Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Cardiol. Mar 26, 2025; 17(3): 103668
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i3.103668
Published online Mar 26, 2025. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v17.i3.103668
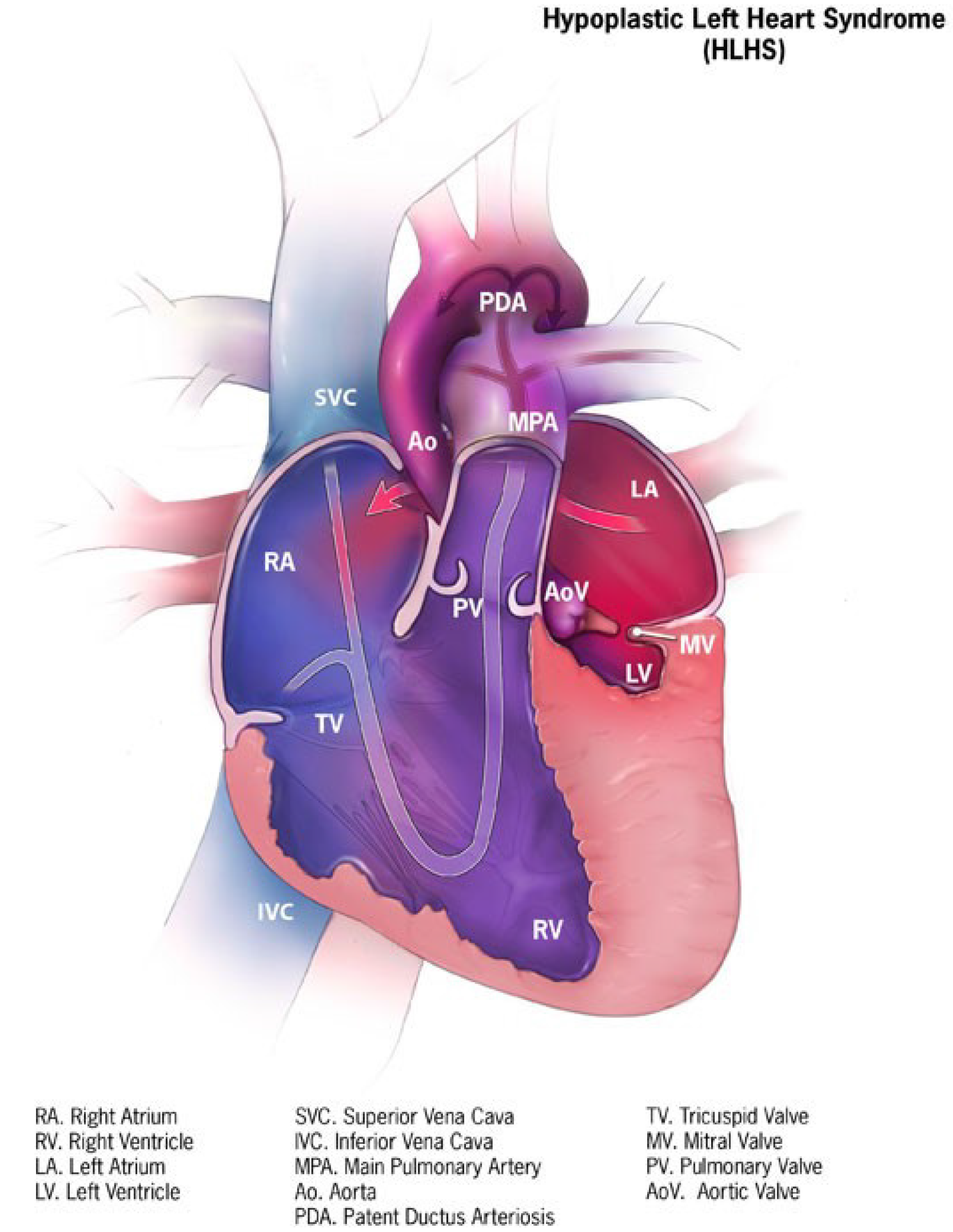
Figure 1 Key cardiac malformations in hypoplastic left heart syndrome[6].
Citation: Connor JA, Thiagarajan R. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2007; 2: 23. Copyright© 2025 published by BioMed Central Ltd unless otherwise stated. A visual representation of the structural abnormalities associated with hypoplastic left heart syndrome, demonstrating underdevelopment of the left ventricle, aorta, and aortic arch, along with mitral valve stenosis or atresia. These abnormalities lead to left ventricular outflow tract obstruction. The figure also highlights compensatory enlargement of the right ventricle and right atrium. HLHS: Hypoplastic left heart syndrome; PDA: Patent ductus arteriosis; SVC: Superior vena cava; AO: Aorta; MPA: Main pulmonary artery; RA: Right atrium; PV: Pulmonary valve; AoV: Aortic valve; LA: left atrium; TV: Tricuspid Valve; LV: Left ventricle; MV: Mitral valve; RV: Mitral valve; right ventricle; IVC: Inferior vena cava.
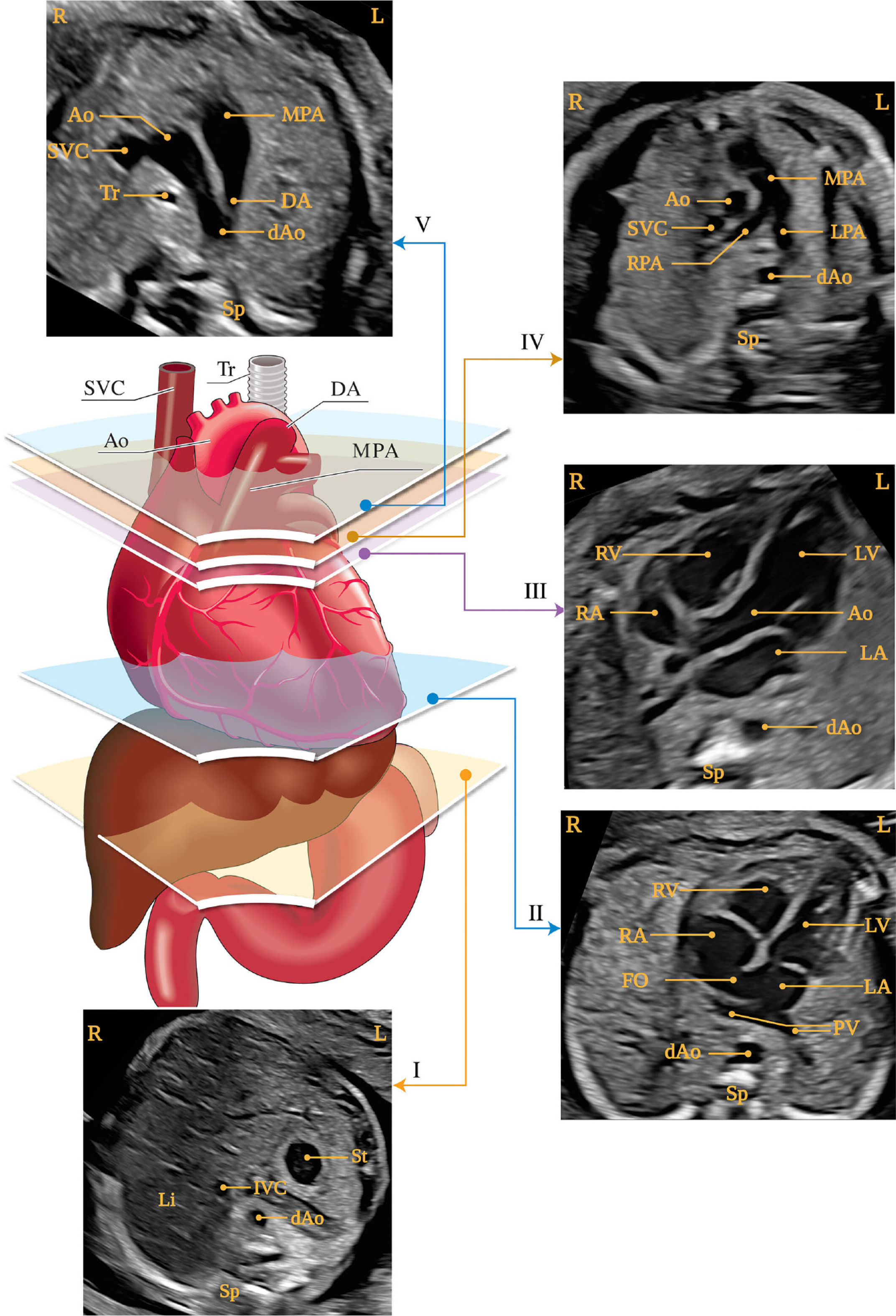
Figure 2 Insonation planes for fetal cardiac assessment using fetal ultrasound[19,20].
Adapted under authorization from Carvalho et al[19] and Yagel et al[20]. Citation: Carvalho JS, Axt-Fliedner R, Chaoui R, Copel JA, Cuneo BF, Goff D, Gordin Kopylov L, Hecher K, Lee W, Moon-Grady AJ, Mousa HA, Munoz H, Paladini D, Prefumo F, Quarello E, Rychik J, Tutschek B, Wiechec M, Yagel S. ISUOG Practice Guidelines (updated): fetal cardiac screening. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2023; 61: 788-803. Copyright© 1999-2025 published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc or related companies. Citation: Yagel S, Cohen SM, Achiron R. Examination of the fetal heart by five short-axis views: a proposed screening method for comprehensive cardiac evaluation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 17: 367-369. Copyright© 1999-2025 published by John Wiley & Sons, Inc or related companies. The diagram illustrates the trachea, heart and major vessels, liver, and stomach, with five insonation planes indicated by polygons, corresponding to grayscale images as shown. I: The most caudal plane depicts the fetal stomach, cross-section of the descending aorta (dAo), inferior vena cava, spine, and liver; II: The four-chamber view of the fetal heart shows the right and left ventricles and atria, the foramen ovale, and pulmonary veins on either side of the dAo; III: The left ventricular outflow tract view includes the proximal ascending aorta, right and left ventricles, right and left ventricles and atria, and cross-section of the dAo; IV: A slightly more cephalad view, the right ventricular outflow tract view, reveals the main pulmonary artery and its bifurcation into the right and left pulmonary arteries, as well as cross-sections of the aorta and dAo; V: The three-vessel-and-trachea view shows the superior vena cava, main pulmonary artery, ductus arteriosus, transverse aortic arch (extending from the proximal aorta to the dAo), and trachea. St: Stomach; dAo: Descending aorta; IVC: Inferior vena cava; Sp: Spine; RV: Right ventricles; LV: Left ventricles; RA: Right atria; LA: Left atria; FO: Foramen ovale; PV: Pulmonary veins; Ao: Aorta; MPA: Main pulmonary artery; RPA: Right pulmonary arteries; LPA: Left pulmonary arteries; SVC: Superior vena cava; DA: Ductus arteriosus; Tr: Trachea.
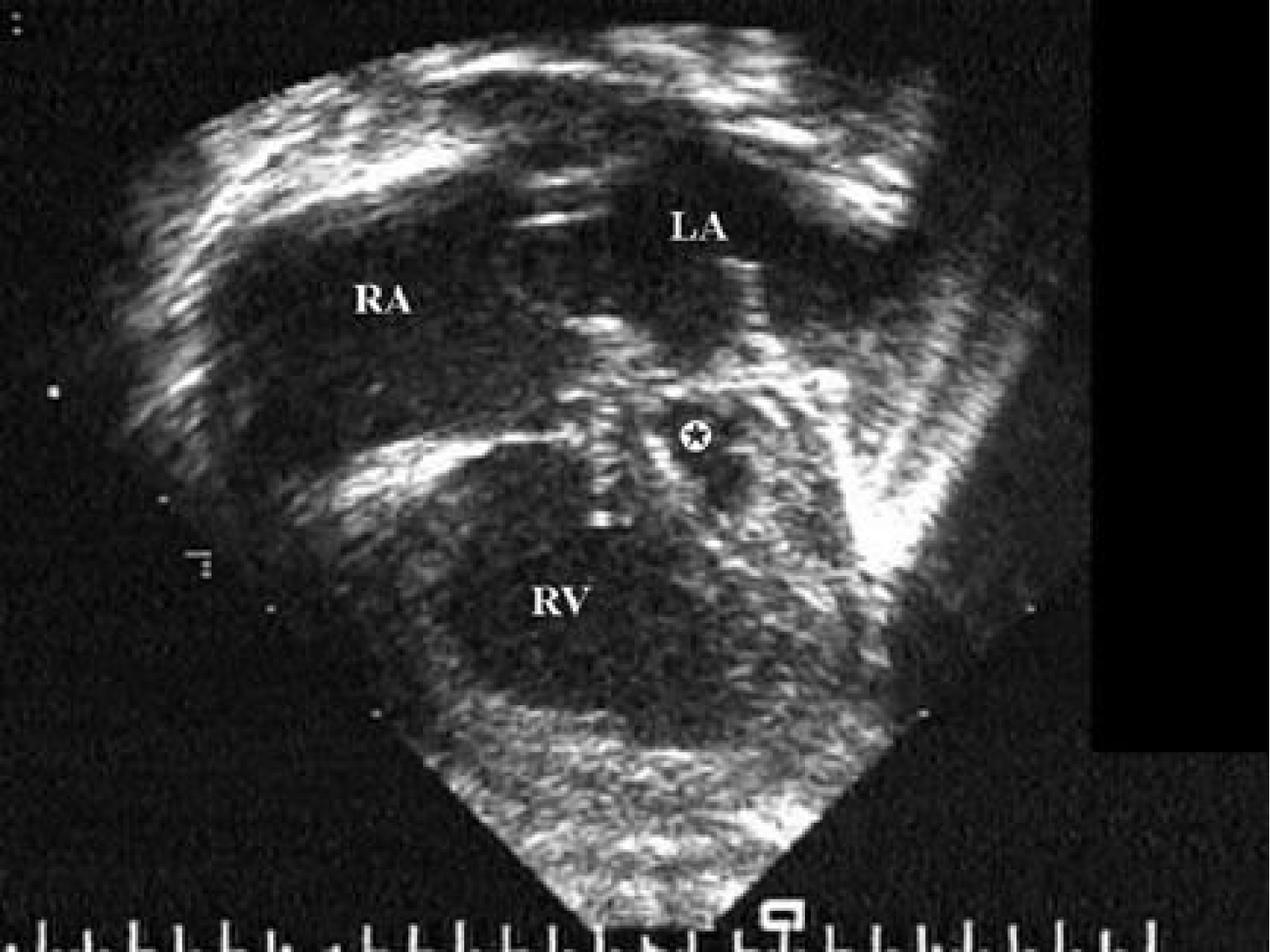
Figure 3 Echocardiographic 4-chamber view of the heart in hypoplastic left heart syndrome[35].
Adapted under authorization from Patnana et al[35]. Citation: Patana SR, Turner DR. Pediatric Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome. Dec 15, 2020. [cited 26 November 2024]. Available from: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/890196-overview#a4. This echocardiographic still frame shows a 4-chamber view of the heart in a patient with hypoplastic left heart syndrome. A large right ventricle and hypoplastic left ventricle (star) are seen. RA: Right atrium; RV: Right ventricle; LA: Left atrium.
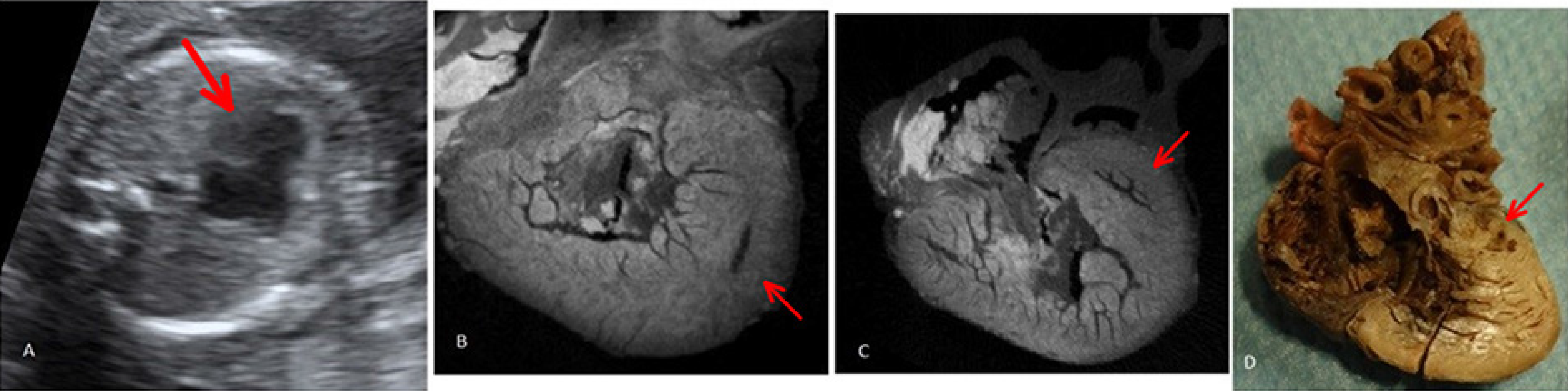
Figure 4 Multimodal visualization of hypoplastic left heart syndrome[36].
Adapted under authorization from Sandrini et al[36]. Citation: Sandrini C, Rossetti L, Zambelli V, Zanarotti R, Bettinazzi F, Soldá R, Di Pace C, Hoxha S, Ribichini FL, Faggian G, Lombardi C, Luciani GB. Accuracy of Micro-Computed Tomography in Post-mortem Evaluation of Fetal Congenital Heart Disease. Comparison Between Post-mortem Micro-CT and Conventional Autopsy. Front Pediatr 2019; 7: 92 Copyright© 2025 published by Frontiers Media S.A. A: Prenatal fetal echocardiography: Four chamber view showing hypoplastic/atretic mitral valve and hypoplastic left ventricle; B: Post-mortem micro-computed tomograph: Short axis view at the level of the ventricle comparing right ventricle with hypoplastic left ventricle; C: Post-mortem micro-computed tomograph: Four chamber view showing the hypoplastic left ventricle; D: Conventional autopsy: Four chamber view showing hypoplastic left ventricle; Arrows: the hypoplastic left ventricle.
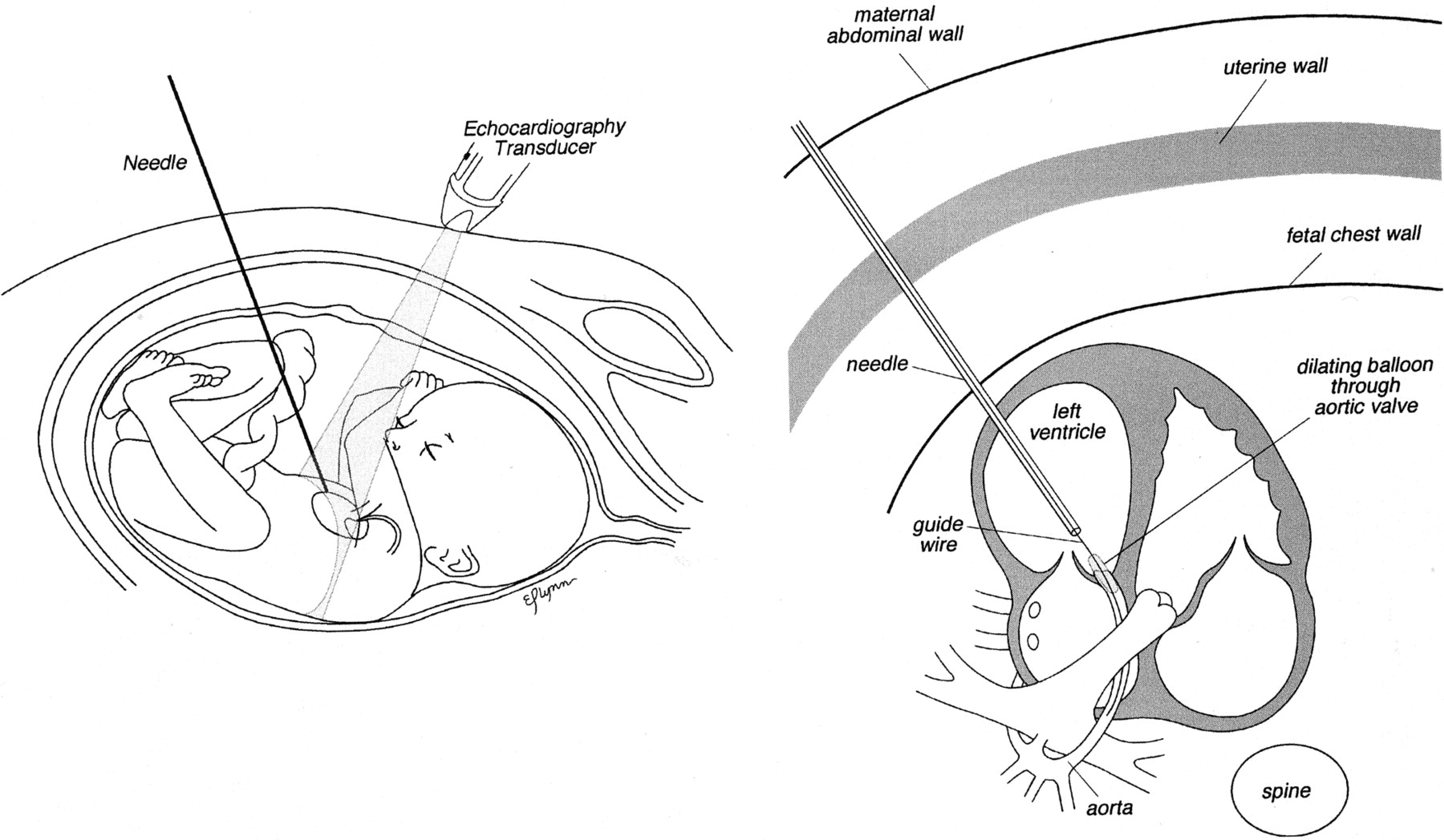
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of the ideal approach to the fetal left ventricle[42].
Adapted under authorization from Tworetzky et al[42]. Citation: Tworetzky W, Wilkins-Haug L, Jennings RW, van der Velde ME, Marshall AC, Marx GR, Colan SD, Benson CB, Lock JE, Perry SB. Balloon dilation of severe aortic stenosis in the fetus: potential for prevention of hypoplastic left heart syndrome: candidate selection, technique, and results of successful intervention. Circulation 2004; 110: 2125-2131. Copyright© 2025 published by American Heart Association, Inc. Balloon dilation of severe aortic stenosis in the fetus.
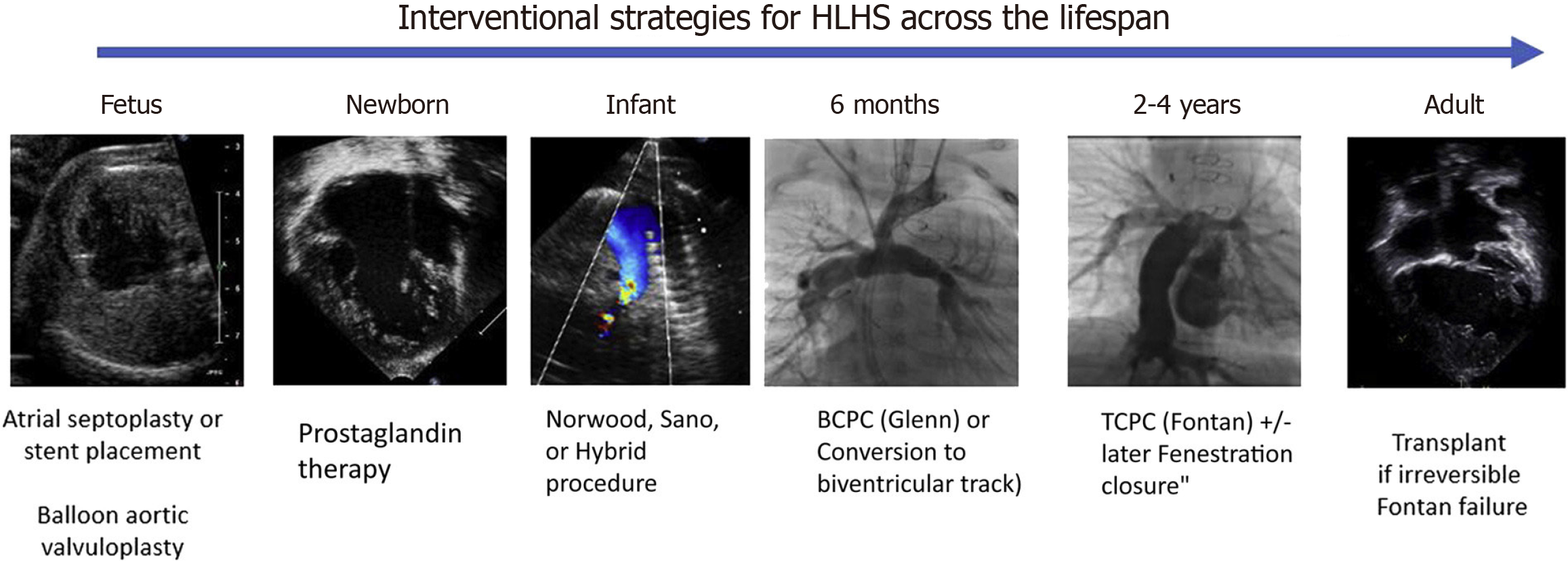
Figure 6 Interventional strategies for hypoplastic left heart syndrome across the lifespan[87].
Adapted under authorization from Wald et al[87]. Citation: Wald RM, Mertens LL. Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Across the Lifespan: Clinical Considerations for Care of the Fetus, Child, and Adult. Can J Cardiol 2022; 38: 930-945. Citation: Copyright© 2025 published by Elsevier Inc. This figure outlines the staged palliative surgical procedures for hypoplastic left heart syndrome, culminating in Fontan circulation. Stage one (Norwood procedure) involves creating systemic circulation using the right ventricle, a pulmonary homograft, and an atrial septectomy. Stage two (bidirectional Glenn shunt) and stage three (Fontan procedure) progressively redirect venous return directly to pulmonary circulation. Hybrid approaches provide less invasive alternatives to the Norwood procedure, employing ductal arteriosus shunts, pulmonary artery bands, and atrial septostomy. The inter-stage period involves continuous monitoring before subsequent surgical stages. HLHS: Hypoplastic left heart syndrome; BCPC: Bidirectional cavopulmonary connection; TCPC: Total cavopulmonary connection.
- Citation: Bokhari SFH, Faizan Sattar SM, Mehboob U, Umais M, Ahmad M, Malik A, Bakht D, Iqbal A, Dost W. Advancements in prenatal diagnosis and management of hypoplastic left heart syndrome: A multidisciplinary approach and future directions. World J Cardiol 2025; 17(3): 103668
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v17/i3/103668.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v17.i3.103668