Published online Feb 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.628
Peer-review started: November 22, 2023
First decision: December 11, 2023
Revised: December 27, 2023
Accepted: January 30, 2024
Article in press: January 30, 2024
Published online: February 27, 2024
Processing time: 95 Days and 3.1 Hours
Collision tumors involving the small intestine, specifically the combination of a hamartomatous tumor and a lipoma, are extremely rare. To our knowledge, no previous case report has described a collision tumor composed of two benign tumors of different origins in the small intestine.
Here, we present the case of an 82-year-old woman who presented with hemo
This case report provides new evidence for the understanding of gastrointestinal collision tumors, emphasizing their diverse clinical presentations and histopathological characteristics. It also offers diagnostic and therapeutic insights as well as an approach for managing benign collision tumors.
Core Tip: Small intestinal collision tumors, specifically those comprising hamartomatous tumors with lipomas, are rare. Most available literature on gastrointestinal collision tumors describes cases with malignant tumor components, and most of these patients are treated surgically. In this report, we present a rare case in which a collision tumor composed of two benign tumors of different origins in the small intestine was accidentally discovered because of hemorrhage-induced hypovolemic shock. Considering the patient’s advanced age, multiple comorbidities, and poor surgical tolerance, we performed a modified endoscopic submucosal dissection procedure. This case demonstrates an approach for managing benign collision tumors in the small intestine.
- Citation: Wu YQ, Wang HY, Shao MM, Xu L, Jiang XY, Guo SJ. Ileal collision tumor associated with gastrointestinal bleeding: A case report and review of literature. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(2): 628-634
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i2/628.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.628
Juvenile polyps (JPs) are commonly classified as hamartomatous polyps and are frequently implicated as a cause of hematochezia. They are typically found in the rectum and sigmoid colon but have been rarely documented in the small intestine[1-3]. Collision tumors, a subtype of mixed tumors, have two distinct components[4]. They are relatively uncommon in pathology, with reported occurrences in various locations, such as the skull, gastroesophageal junction, rectum, and uterus[5]. Small intestinal collision tumors are most frequently observed in the ampulla of Vater[6-9], while documented cases of ileal collision tumors are exceptionally rare[10]. To date, no prior reports have been found on collision tumors predominantly involving JPs that present as hemorrhages. In this report, we present a unique case of hemorrhagic shock in a patient with a collision tumor composed of a JP and lipoma in the small intestine, which was successfully managed using a modified endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) technique.
An 82-year-old woman presented with a one-day history of dark red bloody diarrhea.
The symptoms appeared one day prior to presentation, with the patient experiencing 10 episodes of dark red bloody diarrhea. She reported feeling dizzy and fatigued but denied experiencing any abdominal pain or bloating.
The patient had a medical history of hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and chronic heart failure (NYHA Classification IV). The patient was administered oral dabigatran anticoagulation therapy.
She had no family history of gastrointestinal tumors or psychological or genetic disorders.
Upon admission, the patient appeared apathetic. Physical examination revealed a hypotensive state with a blood pressure of 79/45 mmHg, heart rate of 142 beats/min, and normal body temperature.
Laboratory analysis revealed decreased levels of red blood cells and hemoglobin (8.5 g/dL), along with an elevated ultrasensitive C-reactive protein level of 17.61 mg/L. Coagulation parameters were found to be abnormal, including a prolonged prothrombin time of 18.9 s, activated partial thromboplastin time of 51.4 s, reduced prothrombin activity of 51%, increased international normalized ratio of 1.55, and a fibrinogen level of 4.6 g/L. The patient’s serum potassium level was 3.05 mmol/L, and hepatic and renal functions were within the normal range.
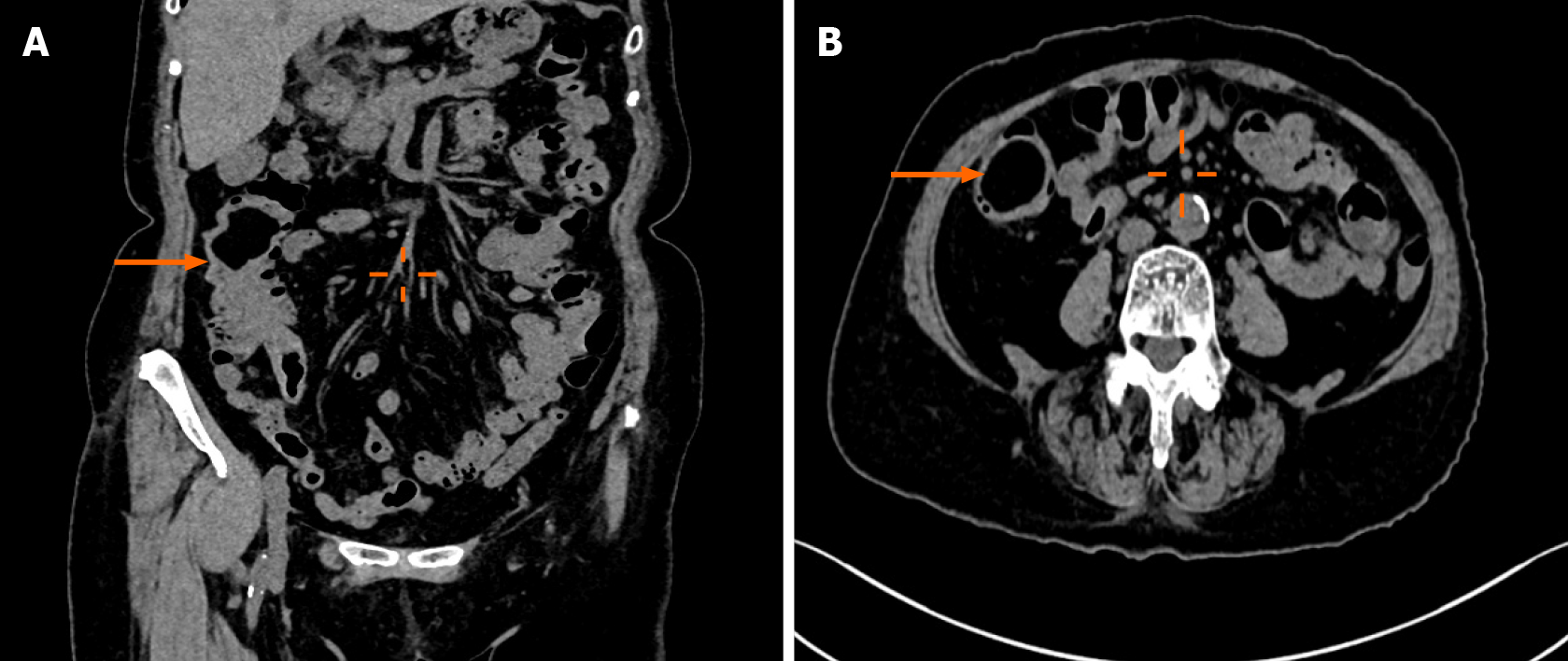
Ultrasound examination revealed a well-defined hypoechoic mass measuring 50 mm × 32 mm × 30 mm at the terminal ileum of the right lower abdomen, suggesting a possible lipoma. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography confirmed the presence of a lipoma with partial intestinal invagination into the ascending colon, indicating the possibility of intestinal intussusception (Figure 1).
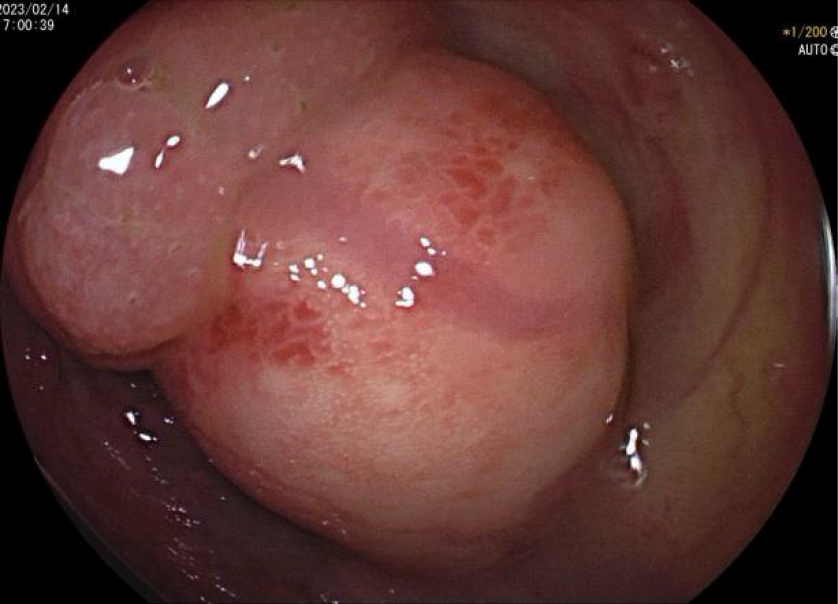
The preliminary clinical diagnosis was hemorrhagic shock. Anticoagulant medication was temporarily discontinued. As the hemoglobin level did not meet the clinical transfusion threshold, she received a comprehensive treatment approach that included fluid resuscitation, combination therapy with proton pump inhibitors and somatostatin to promote hemostasis, correction of coagulation abnormalities, and provision of nutritional support. Subsequent colonoscopy revealed a submucosal elevation 6 cm from the ileocecal valve consisting of two distinct parts with clear demarcation and varying texture upon palpation (softer at the base) (Figure 2). Narrow-band imaging indicated a type II opening (stellate) of the glandular portion at the top of the lesion and a type I opening (consistent with the surrounding mucosa) at the lower end. A specimen was obtained from the upper surface of the lesion for biopsy, and histopathological results indicated a diagnosis consistent with JP.
Based on the patient’s medical history and pathological examination, the final diagnosis was determined to be a collision tumor consisting of a hamartomatous tumor with a concurrent lipoma in the small intestine
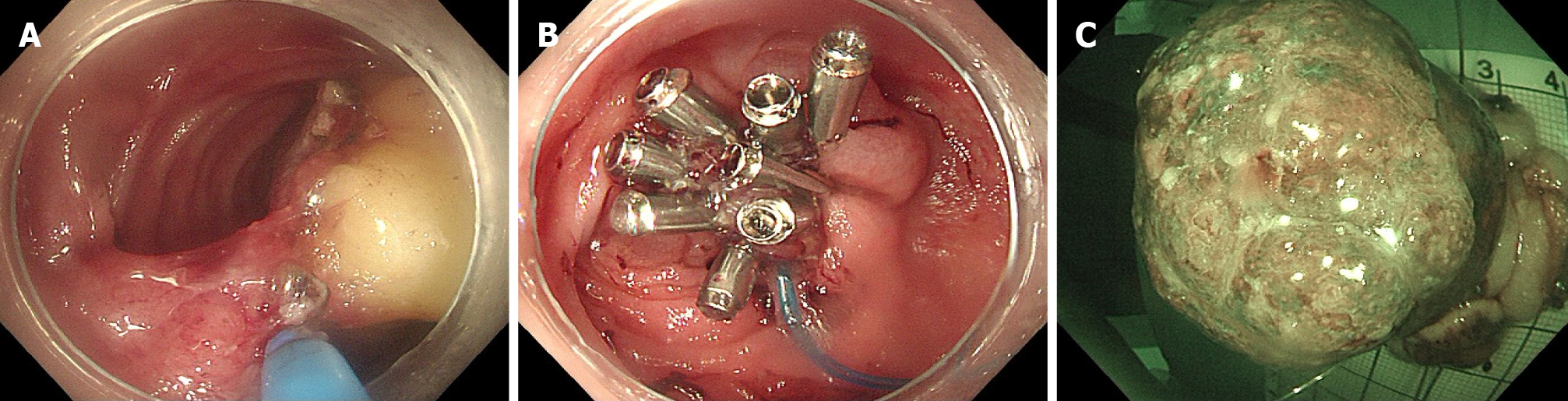
Because of persistent bloody stools and the exclusion of other potential sources of gastrointestinal bleeding through procedures, such as gastroscopy, a multidisciplinary team consultation (MDT) considered the possibility of mechanical stimulation-induced bleeding from a collision tumor located 6 cm away from the ileocecal valve. Considering the patient’s advanced age and multiple comorbidities, which rendered her unsuitable for surgery, the recommended treatment approach was ESD. Following informed consent, a modified ESD procedure was successfully performed with the assistance of a snare device for en bloc resection. This ensured complete removal of the lesion measuring approximately 60 mm × 40 mm, with no significant adverse events (Figure 3).
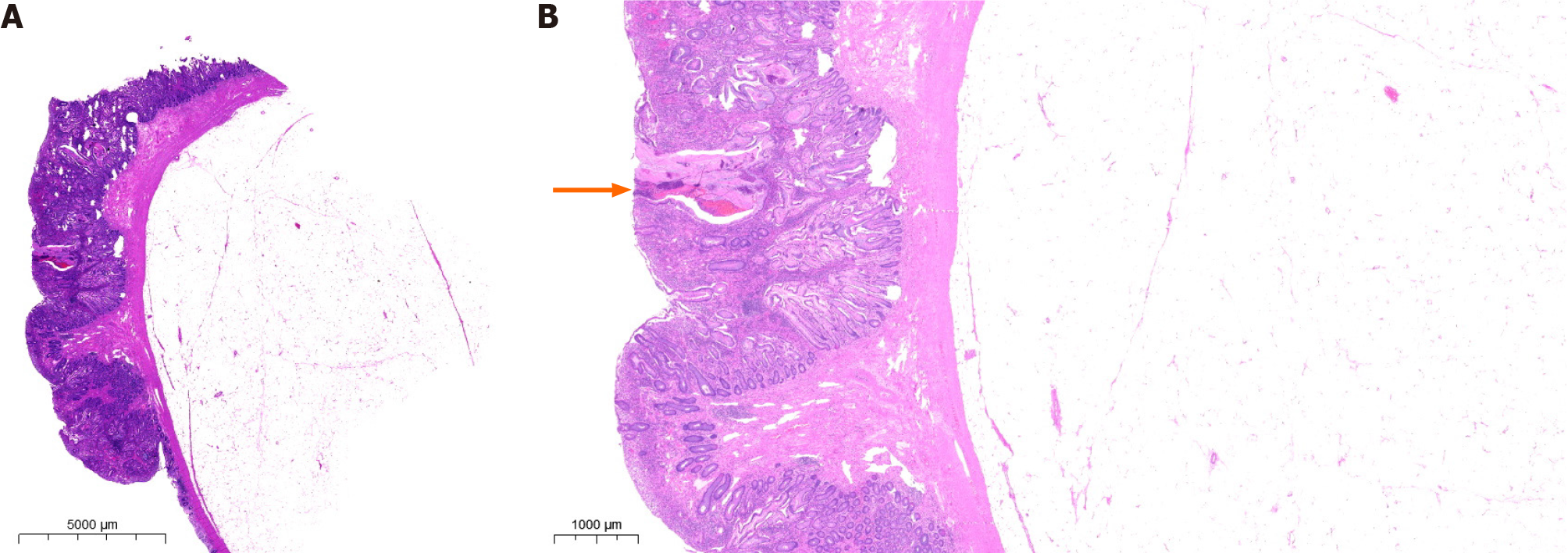
Histopathological examination of the endoscopic biopsy specimen confirmed the presence of a collision tumor (lipoma combined with JP) exhibiting signs of angiodysplasia and surface bleeding (Figure 4). The patient recovered smoothly following surgery, with no recurrence of bloody stools. Three days after the operation, the patient’s hemoglobin level increased by 10 g/L, and she did not report any other concerns. Throughout the six-month follow-up period, the patient’s overall health remained satisfactory and there were no instances of hematochezia recurrence.
This case was accidentally discovered because of hemorrhage-induced hypovolemic shock. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a collision tumor comprising two benign tumors of different origins in the small intestine. JPs belong to the category of hamartomatous polyps, which are more common in children and account for over 90% of pediatric polyps, but are relatively rare in adults[11,12]. JPs usually presents with nonspecific signs and symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloody stools, prolapse, and diarrhea[13]. Because of the highly vascular nature, gastrointestinal bleed
Compared to solitary JPs, lipomas are not rare in the gastrointestinal tract, with an incidence ranging from 0.035% to 4.4%[18]. Among them, the colon accounts for 65%-75%, followed by the small intestine (20%-25%), stomach, and esophagus. As the second most common benign tumor of the small intestine, lipomas are typically located in the ileum (50%) and rarely in the jejunum[19]. Symptomatically, lipomas in the small intestine mainly present as abdominal pain, followed by nausea and vomiting. Approximately 33.3% of patients may experience gastrointestinal bleeding due to lipoma ulceration. Other symptoms include anemia, abdominal distention, constipation, and unintentional weight loss[20]. Furthermore, disruption of the epithelial covering of the surface of lipomas may also contribute to bleeding. The definition of atypical lipomas was proposed by Snover[21], and later, Virgilio et al[22] classified “atypical” lipomas into three types based on malignant changes in the covering epithelium and suggested that in atypical lipomas, mucosal ischemia and inflammatory reactions may lead to mucosal hyperplasia and the development of hyperplastic polyps, as well as the proliferation and adenomatous transformation of the overlying mucosa. Sporadic cases of lipomas have been reported to exhibit proliferative and ulcerative epithelium[23-26].
In clinical practice, both lipomas and JPs can result in the occurrence of hematochezia. However, in the present case of identified submucosal elevation, the top portion was pathologically confirmed to be JP, which led to the patient’s current episode of hematochezia. Therefore, we speculate that, in this case, the occurrence of a small intestinal lipoma may have preceded the development of a hamartomatous polyp with an overlay of epithelium on its surface due to frictional irritation. This may have led to the formation of a collision tumor, ultimately resulting in the rupture and bleeding of the top portion of the JP.
In the treatment of collision tumors, as reported in existing literature, most cases involving gastrointestinal collision tumors contain malignant tumor components. Therefore, surgery is the primary treatment for most patients, and some patients may opt for adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapy[5]. However, in cases in which two benign tumors are combined, the treatment options for lipomas and JPs include surgery, laparoscopy, and endoscopy. Previously, the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy did not recommend the routine use of ESD for duodenal or small bowel lesions, mainly because of its higher incidence of perforation (15% to 37.5%) than that of EMR[27].
Notably, in recent years, there have been increasing number of cases of ESD for the treatment of small intestinal lesions. Morimoto reported the successful peeling of a giant (5 cm) ileal lipoma using endoscopic unroofing and submucosal dissection[28]. Noda et al[29] and Muramoto et al[30] separately reported cases of ESD for lipomas measuring approximately 4 cm in the terminal ileum. Farkas et al[20] summarized different treatment strategies in 147 cases and found that although traditional surgery remains the main choice, endoscopic and laparoscopic techniques have great potential for future use in reducing the use of invasive surgeries, as there were no statistically significant differences in hospitalization time and lipoma size among the different treatment strategy choices. Furthermore, Chen et al[31] recently reported two cases of balloon-assisted ESD for deep intestinal lipomas that showed good clinical feasibility. Considering that the location of collision tumor (terminal ileum), the higher surgical risk for an elderly patient with comorbidities and the feasibility of a successful colonic endoscopic resection[32], our MDT unanimously approved the use of ESD for treatment. We successfully performed ESD to remove a large collision tumor without any postoperative adverse events, providing a new case reference for ESD treatment of small intestinal tumors.
This report presents an exceptionally rare case of a collision tumor consisting of a combination of lipomas and hamartomatous polyps. The patient presented with hematochezia and hemorrhagic shock caused by bleeding from an apical JP located in the terminal ileum. This case provides novel insights into the clinical manifestations and histopathological patterns of collision tumors while also offering valuable diagnostic and therapeutic considerations for managing benign collision tumors.
We sincerely appreciate the patient and her family for their cooperation in information acquisition, treatment, and follow-up.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Elsayed MO, United Kingdom S-Editor: Yan JP L-Editor: A P-Editor: Yuan YY
| 1. | Horrilleno EG, Eckert C, Ackerman LV. Polyps of the rectum and colon in children. Cancer. 1957;10:1210-1220. |
| 2. | Clarke G, Robb A, Sugarman I, McCallion WA. Investigating painless rectal bleeding--is there scope for improvement? J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40:1920-1922. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Krasaelap A, Lerner D, Southern J, Noe J, Chugh A. Endoscopic Removal of a Single, Painless, Juvenile Polyp in the Small Intestine Causing Anemia. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2020;71:491-493. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Bhattacharya A, Saha R, Biswas J, Ghosh B. Collision tumors in the gastrointestinal tract: a rare case series. Int Med Case Rep J. 2012;5:73-77. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Schizas D, Katsaros I, Michalinos A, Damaskos C, Garmpis N, Ntomi V, Agrogiannis G, Stergiopoulos S, Tsaroucha AK. Collision Tumors of the Gastrointestinal Tract: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Anticancer Res. 2018;38:6047-6057. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Ferrando Marco J, Pallas Regueira A, Moro Valdezate D, Fernández Martínez C. Collision tumor of the ampulla of Vater: carcinoid and adenocarcinoma. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2007;99:235-238. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Tachibana M, Kamimura K, Tsukamoto K, Tsutsumi Y. A Rare Collision Tumor: Adenocarcinoma in the Ampulla of Vater and Neuroendocrine Tumor in the Lower Part of the Common Bile Duct. Cureus. 2021;13:e15882. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Suzuki S, Tanioka F, Inaba K, Takatori S, Ochiai H, Suzuki S. A rare collision tumor composed of follicular lymphoma and adenocarcinoma in the ampulla of vater: a case report. Case Rep Pathol. 2014;2014:530727. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Kim HJ, Choi BG, Kim CY, Cho CK, Kim JW, Lee JH, Hur YH. Collision tumor of the ampulla of Vater - Coexistence of neuroendocrine carcinoma and adenocarcinoma: report of a case. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2013;17:186-190. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Saito H, Osaka Y, Tamura K, Kawakita H, Kobayashi N, Nagakawa Y, Katsumata K, Tsuchida A. Collision Tumor of Adenocarcinoma and Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor in the Small Bowel. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2018;12:715-721. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Jelsig AM. Hamartomatous polyps - a clinical and molecular genetic study. Dan Med J. 2016;63. [PubMed] |
| 12. | Popović M, Knežević A, Dolinaj Škopelja J, Đolai M. Juvenile polyp in adults. Acta Clin Croat. 2022;61:354-358. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Dong J, Ma TS, Xu YH, Li P, Chen WY, Tu JF, Chen YW. Characteristics and potential malignancy of colorectal juvenile polyps in adults: a single-center retrospective study in China. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22:75. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Shussman N, Wexner SD. Colorectal polyps and polyposis syndromes. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2014;2:1-15. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 143] [Cited by in RCA: 109] [Article Influence: 9.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Cappello F, Angerilli V, Dal Santo L, Munari G, Sabbadin M, Lo Mele M, Pennelli G, Luchini C, Parente P, Lazzi S, Fassan M. Morphological and molecular characterization of colorectal sessile serrated lesions with dysplasia. Pathol Res Pract. 2022;240:154214. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Wang X, Ding Y, Huang WF. More than meets the eye: Collision tumors of adenocarcinoma and inflammatory fibroid polyp. Am J Med Sci. 2023;366:e12-e14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Elshaer RE, Elgammal ER, Elmistekawy AM, Ghannam WA, Elshamy AE, Abed SY, Zaitone SA. Preoperative Diagnosis Failure for a Rare Gastric Collision Tumor: A Case Report. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Agrawal A, Singh KJ. Symptomatic intestinal lipomas: our experience. Med J Armed Forces India. 2011;67:374-376. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Manouras A, Lagoudianakis EE, Dardamanis D, Tsekouras DK, Markogiannakis H, Genetzakis M, Pararas N, Papadima A, Triantafillou C, Katergiannakis V. Lipoma induced jejunojejunal intussusception. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:3641-3644. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Farkas N, Wong J, Bethel J, Monib S, Frampton A, Thomson S. A systematic review of symptomatic small bowel lipomas of the jejunum and ileum. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2020;58:52-67. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Snover DC. Atypical lipomas of the colon. Report of two cases with pseudomalignant features. Dis Colon Rectum. 1984;27:485-488. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Virgilio E, Mercantini P, Cavallini M. Is endoscopic resection a correct treatment for atypical gastrointestinal lipomas? World J Clin Cases. 2016;4:30-32. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Yeom JO, Kim SY, Jang EC, Yu JY, Chang ED, Cho YS. Colonic lipoma covered by hyperplastic epithelium: Case report. World J Clin Cases. 2013;1:124-127. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Vasiliadis K, Katsamakas M, Nikolaidou A, Christoforidis E, Tsalis K, Tsalikidis A. Submucosal lipoma of the ascending colon as a source of massive lower gastro-intestinal bleeding: a case report. Acta Chir Belg. 2008;108:356-359. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Palma R, Pontone S, Marino IR, Magliocca FM, Frattaroli S, Tonini V, D'Andrea V. Sheep in Wolf's Clothing: Pedunculated Colonic Lipoma with Overlying Hyperplastic and Ulcerated Epithelium. Dig Dis Sci. 2020;65:1951-1953. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Radhi JM, Haig TH. Lipoma of the colon with overlying hyperplastic epithelium. Can J Gastroenterol. 1997;11:694-695. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Pimentel-Nunes P, Libânio D, Bastiaansen BAJ, Bhandari P, Bisschops R, Bourke MJ, Esposito G, Lemmers A, Maselli R, Messmann H, Pech O, Pioche M, Vieth M, Weusten BLAM, van Hooft JE, Deprez PH, Dinis-Ribeiro M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial gastrointestinal lesions: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline - Update 2022. Endoscopy. 2022;54:591-622. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 410] [Cited by in RCA: 352] [Article Influence: 117.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Morimoto T, Fu KI, Konuma H, Izumi Y, Matsuyama S, Ogura K, Miyazaki A, Watanabe S. Peeling a giant ileal lipoma with endoscopic unroofing and submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:1676-1679. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Noda H, Ogasawara N, Tamura Y, Kondo Y, Izawa S, Ebi M, Funaki Y, Sasaki M, Kasugai K. Successful Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of a Large Terminal Ileal Lipoma. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2016;10:506-511. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Muramoto T, Negishi R, Takita M, Minato Y, Ohata K. Successful endoscopic submucosal dissection for a huge lipoma in the terminal ileum. VideoGIE. 2020;5:575-576. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Chen HY, Ning SB, Yin X, Li BR, Zhang J, Jin XW, Sun T, Xia ZB, Zhang XP. Balloon-assisted endoscopic submucosal dissection for treating small intestinal lipomas: Report of two cases. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9:1631-1638. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Wang L, Liu ZQ, Zhang JY, Li QL, Chen SY, Zhong YS, Zhang YQ, Chen WF, Qin WZ, Hu JW, Cai MY, Yao LQ, Ma LL, Zhou PH. Feasibility and safety of endoscopic resection for the jejunoileal lesions. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |