Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Biol Chem. Aug 12, 2024; 15(1): 97938
Published online Aug 12, 2024. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v15.i1.97938
Published online Aug 12, 2024. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v15.i1.97938
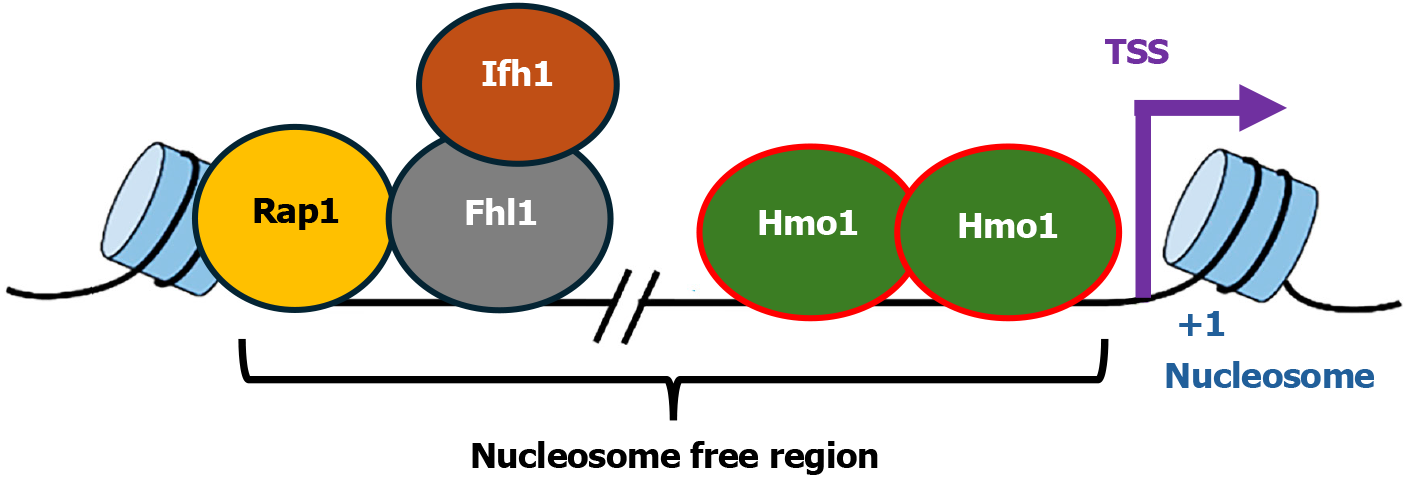
Figure 1 Diagram of the organization of Hmo1 associated Category I ribosome protein gene promoters.
The transcription factors, Rap1, Fhl1, Ifh1, and Hmo1, associated with the promoter are shown. The transcription start site, +1 nucleosome of the gene, and the nucleosome free region, are indicated. TSS: Transcription start site.
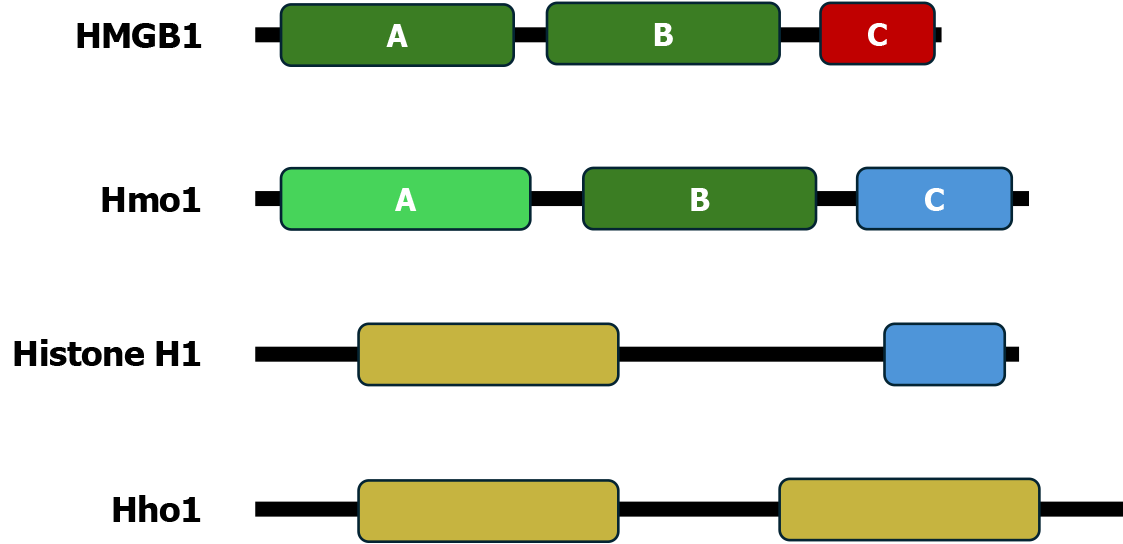
Figure 2 Domain structures of Hmo1 and related chromosomal architecture factors.
Illustrated are the high mobility group boxes (HMGBs) A and B and acidic C-terminal domain (CTD) of human HMGB1; the HMGB-like domain A, the HMGB homolog domain B, and the basic CTD of Hmo1; the globular domain and basic CTD of human linker histone H1.4; and the two globular domains of Hho1, yeast ortholog of linker histone H1. HMGB: High mobility group boxes.
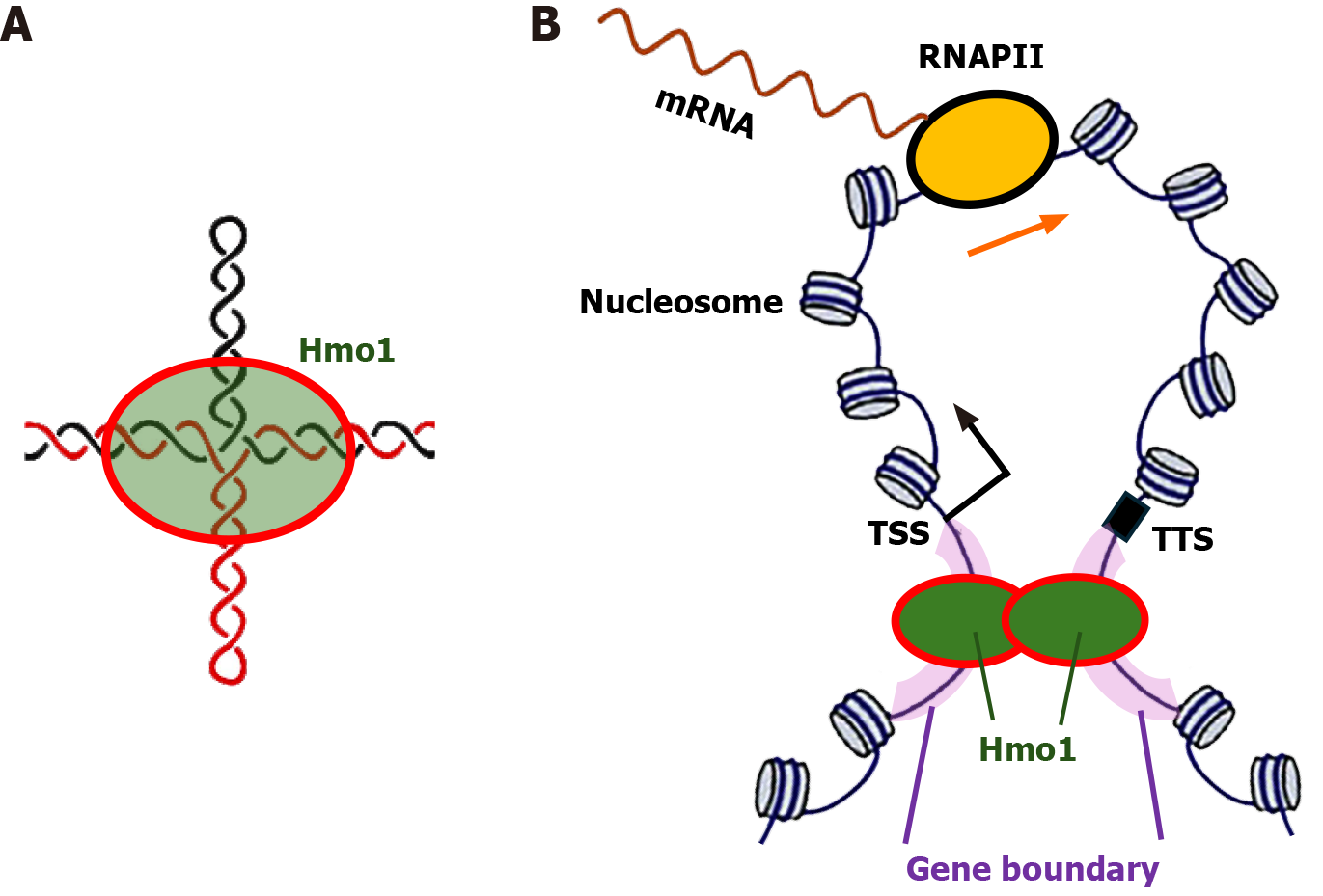
Figure 3 Model for the gene boundary function of Hmo1.
A: Hmo1 binds cruciform structure that may form in negatively supercoiled gene boundaries; B: Diagram of a gene loop structure. The transcriptional start site, transcriptional termination site and gene boundaries are indicated. An RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) transcribing the gene is shown. Note, more than one RNAPII may transcribe the gene at the same time. Hmo1 binds gene boundaries and help maintain the negative supercoiling of DNA in them. Dimerization/oligomerization of Hmo1 promotes the formation and maintenance of gene loop. RNAPII: RNA polymerase II; TSS: Transcriptional start site; TTS: Transcriptional termination site.
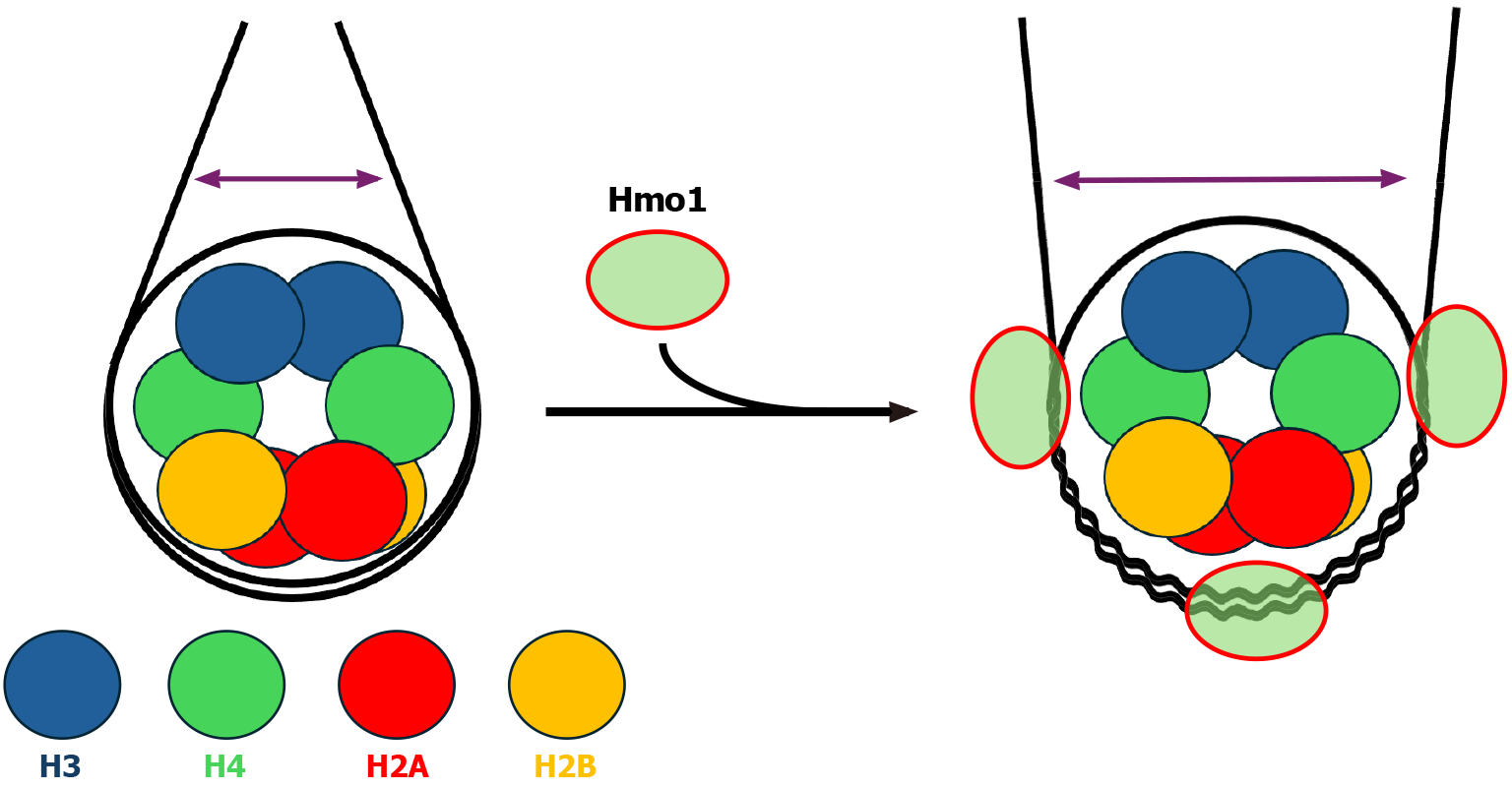
Figure 4 Impact of Hmo1 on nucleosome structure.
Left: Diagram of a nucleosome. Core histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 are shown as color-coded circles. The distance between linker DNA segments is represented by a double headed arrow. Right: Diagram of a Hmo1-bound nucleosome based on results from references[66,67]. Wiggly lines represent DNA strands that are separated from, or interact weakly with, core histones.
- Citation: Bi X. Hmo1: A versatile member of the high mobility group box family of chromosomal architecture proteins. World J Biol Chem 2024; 15(1): 97938
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v15/i1/97938.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v15.i1.97938