Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Aug 26, 2010; 1(8): 254-264
Published online Aug 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i8.254
Published online Aug 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i8.254
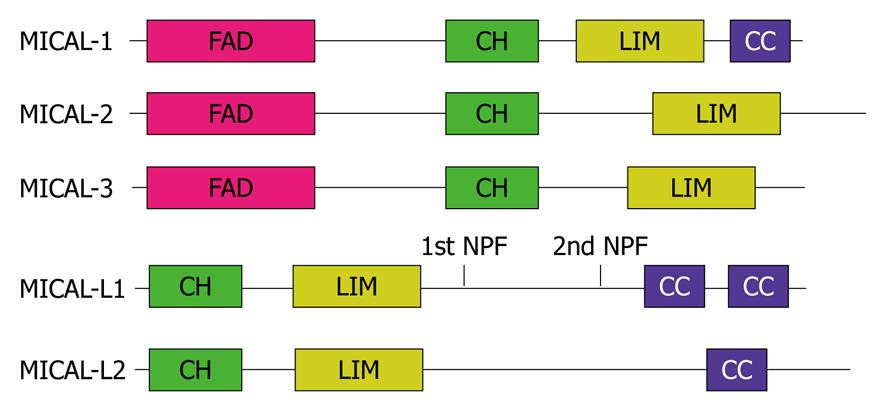
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the MICAL protein family domain architecture.
FAD: Flavin-adenine dinucleotide binding domain; CH: Calponin homology domain; LIM: LIM domain; CC: Coiled-coil; NPF: Asparagine-proline-phenylalanine motif.
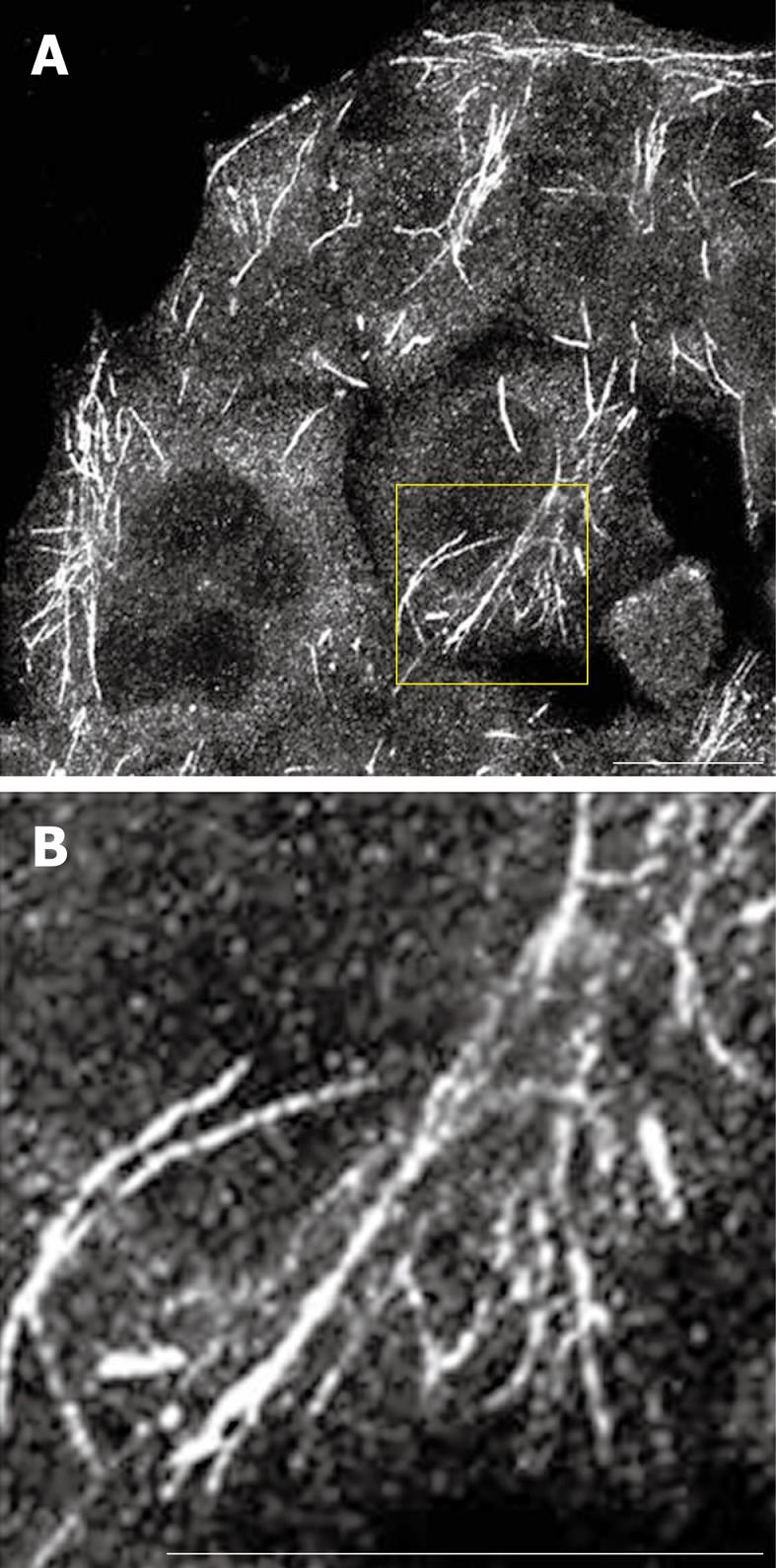
Figure 2 Endogenous MICAL-L1 localized to tubular recycling endosomes.
A and B: HeLa cells were grown on coverslips, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS, immunostained with anti-MICAL-L1 antibody, followed by 568-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody. A: MICAL-L1; B: MICAL-L1 (inset). Bar, 10 μm.
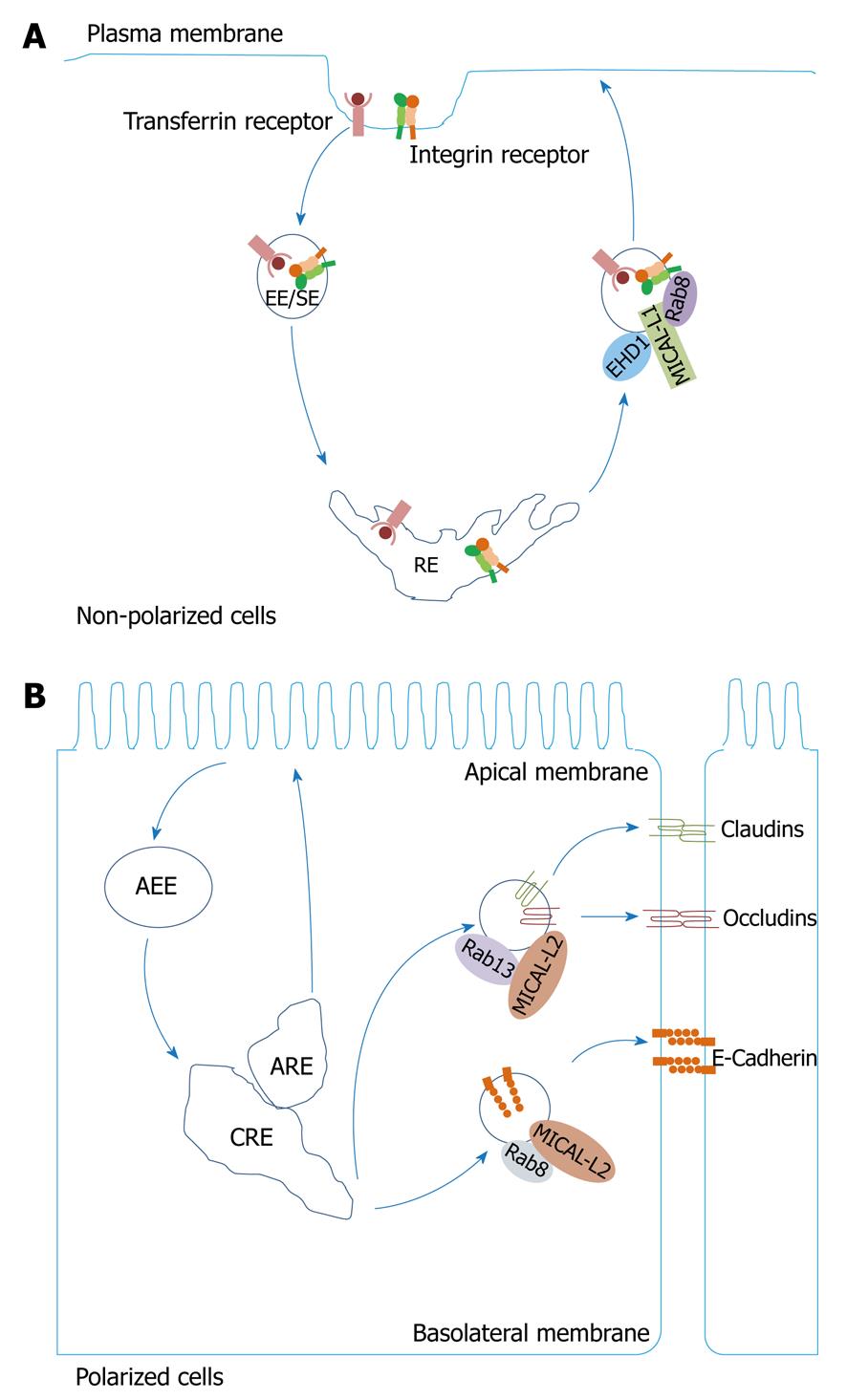
Figure 3 MICAL-L1 and MICAL-L2 regulate endocytic recycling.
A: MICAL-L1 recruits Eps15 homology domain 1 (EHD1) and Rab8A to endocytic membranes and regulates recycling of transferrin and β1 integrin receptors; B: MICAL-L2/Rab13 interactions control transport of claudin-1 and occludin to the plasma membrane, whereas MICAL-L2/Rab8 complexes regulate recycling of E-cadherin. EE/SE: Early endosome/sorting endosome; RE: Recycling endosome; AEE: Apical early endosome; CRE: Common recycling endosome; ARE: Apical recycling endosome.
- Citation: Rahajeng J, Giridharan SSP, Cai B, Naslavsky N, Caplan S. Important relationships between Rab and MICAL proteins in endocytic trafficking. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(8): 254-264
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i8/254.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i8.254