Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2014; 5(2): 224-230
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.224
Published online May 26, 2014. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.224
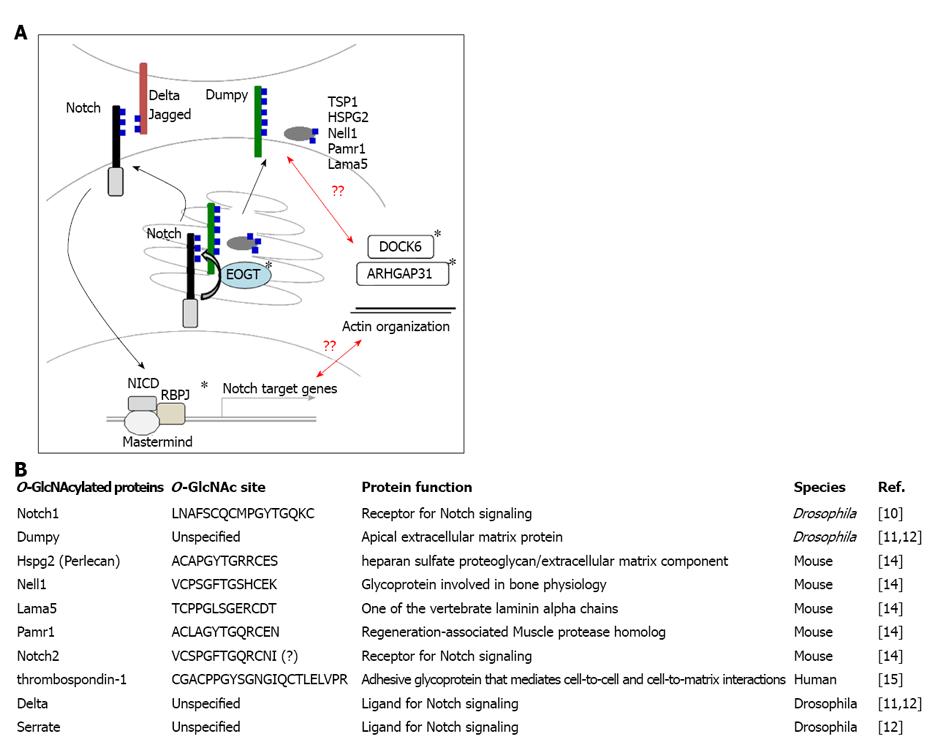
Figure 1 Extracellular O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine.
A: The O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc)ylation of extracellular protein domains is a newly identified translational modification of epidermal growth factor (EGF) domains, including Notch, HSPG2, Pamr1, and Lama5. Extracellular O-GlcNAc is mediated by EOGT in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Mutations in EOGT were recently identified in patients with Adams-Oliver syndrome (AOS). The role of EOGT in the pathogenesis of AOS is currently unknown. Given that RBPJ, a transcriptional factor for Notch signaling, is a causative gene for AOS, O-GlcNAcylation of Notch receptors by EOGT might regulate Notch receptor trafficking or Notch-ligand interactions. ARHGAP31 or DOCK6, another causative gene for AOS, affects the actin cytoskeleton by regulating Cdc42 and Rac1 activity. Thus, another possibility is that the O-GlcNAcylation of unidentified cell adhesion molecules by EOGT affects actin dynamics. It should be noted, however, that Dumpy homologues are not present in mammals. The O-GlcNAcylation of Notch ligands was reported in Drosophila. The causative genes for AOS are shown by asterisks; B: Summary of proteins with extracellular O-GlcNAc identified to date.
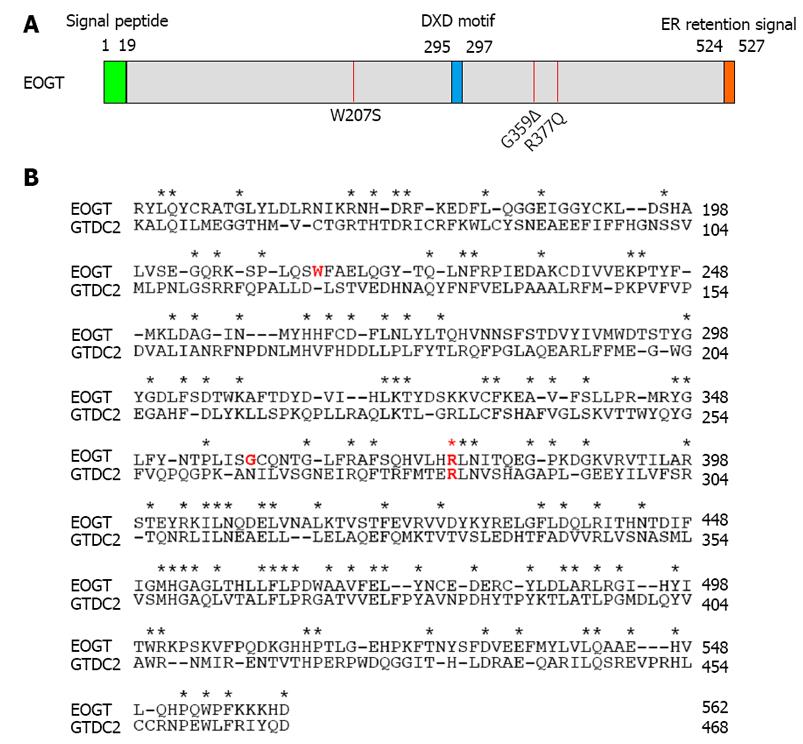
Figure 2 Extracellular O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine mutations found in Adams-Oliver syndrome.
A: A schematic representation of the primary structure of EOGT. The amino-terminal signal peptide is shown in yellow and the carboxyl-terminal Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu-like endoplasmic reticulum (ER) retrieval signal is in orange. The putative DXD motif involved in binding the nucleotide sugar is shown in blue. The position of each mutation is indicated by a red line; B: The amino acid sequence alignment of mouse EOGT (NP_780522, 149-562 aa) and mouse GTDC2/EOGT-L (Q8BW41, 55-468 aa). Identical amino acid residues are indicated by asterisks. Amino acid residues corresponding to the mutations in patients with Adams-Oliver syndrome are highlighted by red letters. EOGT: Extracellular O-linked β-N-acetylglucosamine.
-
Citation: Ogawa M, Furukawa K, Okajima T. Extracellular
O -linked β-N -acetylglucosamine: Its biology and relationship to human disease. World J Biol Chem 2014; 5(2): 224-230 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i2/224.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v5.i2.224