Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Biol Chem. Oct 26, 2010; 1(10): 313-320
Published online Oct 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i10.313
Published online Oct 26, 2010. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i10.313
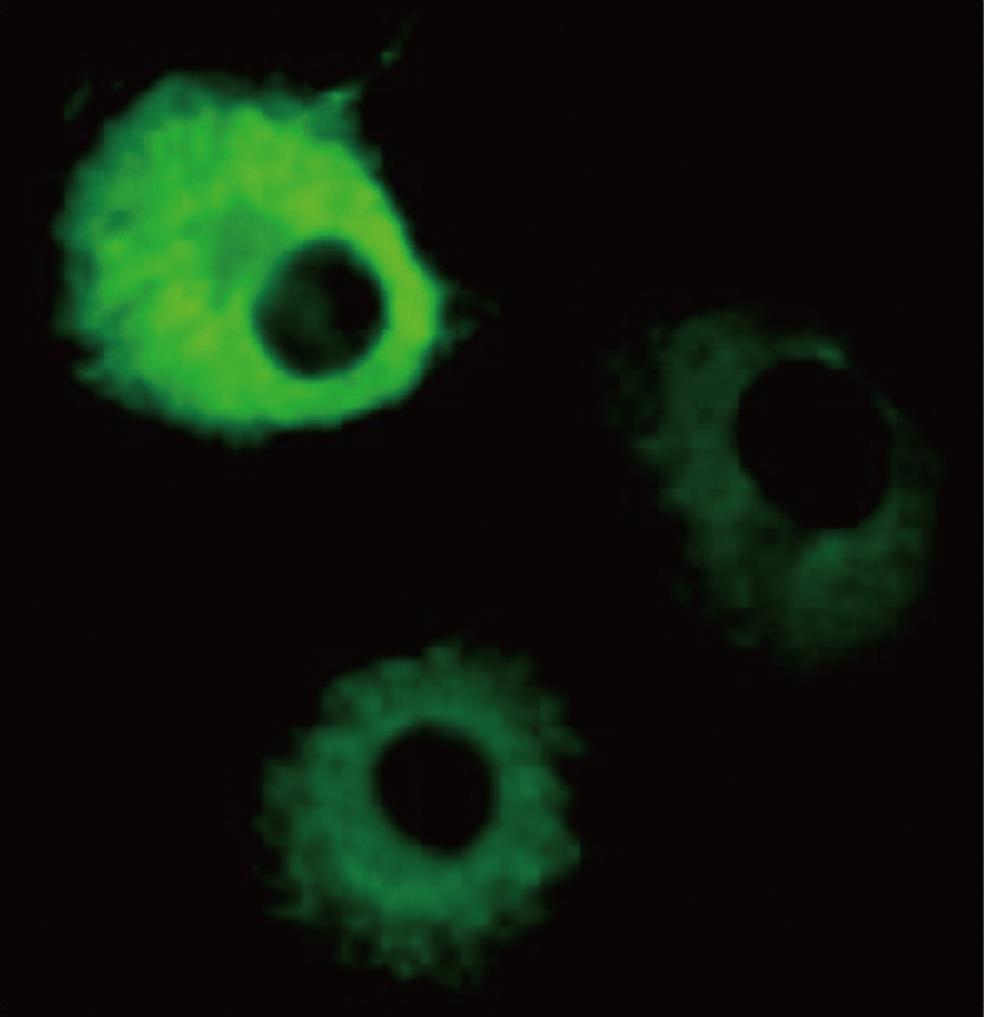
Figure 1 Overexpressed p67 in the cytosol.
COS-1 cells were transfected with a p67 expression vector, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and permeabilized with 0.1% saponin. The cells were incubated with mouse anti-p67 monoclonal antibody or anti-mouse IgG polyclonal antibody. After washing with PBS, the cells were incubated with fluorescein-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibody. The localization of p67 was visualized by fluorescence microscopy.
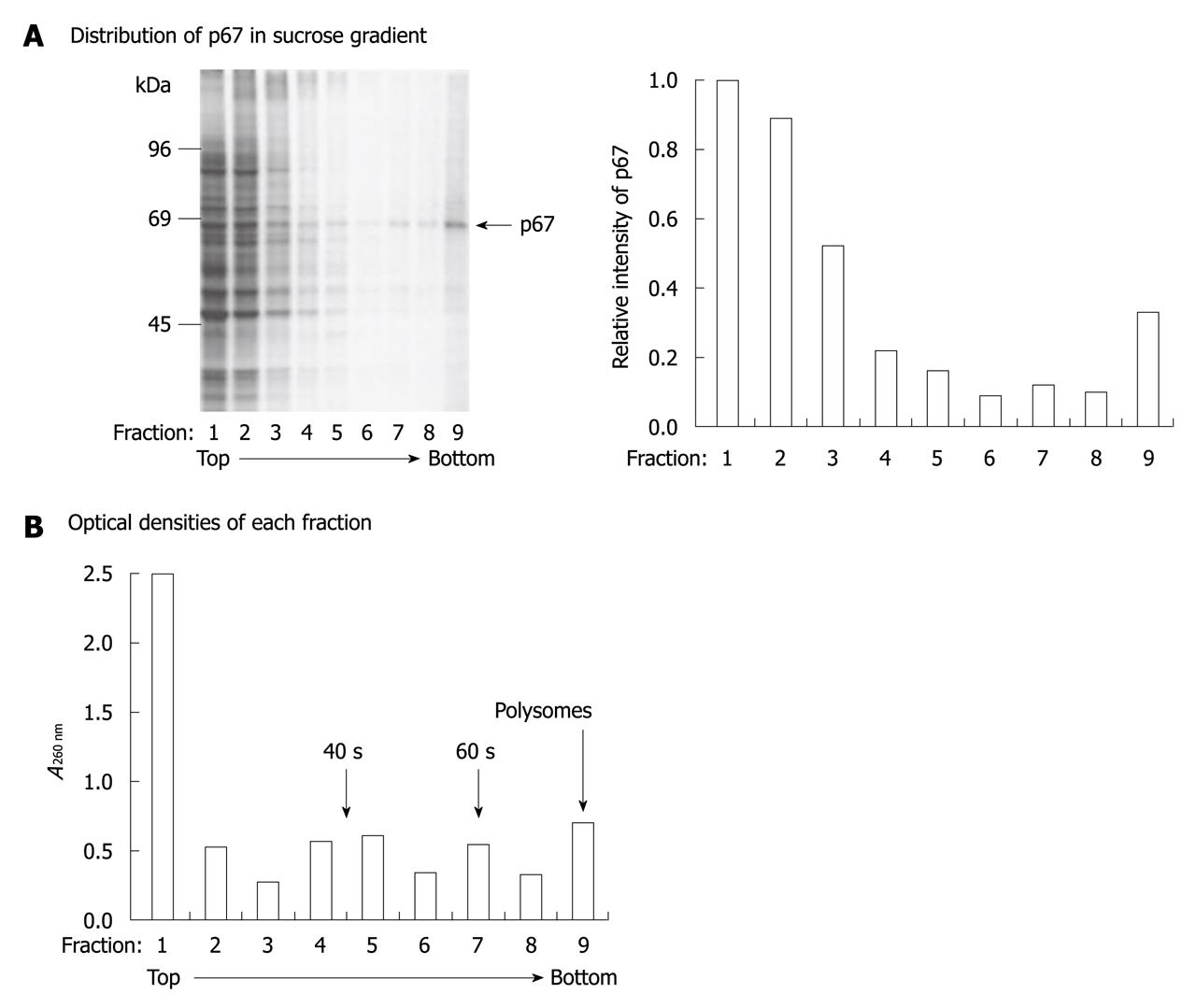
Figure 2 p67 is a ribosome-associated protein.
pETFVA-/p67-transfected cells were labeled with 35S-Met/Cys and lysed with 0.5 mL ribosome binding solution with 0.5% NP-40. The cell extracts were loaded on 4 mL of a 10%-40% linear sucrose gradient. The samples were centrifuged at 150 000 g for 2 h and fractionated into nine portions. A: 20 mL of each fraction was resolved on SDS-PAGE and autoradiographed (right panel). The intensity of p67 was quantitated using NIH image (left panel); B: Optical densities of each fraction were measured at 260 nm.
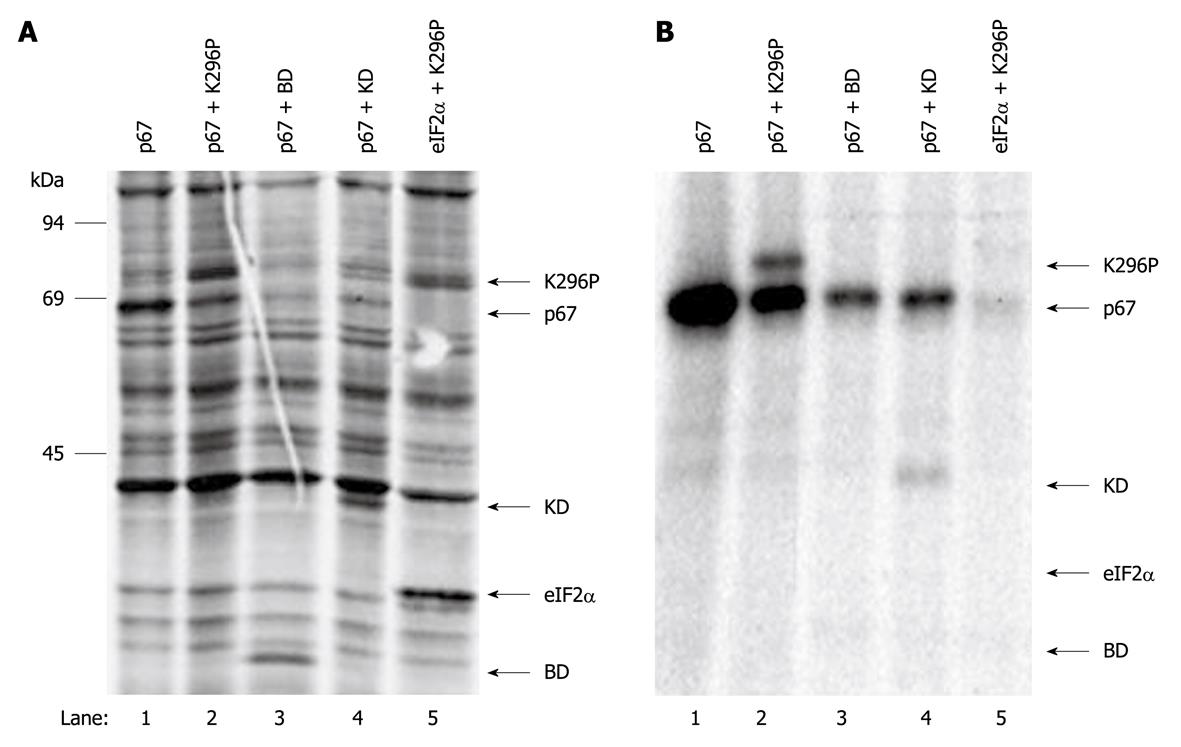
Figure 3 Interaction of p67 and protein kinase.
COS-1 cells were co-transfected with p67 and vector alone (lane 1), K296P (lane 2), binding domain (BD) (lane 3) and K296P-KD (lane 4). COS-1 cells were also co-transfected with eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2α) and K296P (lane 5) as a negative control. At 48 h post-transfection, the cells were labeled with 35S-Met/Cys and lysed with NP-40 lysis buffer. The expressed p67 was immunoprecipitated with anti-p67 monoclonal antibody. The total cell extract (A) and immunoprecipitates (B) were resolved on SDS-PAGE and autoradiographed.
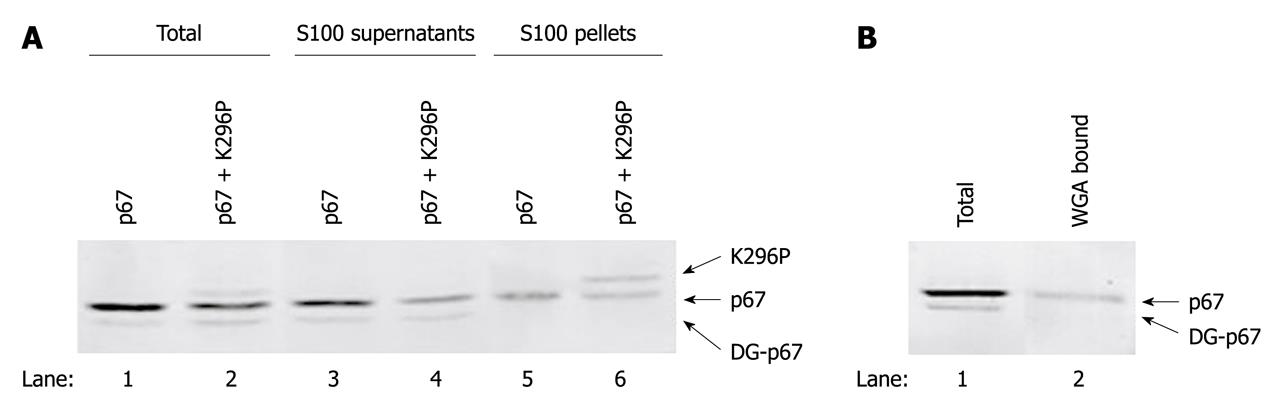
Figure 4 Polysome association of p67 and protein kinase.
COS-1 cells were transfected with pETFVA-/p67 and co-transfected with pETFVA-/p67 and pETFVA--/296P. At 48 h post-transfection, the cells were lysed by ribosome binding solution with 0.5% NP-40 and centrifuged at 100 000 g for 1 h. A: The total cell extracts (lanes 1 and 2), supernatants (lanes 3 and 4) and S100 pellets (lanes 5 and 6) were resolved by SDS-PAGE. The levels of ribosome-associated p67 and protein kinase were probed with corresponding antibodies using Western blotting analysis. B: Overexpressed p67 in the total cell extract was affinity absorbed (lane 2) with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA)-agarose. The total cell extract (lane 1) and WGA binding proteins (lane 2) were resolved with SDS-PAGE, and the level of p67 was detected using Western blotting analysis. Deglycosylated p67 was labeled as DG-p67.
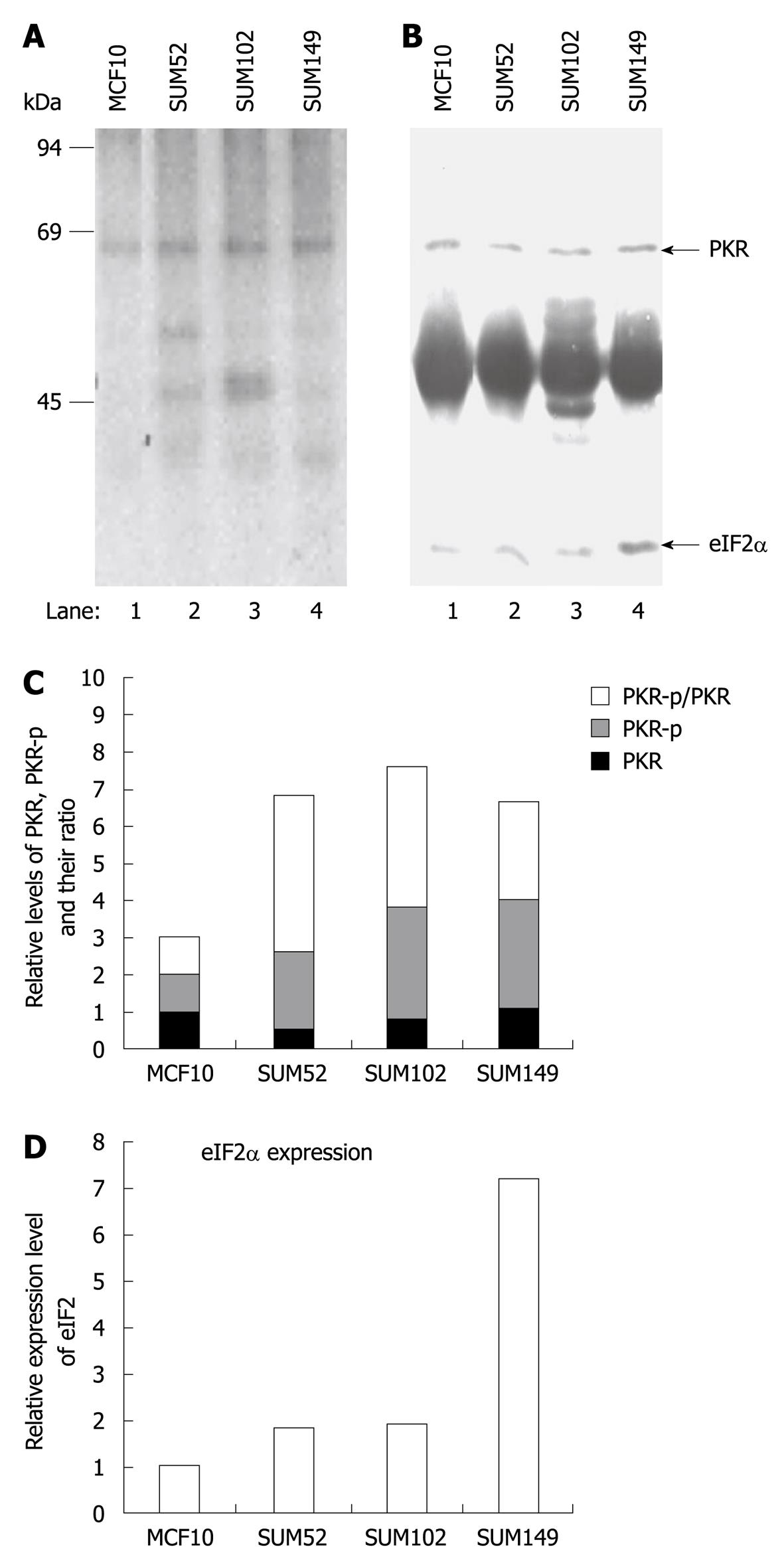
Figure 5 In vivo protein kinase autophosphorylation and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 phosphorylation in normal breast and breast cancer cells.
One established breast cell line (MCF-10, lane 1) and three primary breast cancer cell lines (lanes 2-4) were labeled with [32P] phosphoric acid, and cell extracts were prepared by lysis in NP-40 lysis buffer. Protein kinase (PKR) and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2α) were immunoprecipitated with corresponding antibodies, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and electroblotted to nitrocellulose. A: Incorporation of 32PO4 into PKR and eIF2α was measured by autoradiography; B: Protein levels of PKR and eIF2α on the same membrane were determined by Western blotting analysis; C and D: Semi-quantitative analysis of the levels of phosphorylated PKR, total PKR and eIF2α using ImageJ (v 1.42k, NIH). The levels of the proteins in the cancer cell lines were normalized with the level of the same proteins in MCF10 cells.
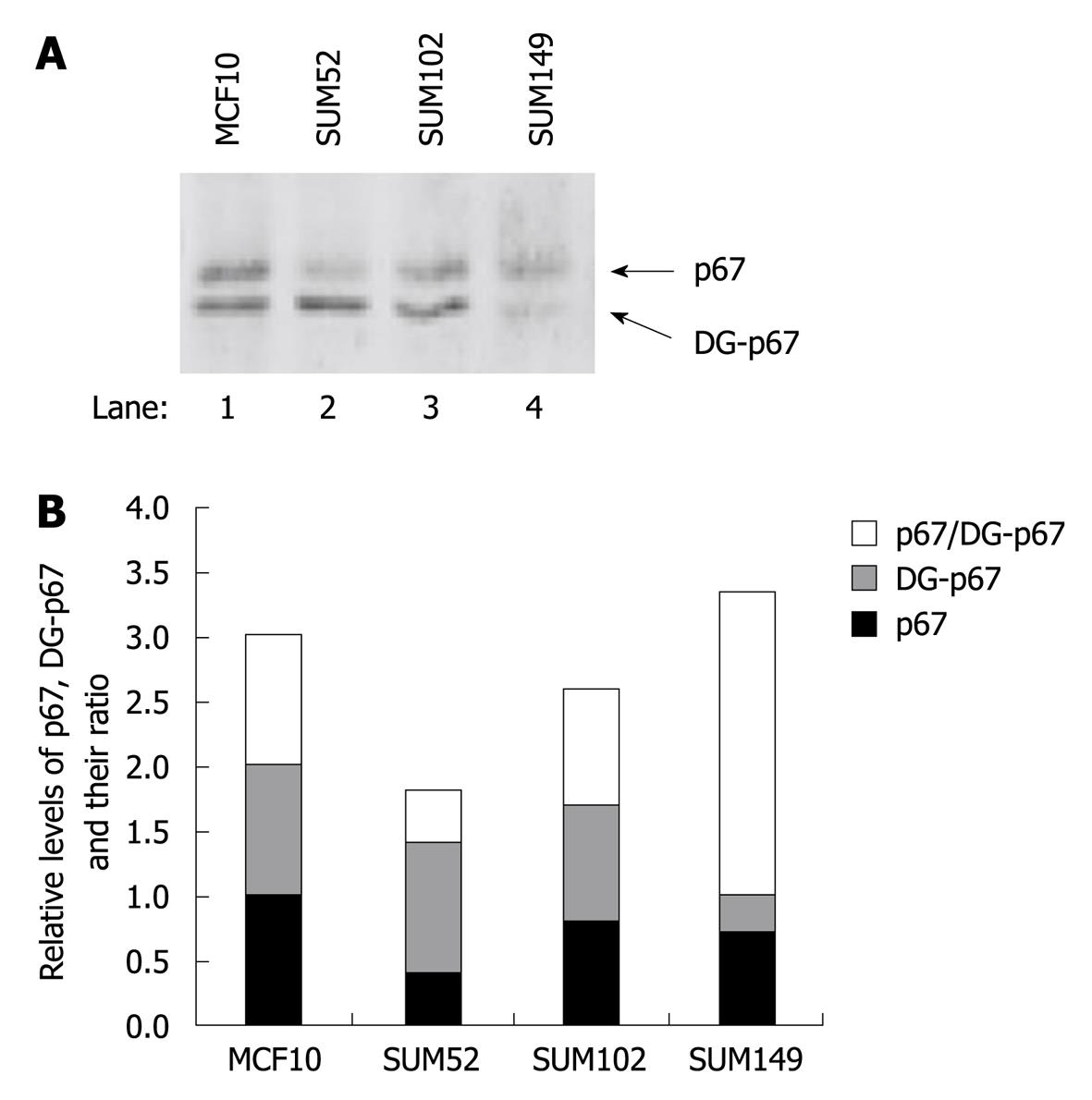
Figure 6 Levels of p67 and deglycosylated p67 in normal breast and breast cancer cells.
Normal established breast cell line (MCF-10, lane 1) and three primary breast cancer cell lines (lanes 2-4) were lysed in NP-40 lysis buffer. A: The levels of p67 and deglycosylated p67 (DG-p67) in the total lysates were detected by Western blotting analysis; B: Semi-quantitative analysis of the levels of p67 and DG-p67 using ImageJ (v 1.42k, NIH). The levels of p67 and DG-p67 were normalized with the level of p67 in MCF10 cells.
- Citation: Wu S. Localization and function of a eukaryotic-initiation-factor-2-associated 67-kDa glycoprotein. World J Biol Chem 2010; 1(10): 313-320
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v1/i10/313.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4331/wjbc.v1.i10.313