Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
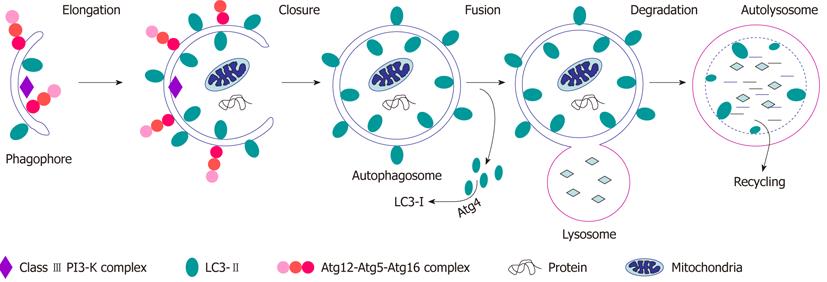
Figure 1 The process of autophagy.
Autophagy is initiated with the formation of the phagophore, mediated by the class III PI3-K complex that includes Vps34, Vps15, Atg14 and Beclin 1, and progresses through a succession of steps: elongation of the phagophore and engulfment of cytoplasmic material targeted for degradation; formation of the autophagosome, with delipidation of LC3-II by Atg4; fusion of the autophagosome with the lysosome to form the autolysosome; degradation of the vesicle content by lysosomal hydrolases; and recycling of the degradation products (amino acids, lipids and sugars) for ATP production. The autophagy machinery consists of two conjugation systems required for the elongation and extension of the phagophore: Atg5-Atg12, which subsequently oligomerizes with Atg16, and LC3-PE, LC3-II. LC3-II is formed as a result of the Atg4-mediated cleavage of cytosolic LC3. The resulting form of LC3, LC3-I is subsequently conjugated to a single PE molecule to form LC3-II, a reaction mediated by Atg3 and Atg7.
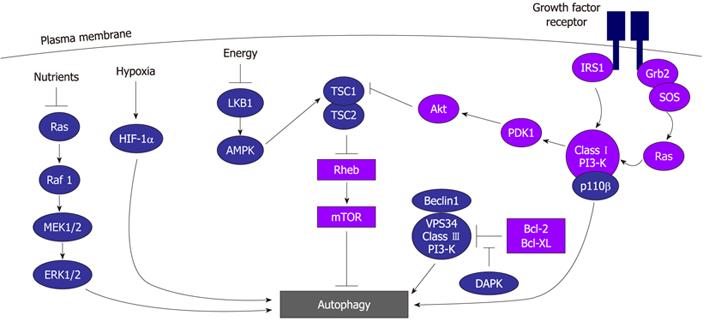
Figure 2 The regulation of autophagy.
Autophagy is regulated by multiple signaling pathways. In response to growth factors, mTOR is activated by the class I PI3-K and Akt, which inhibits tuberous sclerosis protein (TSC)1/TSC2. The activation of this cascade leads to the inhibition of autophagy. mTOR activity is inhibited by AMPK, a kinase activated in response to elevated intracellular AMP/ATP ratio. In addition, the p110-β catalytic subunit of the class I PI3-K can directly stimulate autophagy during starvation, independently of Akt activation, through its association with the class III PI3-K complex. The growth-factor-mediated activation of Ras induces antagonistic effects on autophagy depending on its downstream target, while the activation of the class I PI3-K cascade represses autophagy, and the stimulation of the Raf-1-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 signaling cascade in response to amino acid depletion promotes autophagy. Hypoxia induces autophagy via activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Finally, autophagy is also regulated by death-associated protein kinase, which promotes the initiation of autophagy through the release of Beclin 1 from the Bcl-2/Bcl-XL complex. The DAPk-related protein kinase 1 has also been found to be necessary for the induction of autophagy.
- Citation: Abounit K, Scarabelli TM, McCauley RB. Autophagy in mammalian cells. World J Biol Chem 2012; 3(1): 1-6
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v3/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v3.i1.1