Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Cardiol. Apr 26, 2022; 14(4): 220-230
Published online Apr 26, 2022. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i4.220
Published online Apr 26, 2022. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v14.i4.220
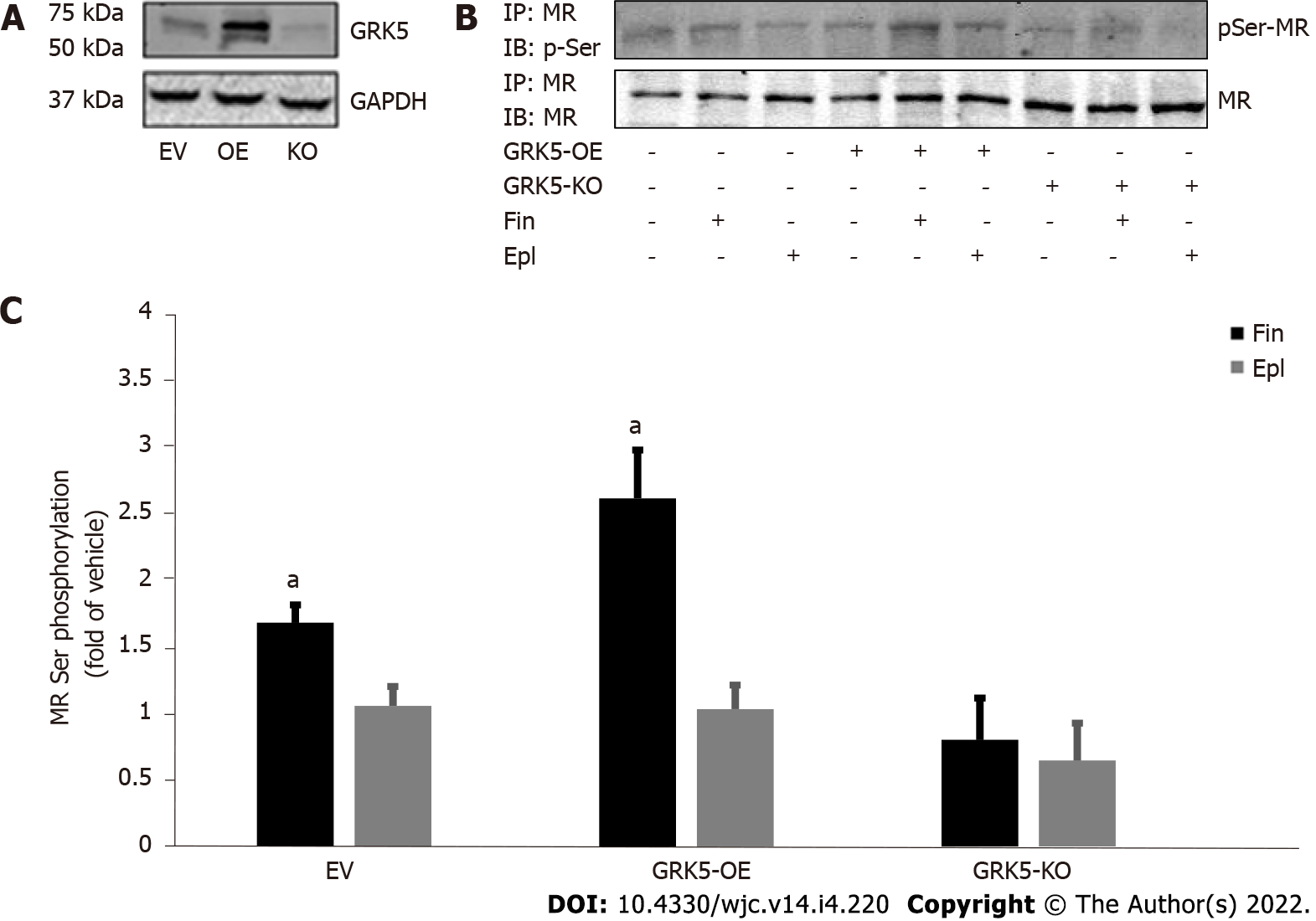
Figure 1 G protein-coupled receptor-kinase 5 phosphorylates the cardiac mineralocorticoid receptor in response to finerenone but not to eplerenone.
A: Western blotting to confirm G protein-coupled receptor-kinase (GRK)-5 overexpression (OE) with a wild type GRK5-encoding lentivirus or deletion (KO) via a GRK5-targeting CRISPR lentivirus in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. GAPDH blotting is also shown as loading control; B, C: Western blotting for the phosphoserine content of the mineralocorticoid receptor in response to 10 mmol/L finerenone (Fin) or 10 mmol/L eplerenone (Epl) in GRK5-overexpressing (GRK5-OE) or in GRK5-KO or in control, empty virus (EV)-infected H9c2 cells. Representative blots are shown in (B) and the densitometric quantitation of three independent experiments in (C). aP < 0.05, vs Epl; n = 3 independent experiments performed in duplicate per cell clone/treatment. EV: Empty vector mock virus-transfected (control) cells; IP: Immunoprecipitation; IB: Immunoblotting.
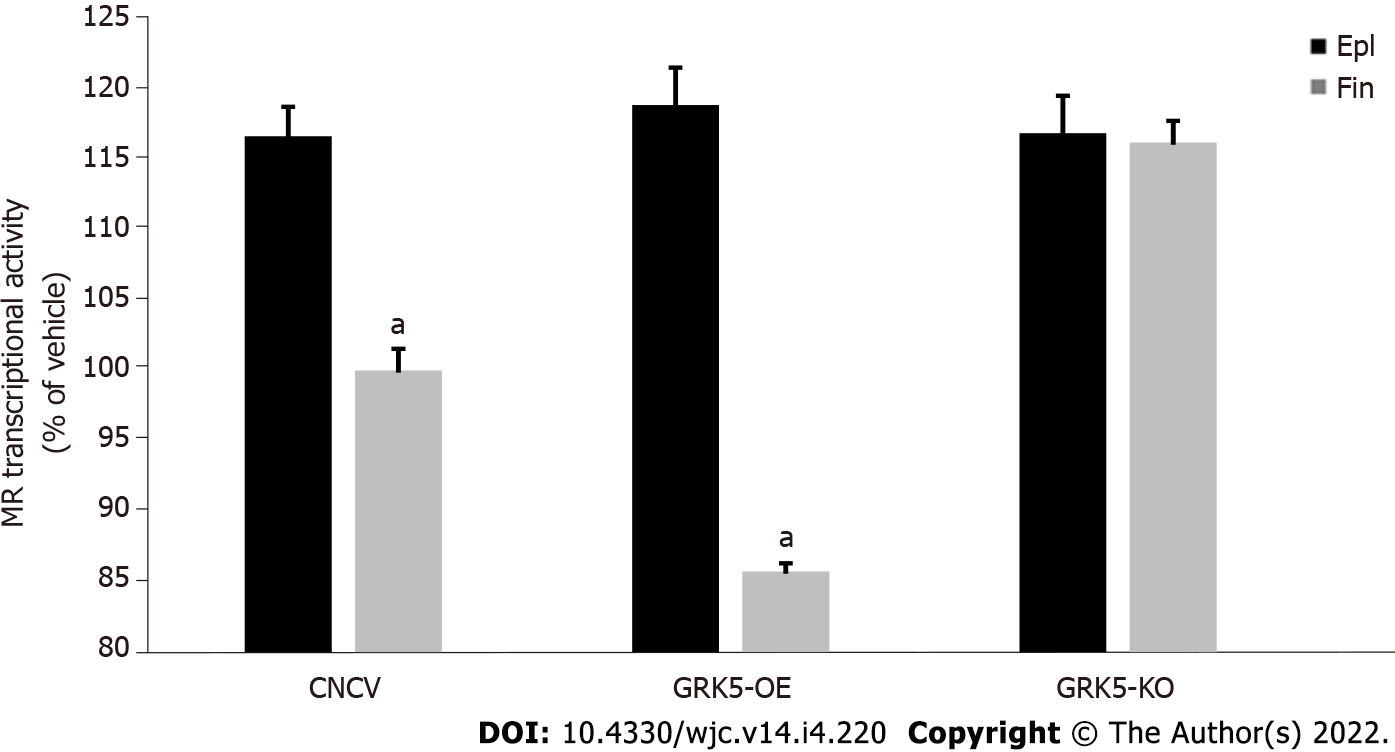
Figure 2 G protein-coupled receptor-kinase 5 inhibits the cardiac mineralocorticoid receptor in response to finerenone but not to eplerenone.
Transcriptional activity of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) in response to either 10 mmol/L eplerenone or 10 mmol/L finerenone in H9c2 cardiomyocytes overexpressing G protein-coupled receptor-kinase (GRK)-5 or having GRK5 genetically deleted via CRISPR (GRK5-KO). Neither agent was able to suppress MR basal transcriptional activity in GRK5-KO cells. aP < 0.05, vs eplerenone; n = 5 independent measurements per cell clone/treatment performed in triplicate. CNCV: CRISPR negative control virus-infected control cells; GRK5-OE: G protein-coupled receptor-kinase 5-overexpressing.
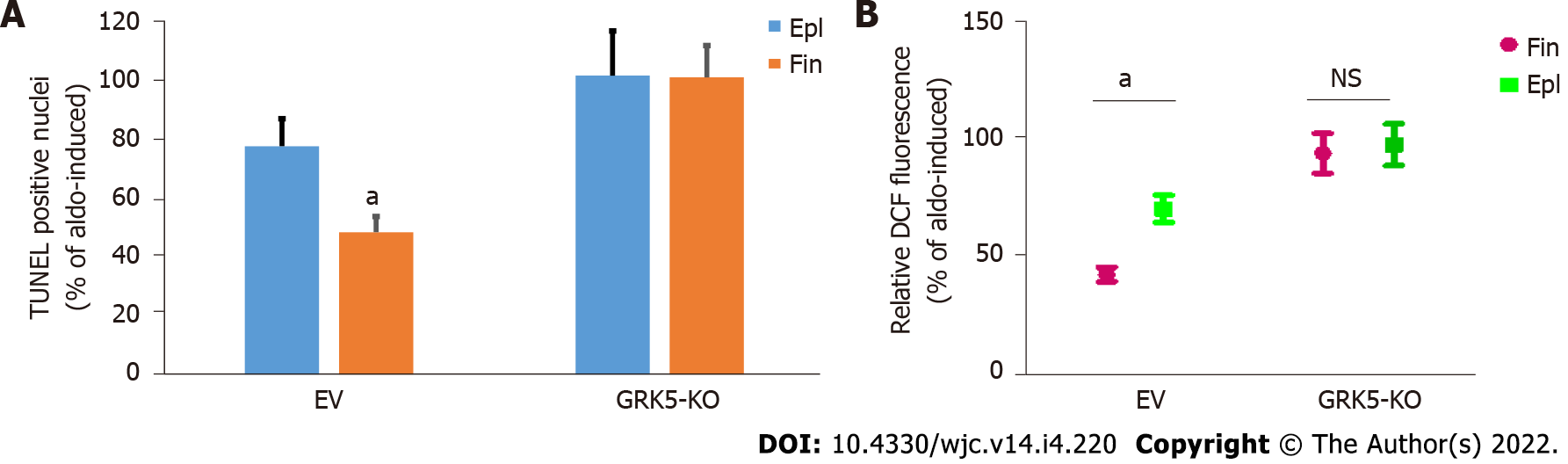
Figure 3 Comparison of anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative efficacies of finerenone vs eplerenone in aldosterone-treated cardiomyocytes in the presence or absence of G protein-coupled receptor-kinase 5.
A: Apoptotic cell death in control, empty vector (mock) virus-infected (EV) cells or in cells having G protein-coupled receptor-kinase (GRK)-5 genetically (CRISPR lentivirus-mediated) deleted (GRK5-KO) and treated with 100 nmol/L aldosterone (Aldo) alone or in the presence of 10 mmol/L eplerenone (Epl) or 10 mmol/L finerenone for 24 h. aP < 0.05, vs Epl; n = 4 independent experiments per transfection/treatment. Essentially no inhibition of Aldo-induced apoptosis could be detected with either drug in GRK5-KO cells; B: ROS generation in these cells, as measured via the DCF assay. aP < 0.05. Not significant at P = 0.05; n = 4 independent experiments per transfection/treatment. EV: Empty virus; Epl: Eplerenone; Fin: Finerenone; NS: Not significant.
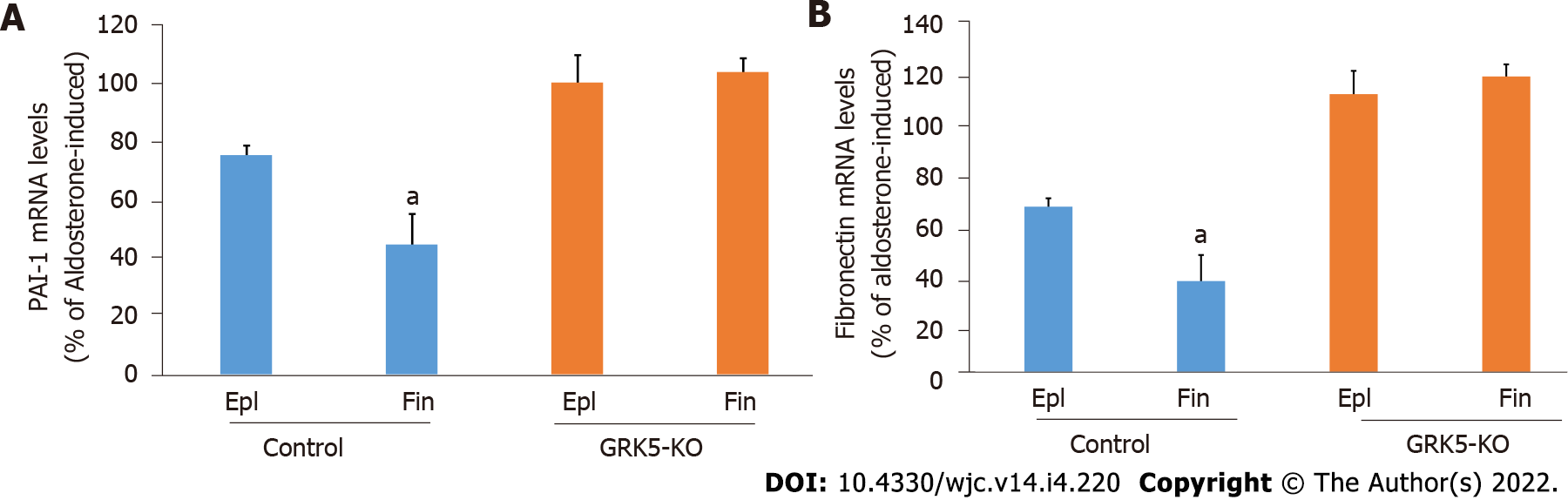
Figure 4 Comparison of the anti-fibrotic efficacies of finerenone vs eplerenone in aldosterone-treated cardiomyocytes in the presence or absence of G protein-coupled receptor-kinase 5.
mRNA levels of PAI-1 (A) and fibronectin (B), in response to a 2-h-long treatment of 100 nmol/L aldosterone in the presence of either 10 mmol/L eplerenone (Epl) or 10 mmol/L finerenone in control (mock, empty vector CRISPR lentivirus-infected) or in G protein-coupled receptor-kinase (GRK)-5-KO (rat GRK5-targeting CRISPR lentivirus-infected) cells. 18S rRNA levels were used for normalization of the results. aP < 0.05, vs Epl; n = 3 independent measurements per cell clone/treatment performed in triplicate. Epl: Eplerenone; Fin: Finerenone.
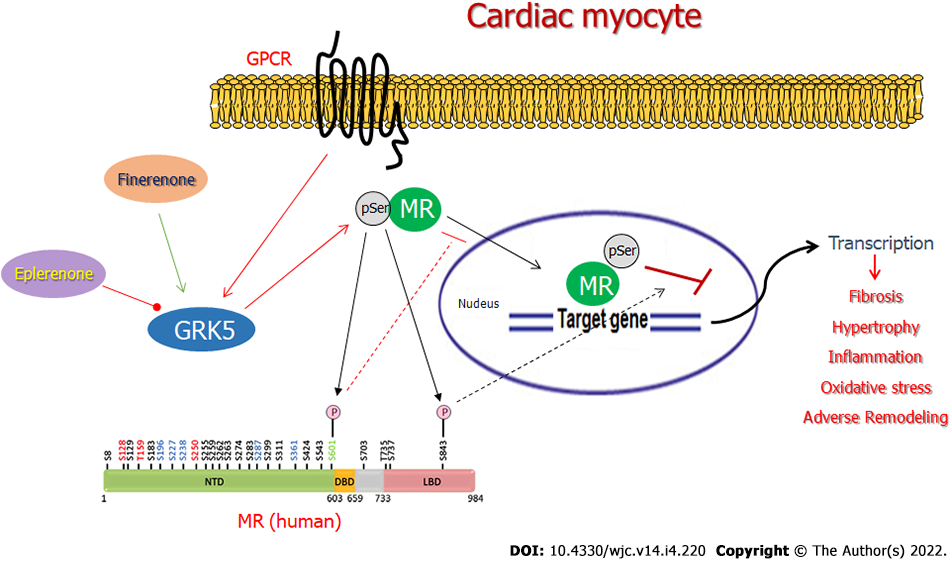
Figure 5 Schematic illustration of the differential effects of finerenone vs eplerenone on G protein-coupled receptor-kinase 5-dependent repression of the cardiac mineralocorticoid receptor.
Finerenone, unlike eplerenone, stimulates G protein-coupled receptor-kinase (GRK)-5 to phosphorylate the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR). The two main (putative) GRK5 phosphorylation sites on the human MR protein, Ser601 and Ser843, are highlighted, along with their functional impacts for the MR (pSer601 blocks nuclear translocation; pSer843 suppresses Aldo-induced transcriptional activity)[24,30]. GPCR: G protein-coupled receptor; NTD: N-terminal domain; DBD: DNA-binding domain; LBD: Ligand-binding domain; pSer: Phosphoserine. See text for more details and for all other molecular acronyms' descriptions.
- Citation: Pollard CM, Suster MS, Cora N, Carbone AM, Lymperopoulos A. GRK5 is an essential co-repressor of the cardiac mineralocorticoid receptor and is selectively induced by finerenone. World J Cardiol 2022; 14(4): 220-230
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v14/i4/220.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v14.i4.220