Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Cardiol. Mar 26, 2024; 16(3): 118-125
Published online Mar 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i3.118
Published online Mar 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i3.118
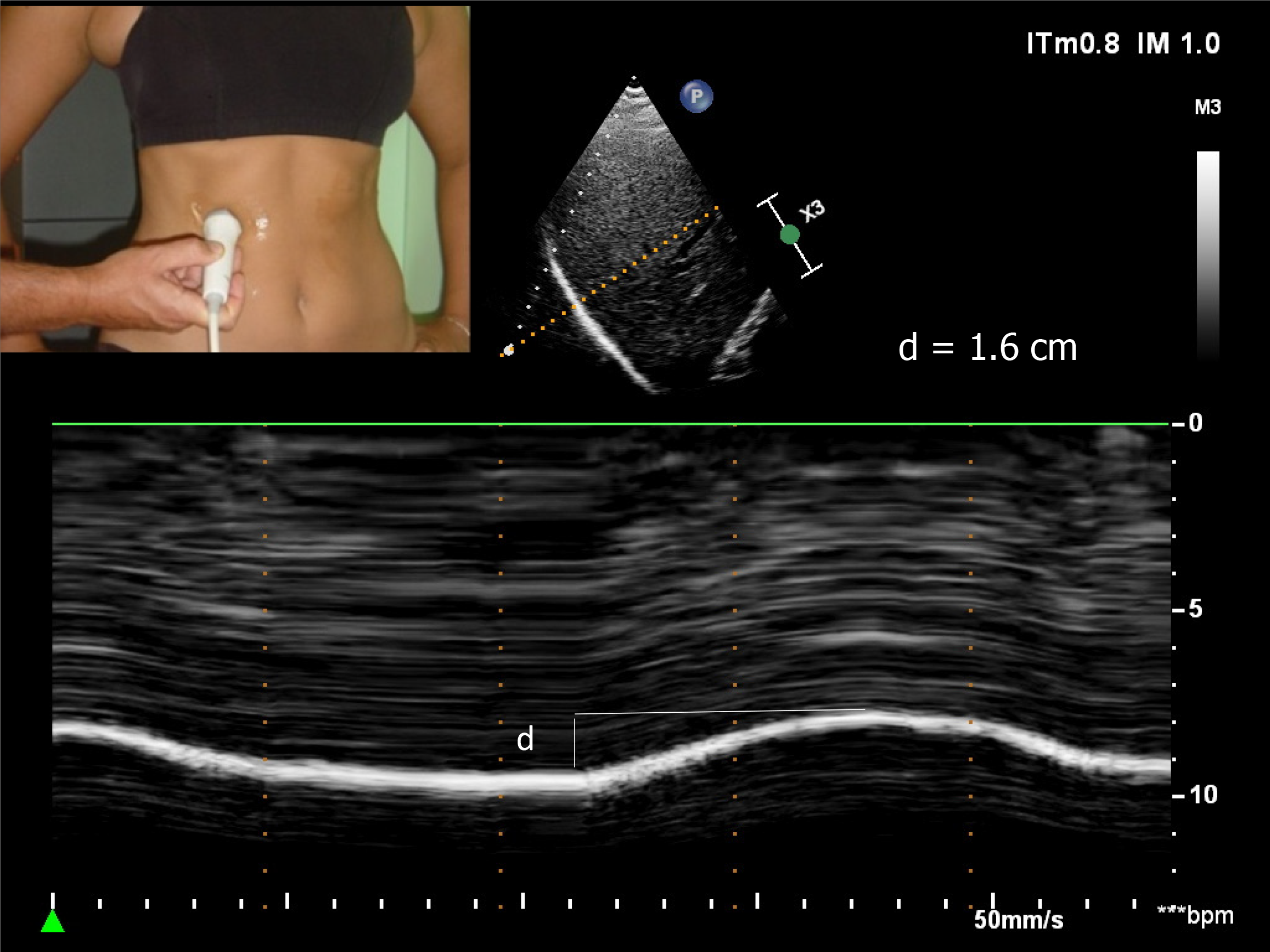
Figure 1 Diaphragmatic motion recorded by M-mode ultrasonography during quiet breathing d: Measurement of diaphragm excursion = 1.
6 cm.
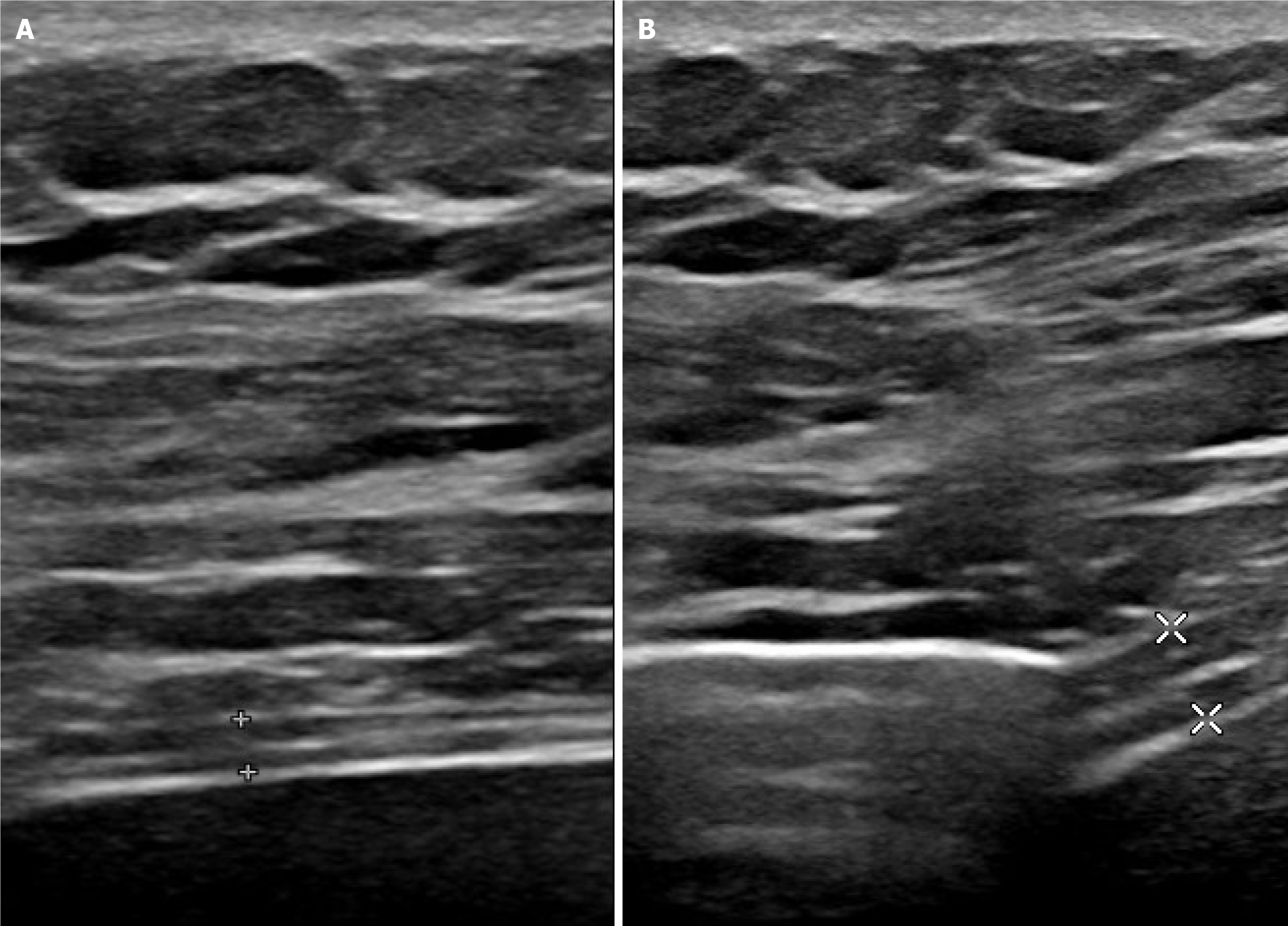
Figure 2 Measurement of thickening fraction using B mode ultrasonography.
A: End of expiration (1.7 mm); B: End of maximal inspiration (3.8 mm). Measurement of diaphragm thickness at expiration (1.7 mm), and at deep inspiration (3.8 mm) – here thickening fraction = (3.8–1.7)/ 1.7 = 123%.
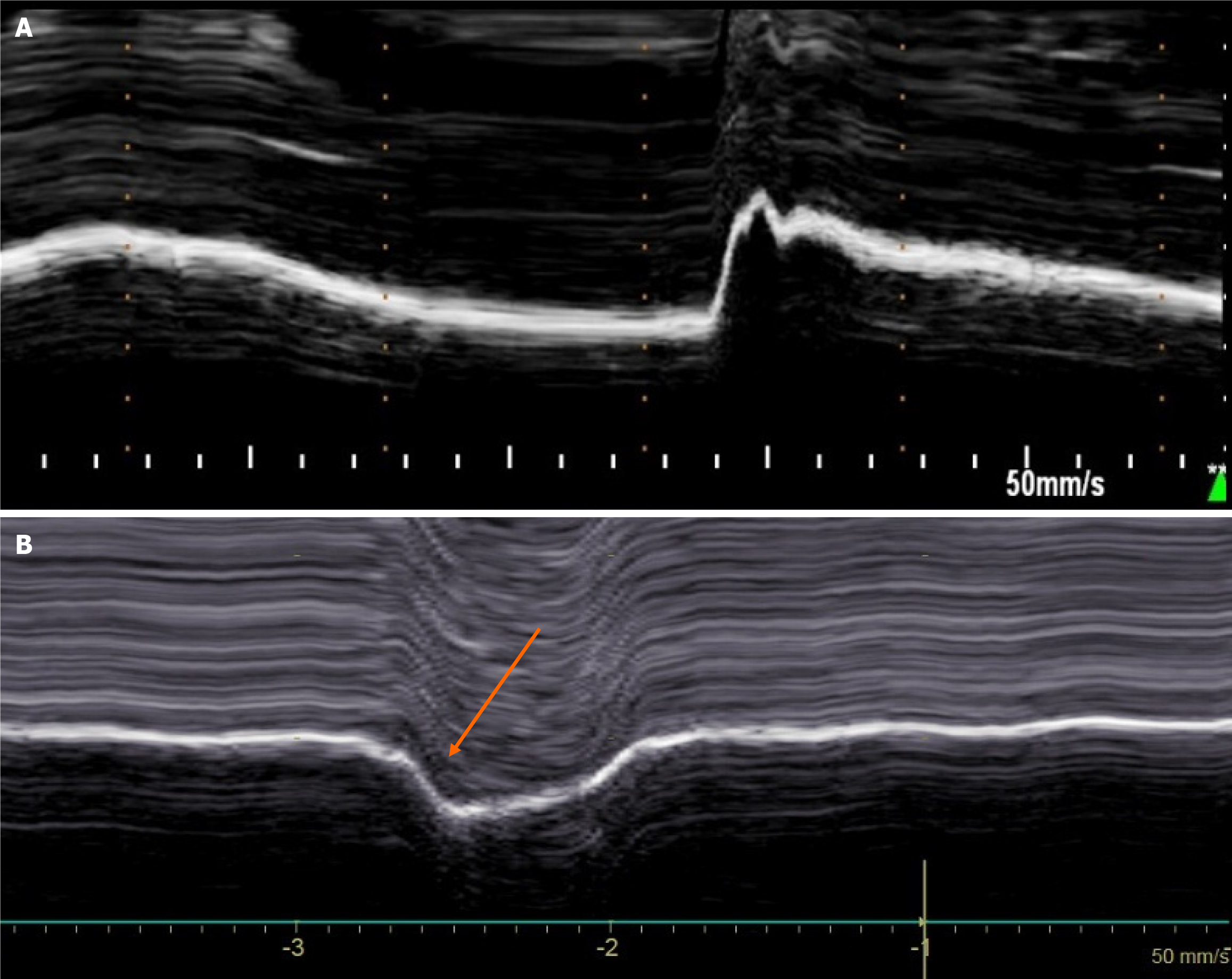
Figure 3 Diaphragmatic motion recorded by M-mode ultrasonography during voluntary sniffing.
A: Normal motion; B: Paradoxical movement (arrow) in patient with hemidiaphragm paralysis.
- Citation: Boussuges M, Blanc P, Bregeon F, Boussuges A. Interest of thoracic ultrasound after cardiac surgery or interventional cardiology. World J Cardiol 2024; 16(3): 118-125
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v16/i3/118.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i3.118