Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Cardiol. Aug 26, 2024; 16(8): 484-490
Published online Aug 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i8.484
Published online Aug 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i8.484
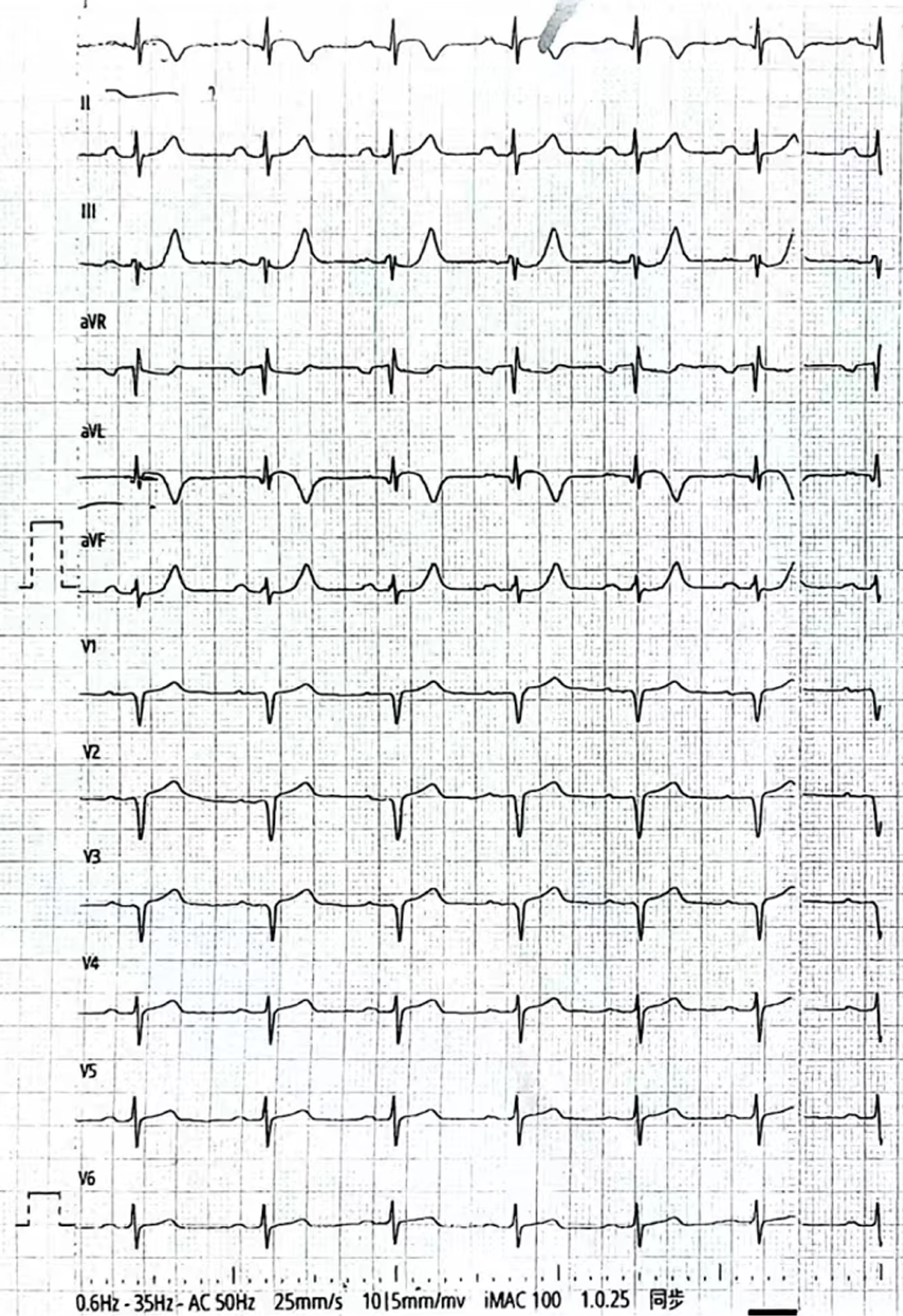
Figure 1
Electrocardiogram examination on admission.
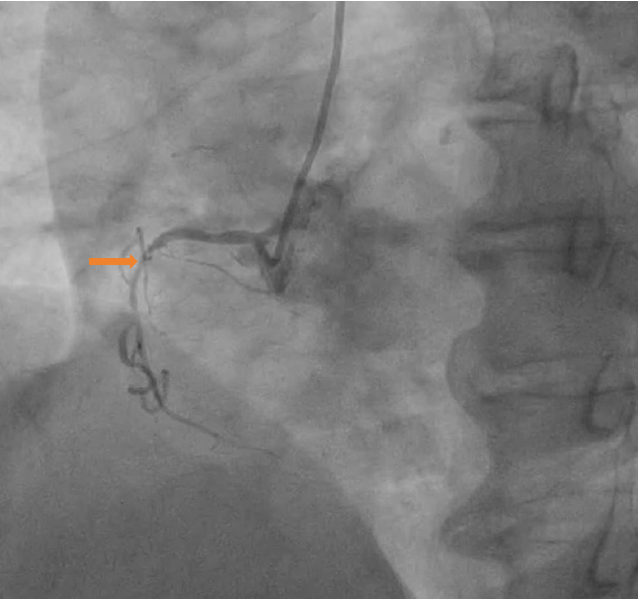
Figure 2 Preoperative images.
Right coronary angiography (Left anterior position).
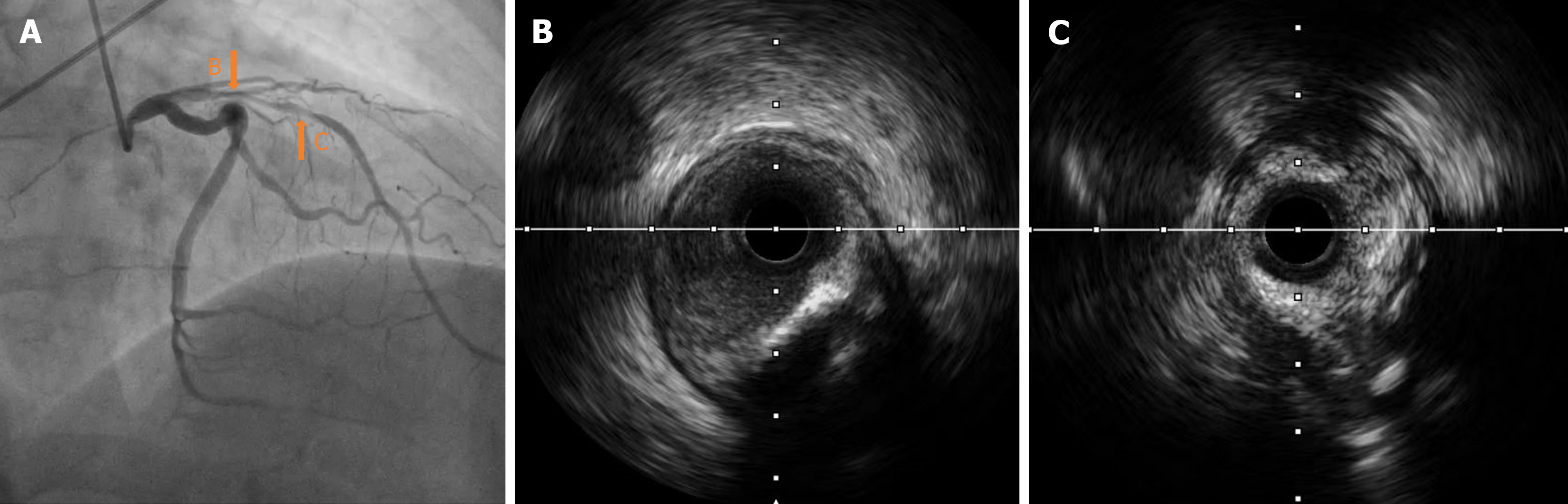
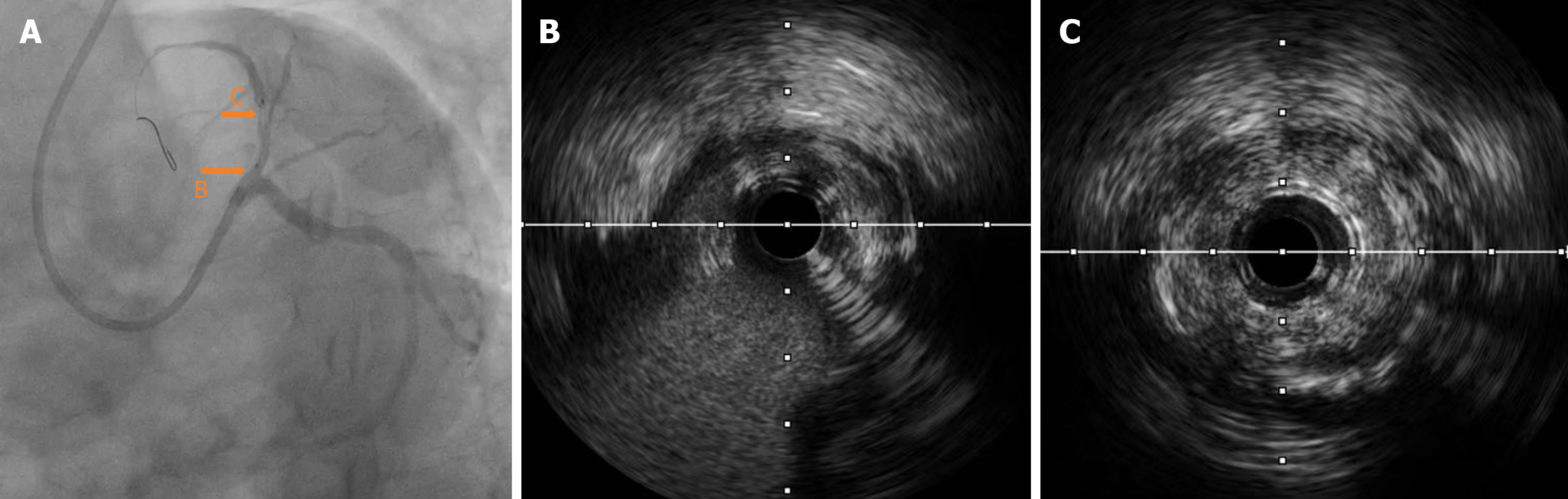
Figure 3 Preoperative images.
A: Left coronary angiography (right shoulder position); B: Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) of the proximal segments of the left anterior descending artery (LAD); C: IVUS of the middle segments of the LAD.
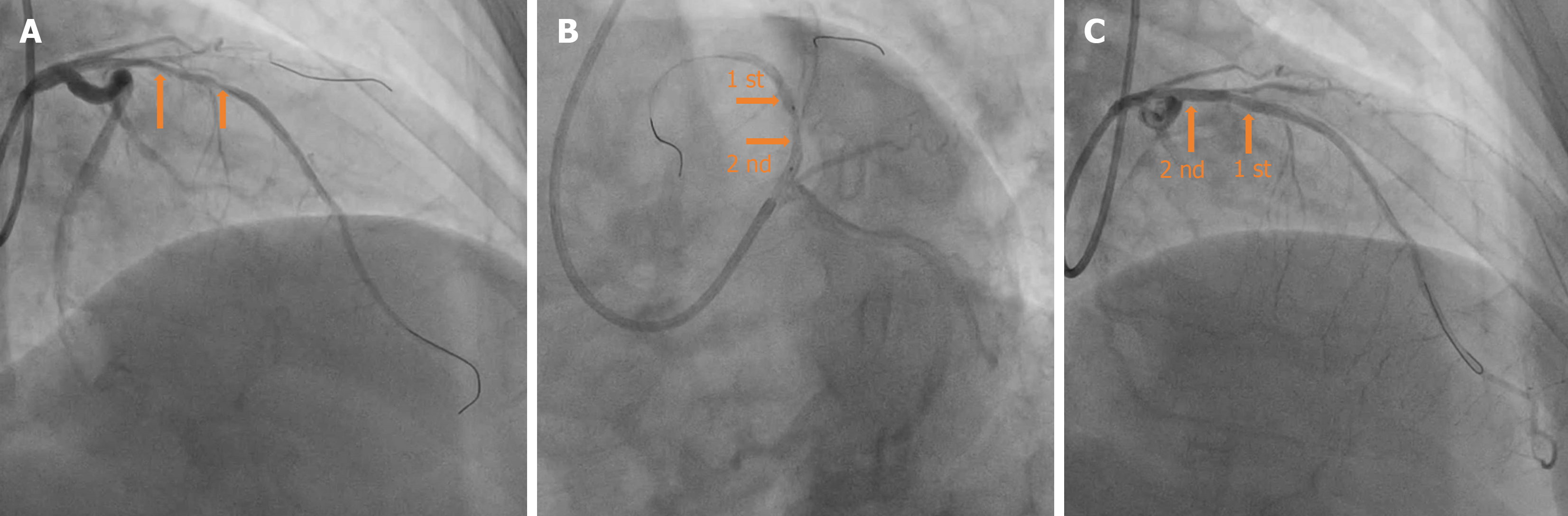
Figure 4 Intraoperative stent position.
A: Angiography (right shoulder position) after balloon dilation of the proximal and middle segments of the left anterior descending artery; B: Angiography (spider position) Positioning of the second bioresorbable stents (BRS) after the first BRS implantation in the middle descending artery; C: Postoperative images after BRS in situ expansion from proximal segment to left main trunk in the right shoulder position.
Figure 5 Angiography (spider position).
A: Imaging changes in the proximal segment of the left anterior descending artery; B: Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) of the proximal end of the unloaded bioresorbable stents (BRS) stent; C: IVUS of the distal end of the unloaded BRS stent.
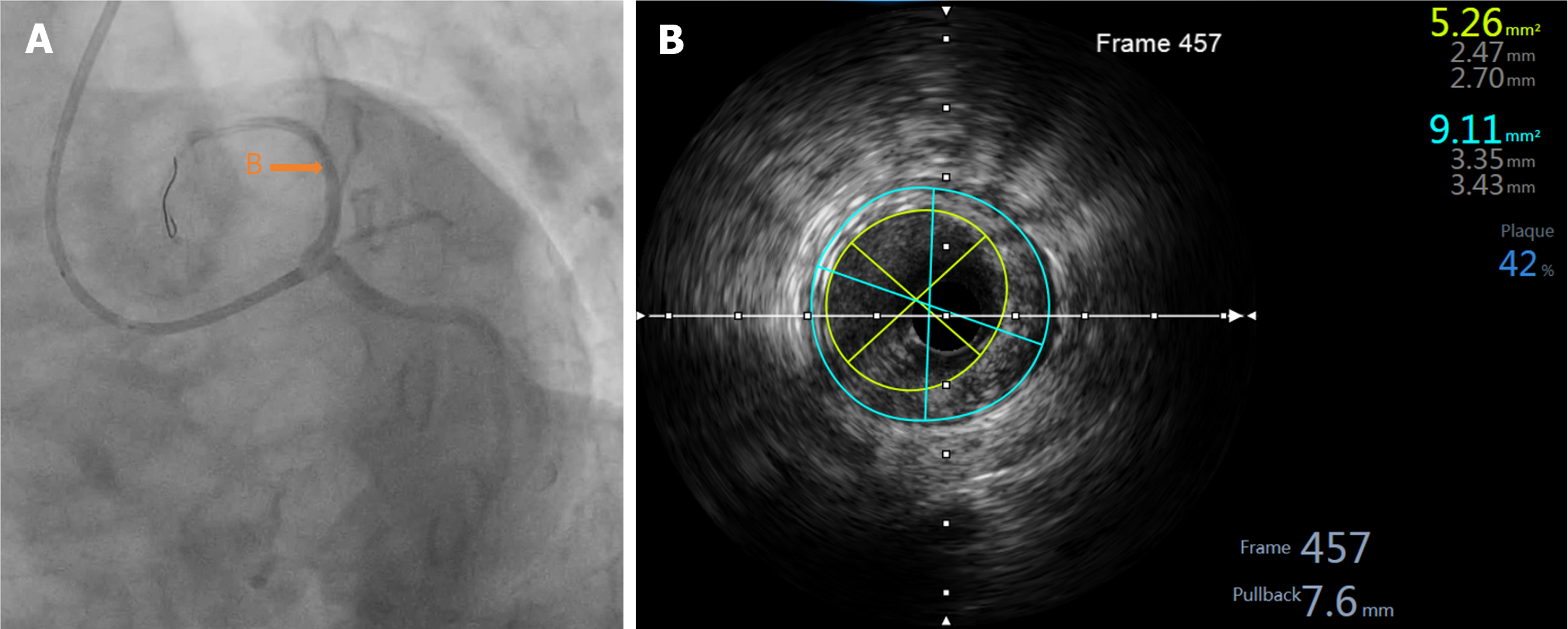
Figure 6 Postoperative images.
A: After bioresorbable stents in situ expansion from proximal segment to left main trunk: In the spider position; B: Intravascular ultrasound of the proximal of left anterior descending artery after bioresorbable stents expansion: The minimum lumen area was 5.26 mm².
- Citation: Sun T, Zhang MX, Zeng Y, Ruan LH, Zhang Y, Yang CL, Qin Z, Wang J, Zhu HM, Long Y. Unloading and successful treatment with bioresorbable stents during percutaneous coronary intervention: A case report. World J Cardiol 2024; 16(8): 484-490
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v16/i8/484.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i8.484