Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Biol Chem. Sep 27, 2021; 12(5): 70-86
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i5.70
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v12.i5.70
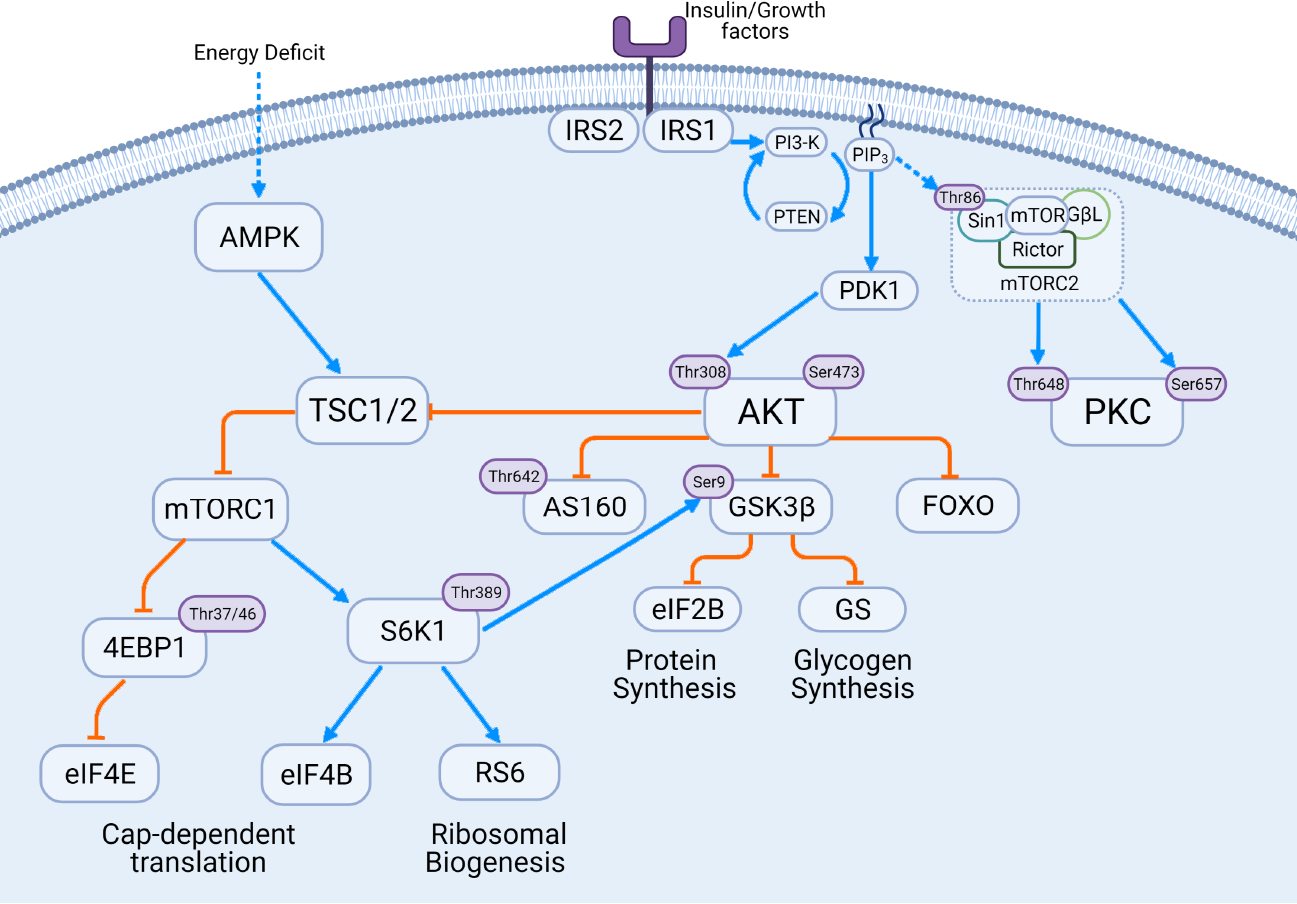
Figure 1 Insulin signaling cascade involving both glucoregulatory and anabolic pathways.
Phosphorylation sites of interest indicated on figure. Blue arrows (→) indicate activation of the substrate, orange bars (Ʇ) indicate inhibitory action on the substrate. Figure created with BioRender.com. mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; mTORC: mTOR complex; S6K1: S6 kinase beta-1; IRS: Insulin receptor substrates; PKC: Protein kinase C; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; TSC: Tuberous sclerosis complex; GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β; PIP3: phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphates.
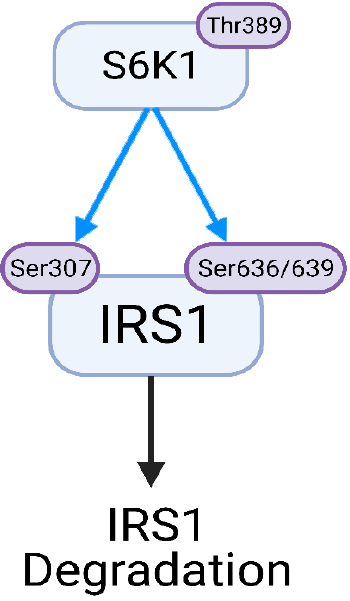
Figure 2 Downstream mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 substrate S6 kinase beta-1 phosphorylation of insulin receptor sub
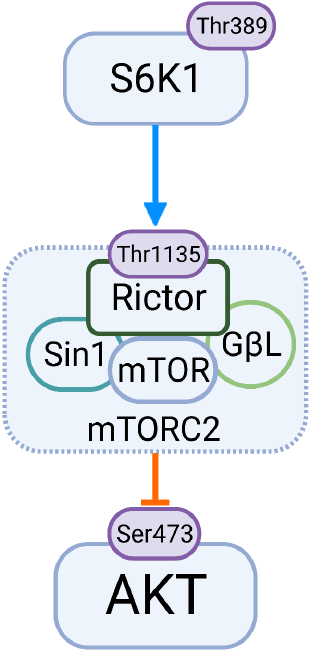
Figure 3 Downstream mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 substrate S6 kinase beta-1 is the primary kinase responsible for phosphorylation of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 component Rictor at Thr1135 which has been implicated in phos
- Citation: O'Reilly CL, Uranga S, Fluckey JD. Culprits or consequences: Understanding the metabolic dysregulation of muscle in diabetes. World J Biol Chem 2021; 12(5): 70-86
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v12/i5/70.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v12.i5.70