Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. Aug 26, 2014; 5(3): 308-320
Published online Aug 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i3.308
Published online Aug 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i3.308
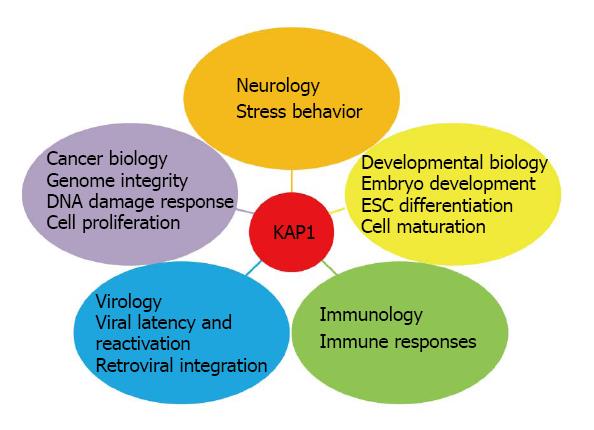
Figure 1 KRAB domain-associated protein 1 is involved in multiple aspects of cellular physiology.
Neurology: Kap1 knockout in mouse forebrain induces higher level of anxiety-like behavior. Developmental Biology: Several conditional kap1 deletions impair normal cell development including embryonic stem cell (ESC) differentiation, spermatogenesis, erythropoiesis, and the development of T-cell and B-cell. Immunology: KAP1 is involved in immune responses by regulating T/B cell activity and immune tolerance. Virology: KAP1 is critical to suppress retroviral activation and prevent HIV integration. Cancer Biology: KAP1 is positively or negatively correlated with prognosis in different cancer types. The roles of KAP1 in maintaining genome stability, mediating DNA damage response and affecting cell proliferation in vitro imply its potential roles during tumorigenesis.
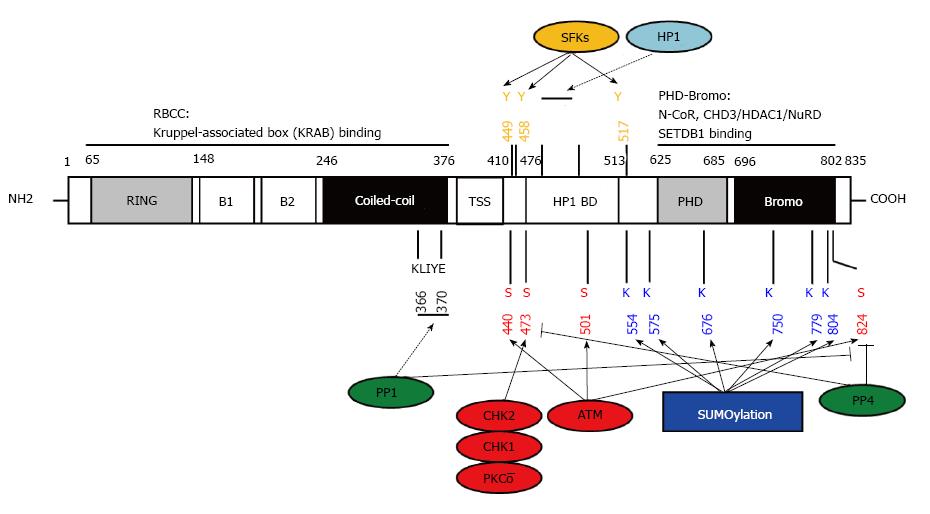
Figure 2 KAP1 structure, post-translational modifications and interacting proteins.
KAP1 has multi-domains for protein-protein interaction and post-translational modification. RBCC: RING-B1-B2-coiled-coil; TSS: TIF signature sequence; HP1 BD: HP1 binding domain; PHD: Plant homeo domain. Numbers represent the sequence of amino acids; Blue: SUMOylation sites; Red: Serine phosphorylation sites targeted by the indicated kinases (shown in red) or antagonized by phosphatases (shown in green); Orange: Tyrosine phosphorylation sites targeted by the indicated kinase family; KLIYF: PP1 binding site; PxVxL: HP1 binding site; Dotted lines: Protein-protein interaction; SFKs: Src family kinases; HP1: Heterochromatin-associated protein 1; ATM: Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated; PP1: Protein phosphatase 1; CHD3/NuRD: Chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 3/nucleosome remodeling deacetylase; HDAC: Histone deacetylase.
- Citation: Cheng CT, Kuo CY, Ann DK. KAPtain in charge of multiple missions: Emerging roles of KAP1. World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(3): 308-320
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i3/308.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i3.308