Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Cardiol. Oct 26, 2024; 16(10): 564-573
Published online Oct 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i10.564
Published online Oct 26, 2024. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v16.i10.564
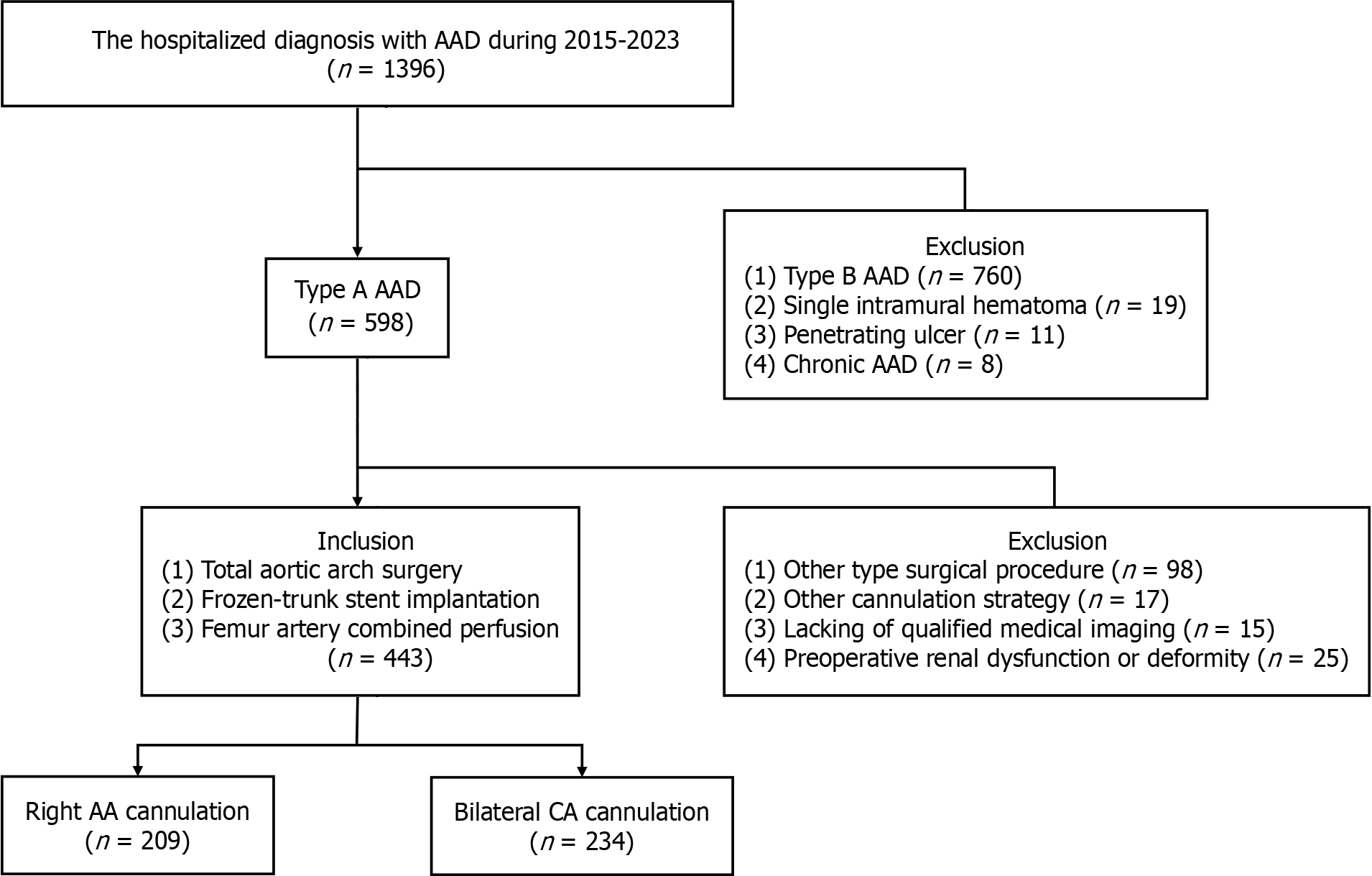
Figure 1 Study protocol.
AA: Axillary artery; AAD: A aortic dissection; CA: Carotid artery.
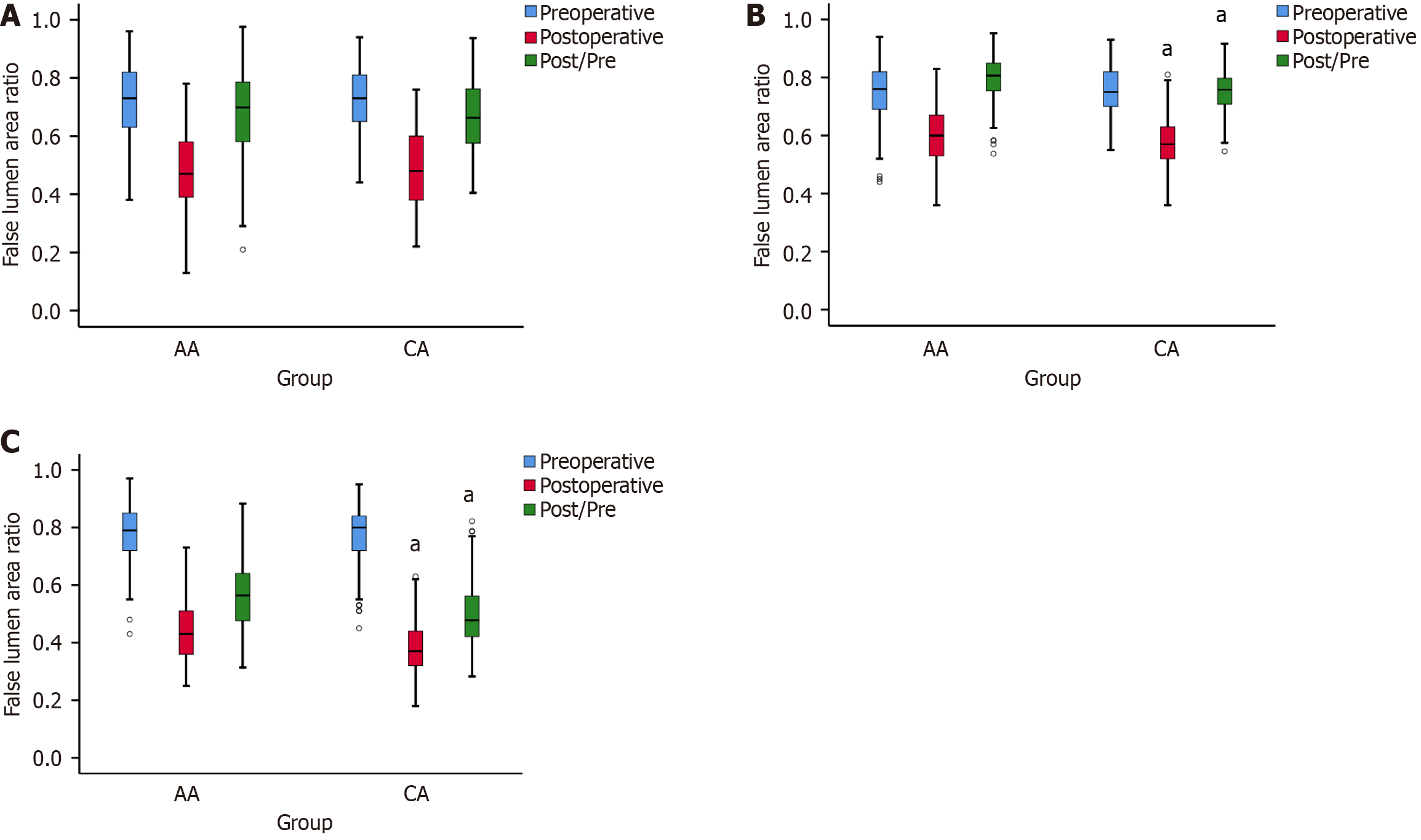
Figure 2 Segment changes in the false lumen area ratio in the descending aorta of the axillary artery and carotid artery groups calculated by computed tomography angiography.
A: The preoperative (left), postoperative (middle), and postoperative/preoperative (right) false lumen area ratio (FLAR) of the S1; B and C: S2 and S3 segments in the AA and CA groups. S1: Thoracic segment; S2: Upper abdominal segment; S3: Lower abdominal segment. aIndicates a significant difference between the two groups (P < 0.01).
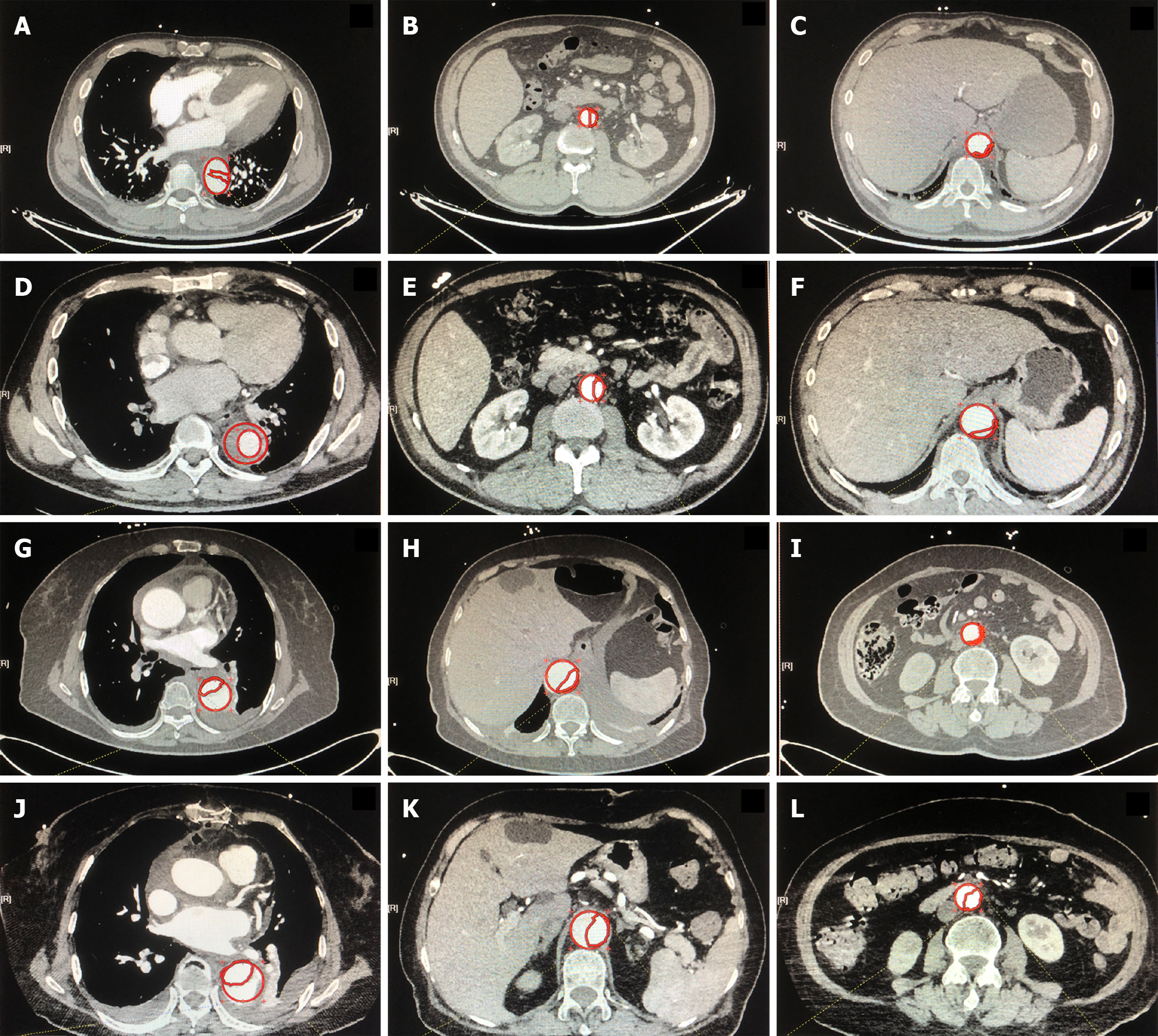
Figure 3 Typical preoperative and postoperative imaging for the false lumen area ratio in the descending aorta of the axillary artery and carotid artery groups by computed tomography angiography.
A-F: Typical preoperative and postoperative imaging of the false lumen area ratio (FLAR) in S1 (A and D), S2 (B and E) and S3 (C and F) in the CA group; G-L: Typical preoperative and postoperative imaging of FLAR in S1 (G and J), S2 (H and K) and S3 (I and L) in the AA group. False lumen area was defined as the traced area of the whole aorta (full line) minus the traced area of the true lumen (dotted line). S1: Thoracic segment; S2: Upper abdominal segment; S3: Lower abdominal segment.
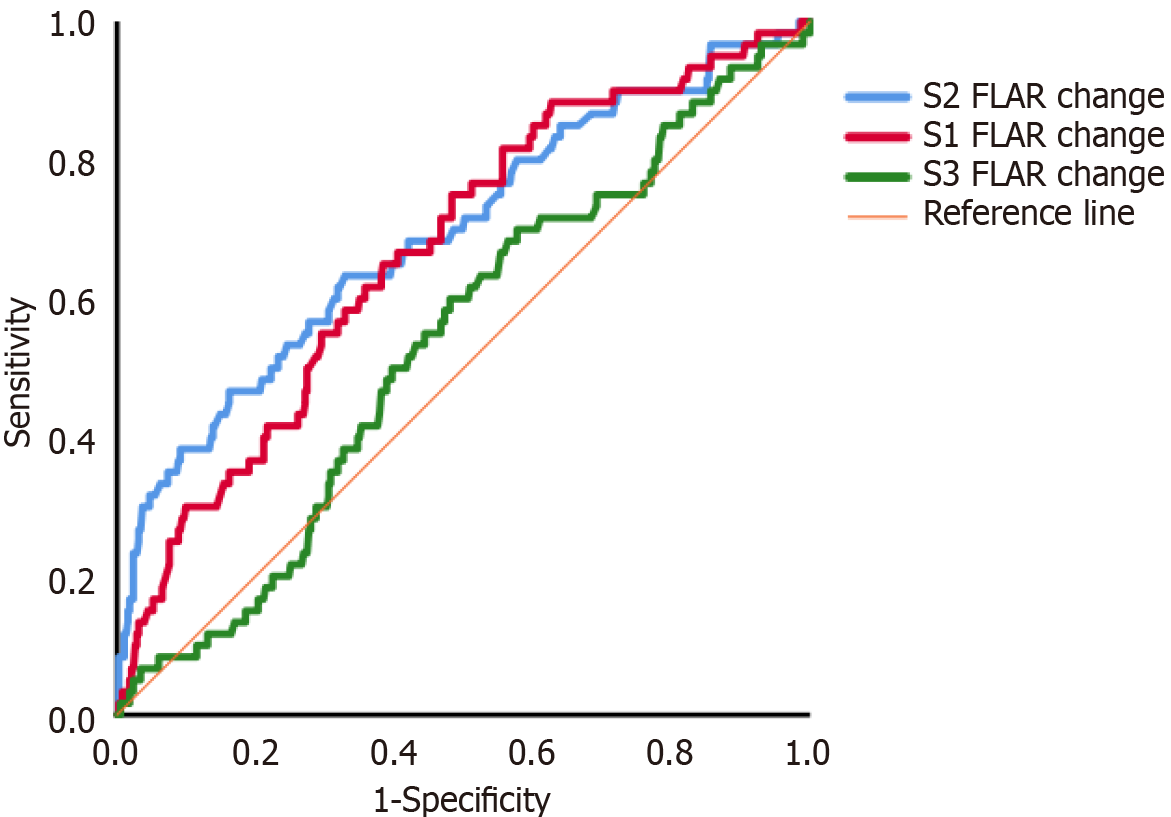
Figure 4 Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of changes in the false lumen area ratio in segments of the descending aorta and the prediction of renal replacement therapy.
The results of receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of the postoperative/preoperative false lumen area ratio (FLAR) for the prediction of renal replacement therapy were: S1, 0.668 (95%CI: 0.595-0.741, P < 0.001); S2, 0.693 (95%CI: 0.615-0.771, P < 0.001); and S3, 0.535 (95%CI: 0.459-0.610, P = 0.387). S1: Thoracic segment; S2: Upper abdominal segment; S3: Lower abdominal segment.
- Citation: Jiang Q, Yu T, Huang KL, Liu K, Li X, Hu SS. Carotid versus axillary artery cannulation for descending aorta remodeling in type A acute aortic dissection. World J Cardiol 2024; 16(10): 564-573
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v16/i10/564.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v16.i10.564