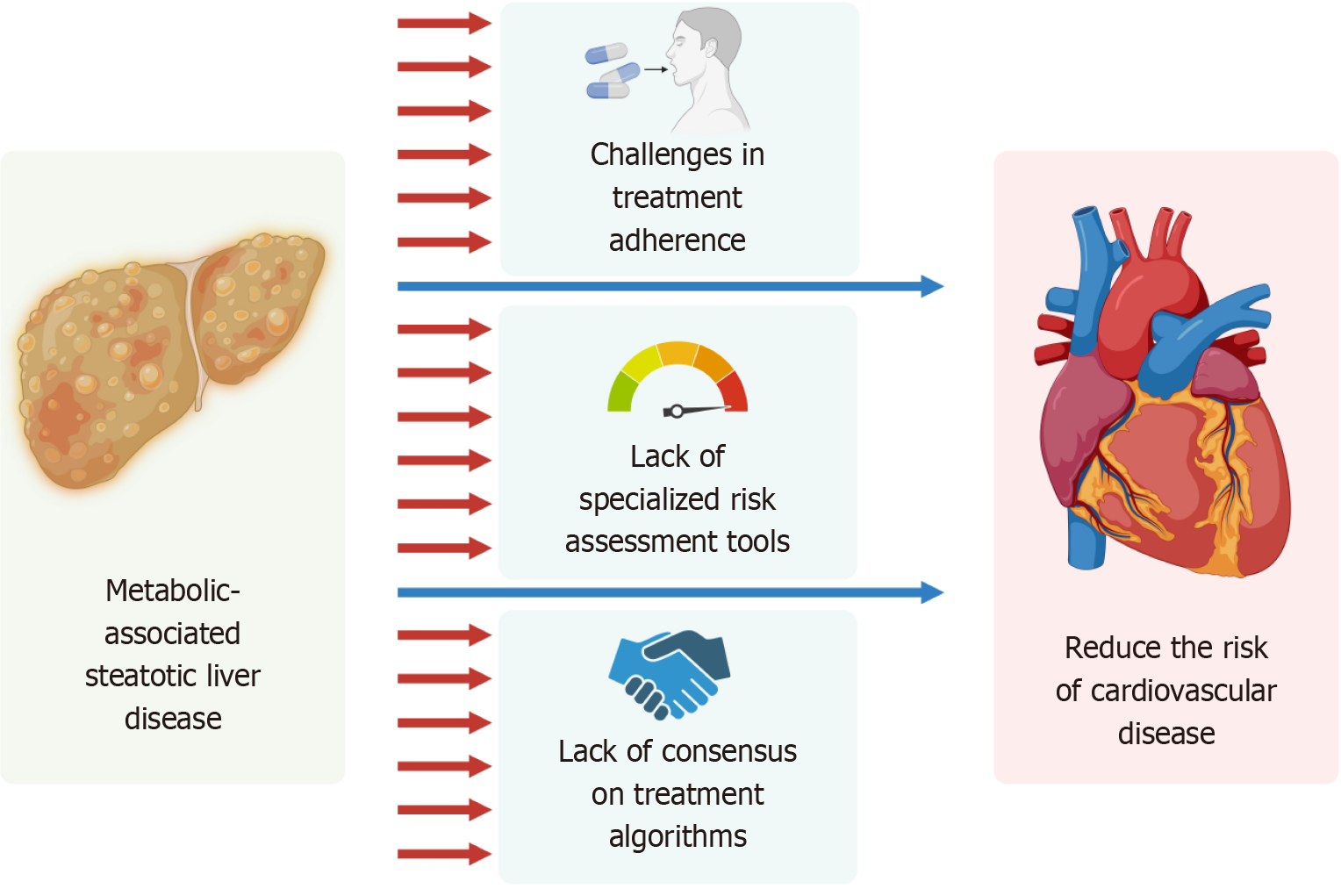
Figure 2
Key challenges in managing cardiovascular risk in patients with metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease.
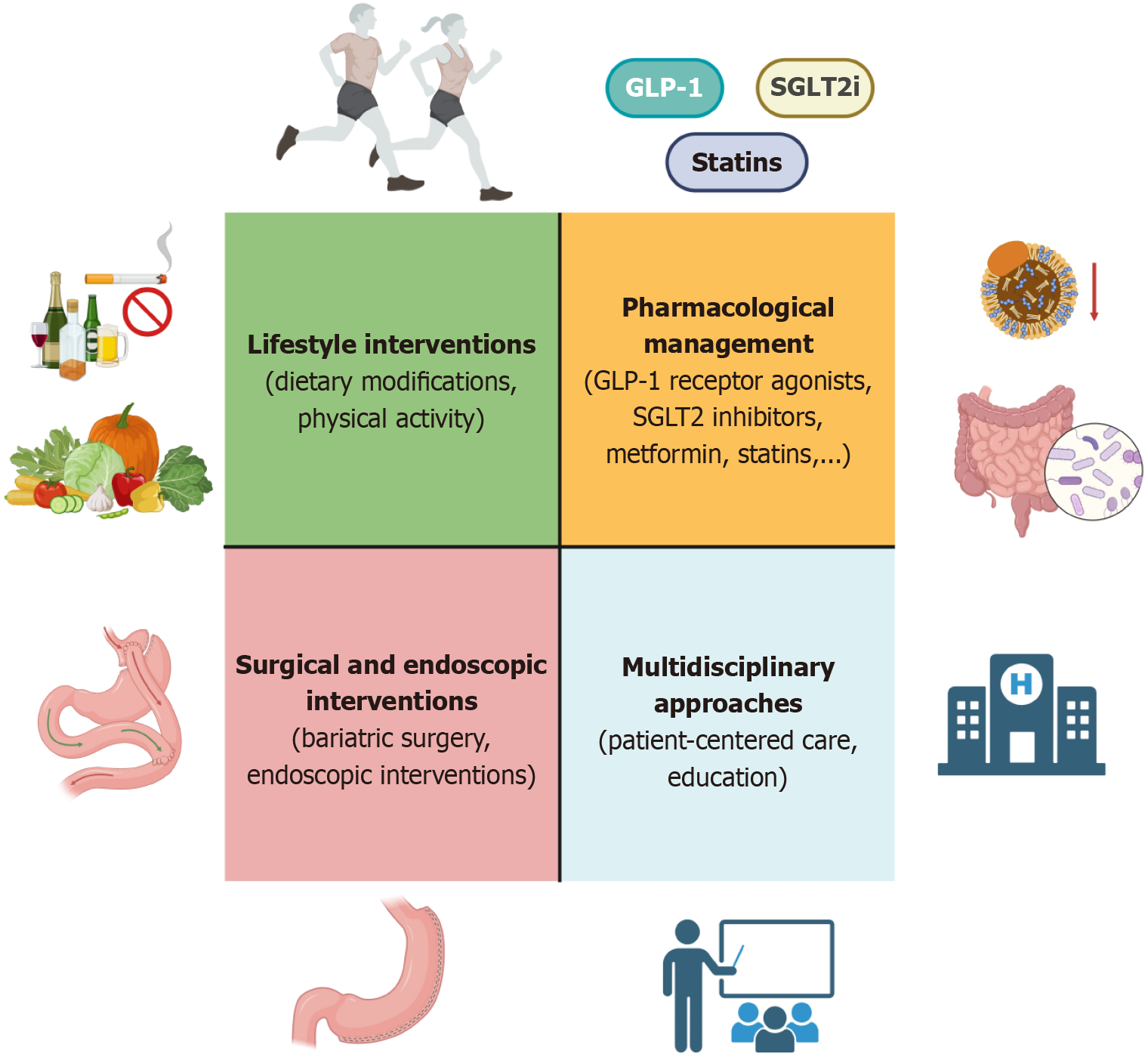
Figure 3 Strategic approaches to cardiovascular risk management in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
This figure illustrates a comprehensive framework for managing cardiometabolic risk in individuals with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). The approach is grounded in four synergistic pillars: (1) Lifestyle interventions, including dietary modifications and regular physical activity, serving as the foundation of care; (2) Pharmacological management with agents such as GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, metformin, and statins, aimed at optimizing metabolic control and reducing hepatic and cardiovascular burden; (3) Surgical and endoscopic interventions like bariatric surgery, reserved for eligible patients with obesity-related complications; and (4) Multidisciplinary approaches, encompassing patient-centered care models and educational strategies to personalize treatment and promote long-term adherence. This holistic strategy integrates hepatology, cardiology, and metabolic medicine to address the overlapping risks and therapeutic opportunities in MASLD.
- Citation: Luong TV, Tran H, Hoang Thi BN, Vu HM, Le TT, Le TT, Tran Thi HT, Nguyen HM, Doan TC, Ho BA, Hoang TA, Dang HNN. Integrating liver and heart health: Cardiovascular risk reduction in patients with metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(7): 107751
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i7/107751.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i7.107751