Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Biol Chem. Nov 26, 2015; 6(4): 310-323
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.310
Published online Nov 26, 2015. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.310
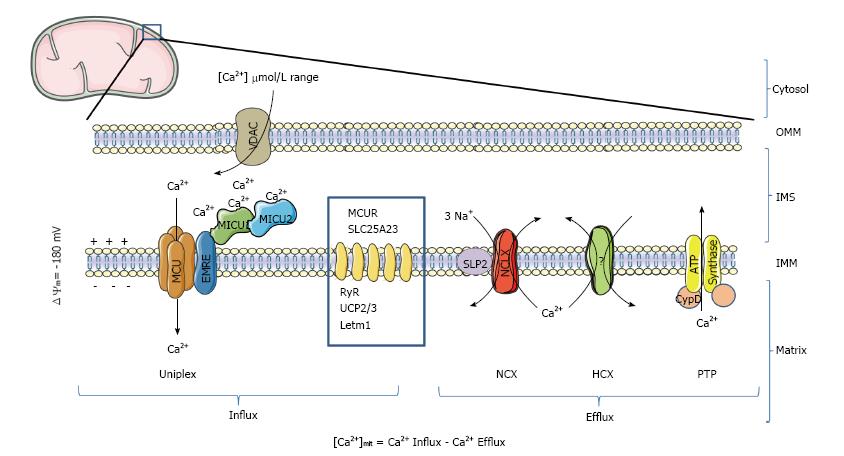
Figure 1 Ca2+ transport proteins of mitochondria.
In mammalian mitochondria, the uptake of Ca2+ is mediated by the Ca2+-selective channel MCU, which is part of a high molecular weight protein complex called Uniplex. At least 4 additional proteins (MCUb, MICU1, MICU2 and EMRE) regulate MCU activity. Ca2+ is then extruded by a sodium/calcium exchange (NCX) or proton/calcium exchange (HCX). If the protein NCLX has been confirmed to be the mitochondrial NCX, which is down-regulated by the protein SLP-2, the molecular nature of the mitochondrial HCX is still debated. Dimers of mitochondrial ATP synthase have been proposed to form the PTP, a mitochondrial channel regulated by CypD, that facilitates PTP opening by desensitizing PTP to Ca2+. Besides being activated by Ca2+, PTP has also been proposed to act as a reversible fast Ca2+ release channel. Other non-MCU mitochondrial proteins with an indirect or debated effect on Ca2+ transport are represented in the blue square (MCUR; SLC25A23; ryanodine receptor, RyR; UCP2; UCP3; LETM1). OMM: Outer mitochondrial membrane; IMS: Inter-membrane space; IMM: Inner mitochondrial membrane; VDAC: Mitochondrial porin; PTP: Permeability transition pore; CypD: Cyclophilin D; MCU: Mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter; MCUR1: Mitochondrial calcium uniporter regulator 1; MICU1: Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake protein 1; MICU2: Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake protein 2; EMRE: Essential MCU regulator.
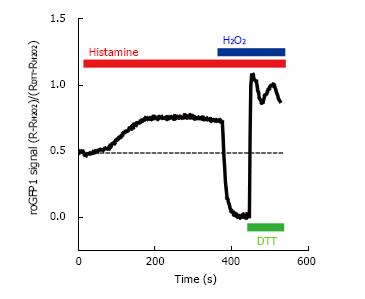
Figure 2 Ratiometric fluorescence intensity response of roGFP1 to histamine stimulation and exogenous H2O2 and DL-dithiothreitol in living HeLa cells.
HeLa cells were transfected with the mitochondrial targeted redox sensor roGFP1. Cells were excited at 410 and 480 nm and emission was collected at 535 nm. The 410/480 fluorescence ratio (R) was normalized to the minimum of fluorescence (obtained after the addition of 1 mmol/L H2O2) and the maximum (after the addition of 10 mmol/L dithiothreitol, DL-dithiothreitol). The effect of intracellular Ca2+ was assessed by stimulating the cell with 100 μmol/L histamine. DTT: DL-Dithiothreitol.
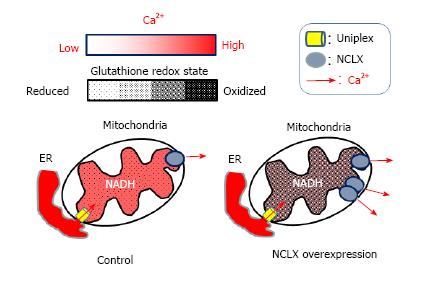
Figure 3 Proposed model for the modulation of the matrix redox signaling by mitochondrial Ca2+.
After cell stimulation, Ca2+ released from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) enters in mitochondria by the mitochondrial uniplex (left), stimulating matrix Ca2+-dependent dehydrogenases, which increase NADH levels and promoting a reduction of the mitochondrial glutathione pool. In cells over-expressing the mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCLX, right) Ca2+ extrusion is more efficient and therefore Ca2+-dependent dehydrogenases less activated. Such lowering the mitochondrial Ca2+ response blunts NADH formation and prevents matrix redox changes of the mitochondrial glutathione pool. NADH: Reduced form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide; NCLX: Mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger.
- Citation: Santo-Domingo J, Wiederkehr A, De Marchi U. Modulation of the matrix redox signaling by mitochondrial Ca2+. World J Biol Chem 2015; 6(4): 310-323
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v6/i4/310.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v6.i4.310