Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. May 26, 2010; 1(5): 133-143
Published online May 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.133
Published online May 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.133
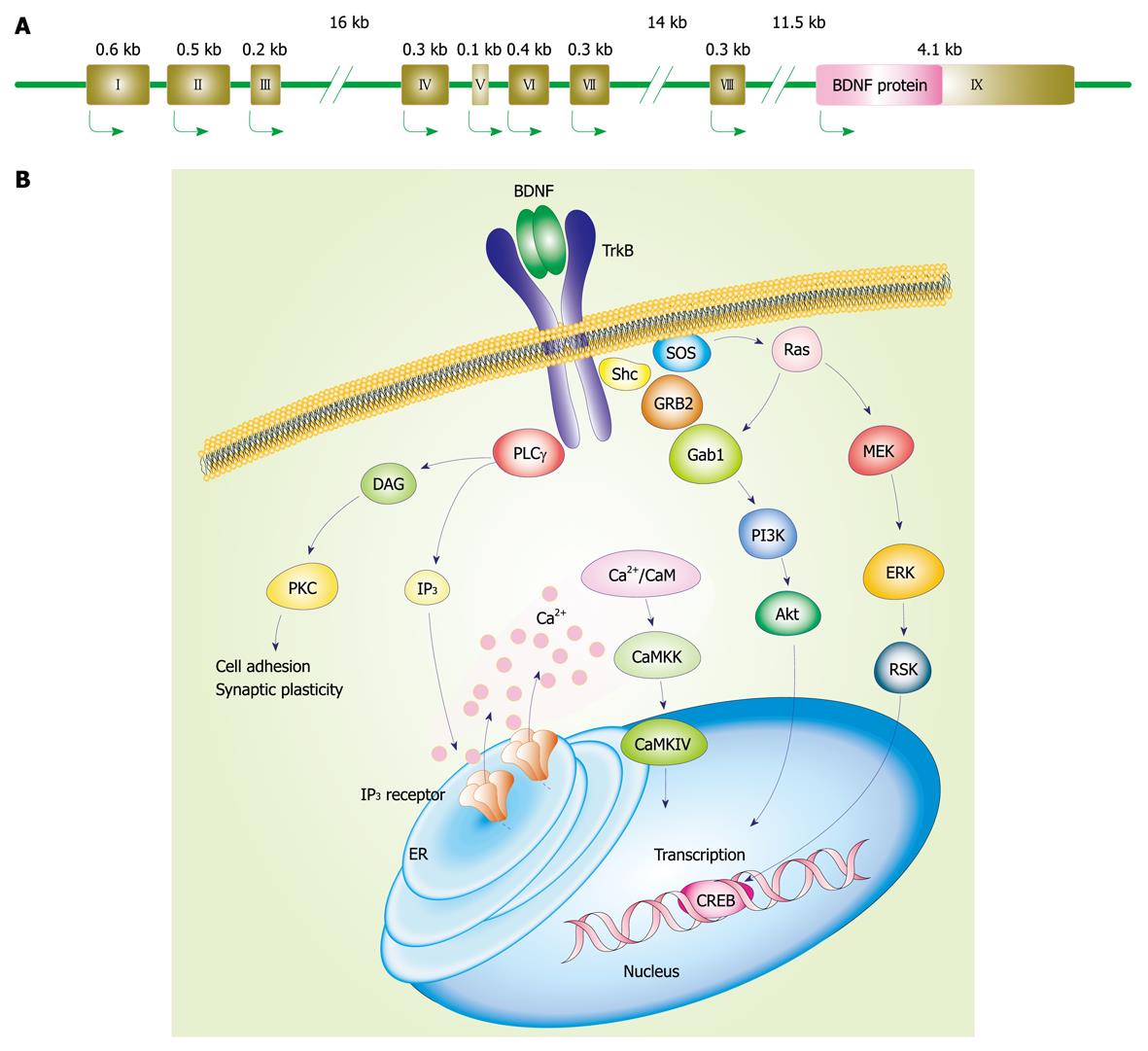
Figure 1 Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene and stimulated intracellular signaling cascades after activation of tropomyosin-related kinase (Trk)B.
A: Mouse and rat BDNF genes (we referred to the description by Aid et al[15]). Each BDNF transcript is comprised of one of eight 5’ untranslated exons (exon I-VIII) and the common 3’ protein coding exon IX; B: Intracellular signaling after TrkB activation. Following BDNF binding, TrkB dimerization and its phosphorylation at intracellular tyrosine residues occur. Then, the activated TrkB stimulates three main signaling pathways: (1) mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/ERK); (2) phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K); and (3) phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ) pathways. MAPK pathway, in which MAPK/ERK kinase (MEK) is involved, plays a role in the neuronal differentiation and outgrowth. PI3K signaling promotes neuronal survival via Ras or GRB-associated binder 1 (Gab1). Following PLCγ activation, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) are both produced. DAG activates protein kinase C (PKC), which is important for regulation of synaptic plasticity. Meanwhile, IP3 increases intracellular Ca2+ concentration via IP3 receptors on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), resulting in activation of Ca2+/calmodulin (CaM)-dependent protein kinase including CaMKII, CaMKK, and CaMKI. These MAPK/ERK, PI3K, and PLCγ pathways can regulate gene transcription.
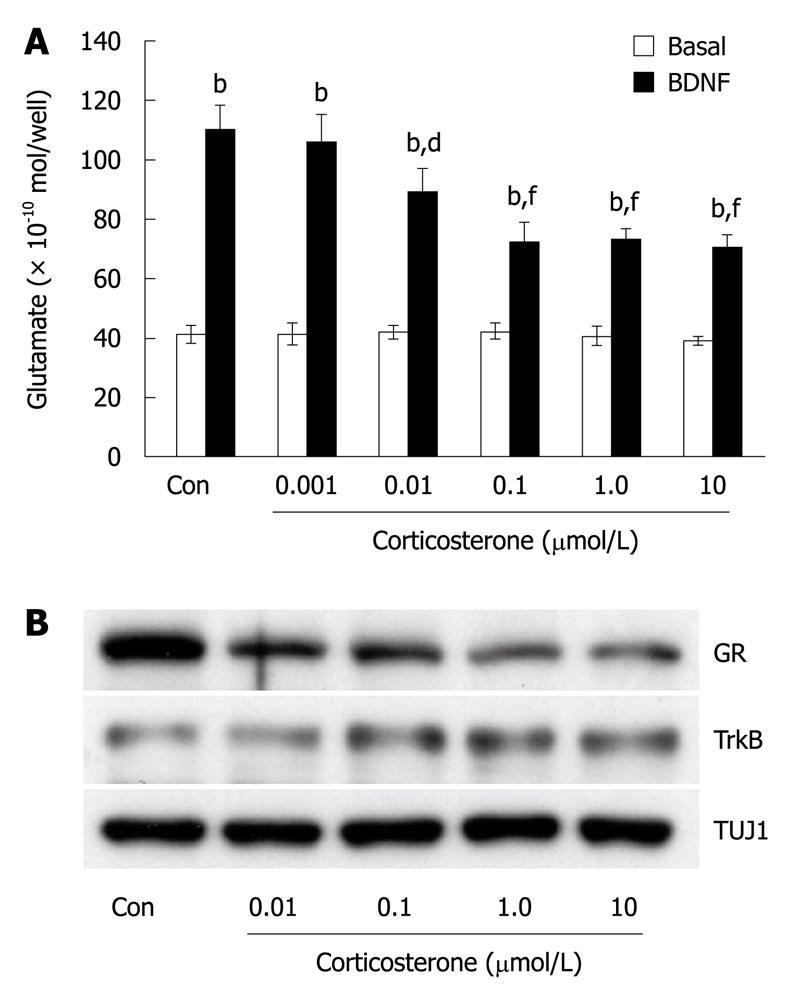
Figure 2 Glucocorticoids depressed BDNF-induced release of glutamate and expression of GR in cultured cortical neurons.
A: Dose-dependent inhibitory effect of corticosterone pretreatment on BDNF-induced glutamate release. Corticosterone (0.001-10 μmol/L) was applied at DIV4. Forty-eight hours later, BDNF (100 ng/mL, 1 min) was added and released glutamate was measured by HPLC. Prior to performing the BDNF application, samples were collected without stimulation as the basal release (1 min). Con means no application of corticosterone. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 4). bP < 0.001 vs basal, dP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs BDNF-induced release in Con (t-test); B: Endogenous expression of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) was decreased after corticosterone (0.01-10 μmol/L) was applied at DIV4. Forty-eight hours later, cell lysates were collected for western blotting. Endogenous expression of TrkB was unchanged after exposure to corticosterone. Levels of TUJ1 (class III β-tubulin), a neuronal marker, are shown as control.
- Citation: Numakawa T, Yokomaku D, Richards M, Hori H, Adachi N, Kunugi H. Functional interactions between steroid hormones and neurotrophin BDNF. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(5): 133-143
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i5/133.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i5.133