Published online Jun 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i6.1007
Peer-review started: January 27, 2023
First decision: March 14, 2023
Revised: April 10, 2023
Accepted: April 24, 2023
Article in press: April 24, 2023
Published online: June 27, 2023
Processing time: 138 Days and 12.9 Hours
The disease burden of diverticulitis is high across inpatient and outpatient settings, and the prevalence of diverticulitis has increased. Historically, patients with acute diverticulitis were admitted routinely for intravenous antibiotics and many had urgent surgery with colostomy or elective surgery after only a few episodes. Several recent studies have challenged the standards of how acute and recurrent diverticulitis are managed, and many clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) have pivoted to recommend outpatient management and individualized decisions about surgery. Yet the rates of diverticulitis hospitalizations and operations are increasing in the United States, suggesting there is a disconnect from or delay in adoption of CPGs across the spectrum of diverticular disease. In this review, we propose approaching diverticulitis care from a population level to understand the gaps between contemporary studies and real-world practice and suggest strate
Core Tip: Diverticulitis-associated hospitalization and colectomy are costly and have increased over the past decade, despite professional society guidelines advocating for outpatient management and individualized decisions about surgery. These trends raise flags about how to best measure guideline-concordant clinical practice in the modern era. Strategies to improve guideline-concordant care may consist of improved population-level data in diverticulitis care, regionalization of care, and system wide quality improvement initiatives for guideline implementation.
- Citation: Stovall SL, Kaplan JA, Law JK, Flum DR, Simianu VV. Diverticulitis is a population health problem: Lessons and gaps in strategies to implement and improve contemporary care. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(6): 1007-1019
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i6/1007.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i6.1007
Diverticular disease is the most common benign pathology of the colon and exhibits an unpredictable, relapsing-remitting course[1]. The rate of symptomatic diverticulitis is estimated to range from < 5% to 25%, though its precise incidence is controversial. Of patients with symptomatic disease, 15% will develop acute or chronic complications such as abscess, fistula, obstruction, bleeding, or perforation[2-4]. Advanced age, obesity, smoking, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, sedentary lifestyle, and Western diets are all risk factors for diverticulitis[1,5-9]. It is unsurprising, therefore, that diverticular disease is pervasive in Western countries and its prevalence has increased in the recent past[1-3,10-12]. Indeed, diverticulitis is one of the top five gastrointestinal admission diagnoses in the United States, accounting for nearly 980000 hospital days, approximately 208000 admissions, and over $5.5 billion in combined inpatient and emergency department costs in 2018[3,12].
To curb this healthcare burden, several recent studies have challenged the standards of how acute and chronic diverticulitis are managed. The admission rate after selective outpatient management of uncomplicated diverticulitis is low and confers significant healthcare savings, ranging from 42%-82% compared to inpatient care[10,13]. Similarly, recent studies showed no significant difference in the rate of emergency surgery or recurrence after prophylactic colectomy for uncomplicated disease[10,14]. These data prompted many professional societies’ clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) to shift toward outpatient management and individualized decisions about surgery[15-19].
Despite these two paradigm shifts over the past decade, the rate of hospitalization and surgery for diverticulitis rose, which lead to an increase in costs for diverticulitis care[3,14,20-22]. The specific factors contributing to this increase in hospitalization, surgery, and costs are poorly understood. It is not clear whether increased hospitalizations and surgery are necessary, driven by patients or their providers, or reflect overuse, under use, or concordance with CPGs across the spectrum of diverticular disease. Hospitalization and surgery are major drivers of healthcare costs and understanding the factors driving their use is necessary to better risk stratify patients, improve quality of care, and control costs. In this review, we propose approaching diverticulitis care from a population level to understand gaps between CPGs and real-world practice and suggest strategies to implement and improve future care.
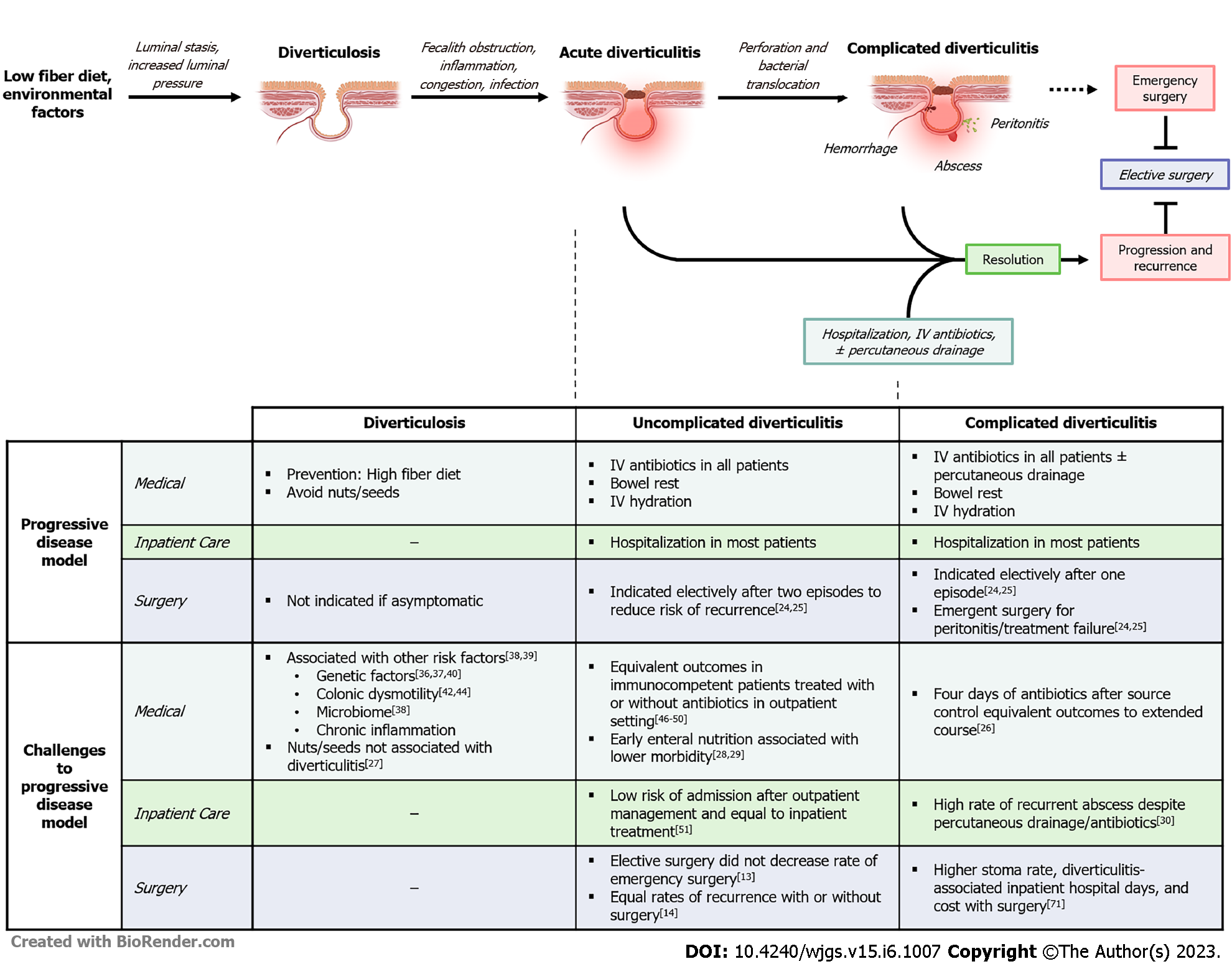
Diverticular disease was once considered a progressive condition arising from environmental factors, primarily a low fiber diet[1,2]. This model implicated fiber deficiency as a driver of luminal stasis and increased intraluminal pressure leading to the formation of colonic pseudodiverticula. Obstruction of these diverticula by fecaliths was thought to cause inflammation, congestion, inflammation/infection, and eventual microperforation, bacterial translocation, and abscess formation[1,2]. Predicated on this pathogenesis, aggressive care with broad-spectrum IV antibiotics, bowel rest, and hospitalization was the mainstay of diverticulitis treatment. To prevent recurrence, surgical guidelines advocated for early colectomy after two episodes of uncomplicated or a single episode of complicated diverticulitis[23,24]. Epidemiological studies addressing the natural history of diverticular disease, however, do not support this progressive disease model and have called into question the foundation of these guidelines (Figure 1)[25-30].
For example, a progressive disease model predicts more frequent/severe relapses and complications in subsequent diverticulitis episodes. While the risk of recurrence increases, the rate of complicated diverticulitis actually decreases with each subsequent episode in observational studies[3,31]. Addi
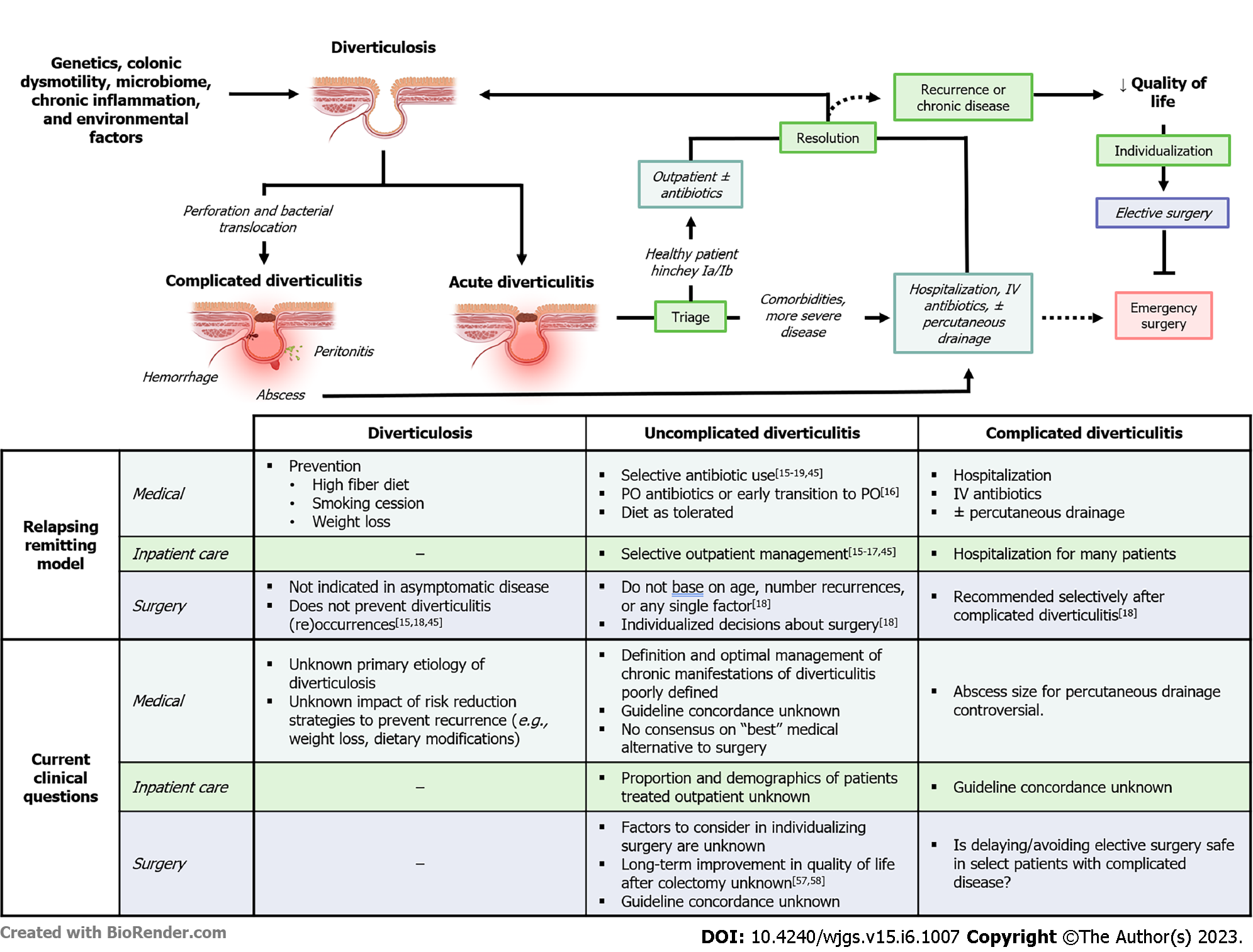
Historically, diverticulitis was considered an infectious process requiring routine antibiotics. However, multiple randomized controlled trials, as well as several metanalyses, have shown no significant difference in outcomes in patients with uncomplicated diverticulitis treated with or without antibiotics[45-49]. In response to these data, the American Gastrological Association (AGA) and American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS) now recommend selective use of antibiotics in immunocompetent patients (Table 1)[18,19]. Concurrently, the recommendation for hospitalization in uncomplicated disease was similarly challenged by clinical data showing similar outcomes in select patients receiving outpatient treatment with or without antibiotics[50]. While the ASCRS and AGA do not make explicit recommendations regarding the appropriateness of outpatient management in any subset of diverticular disease, nearly one in five low-risk patients with uncomplicated acute diverticulitis are probably now managed in the outpatient setting[51].
| Medical society guidelines | Surgical society guidelines | ||||||
| AGA[19], 2015 | AAFP[16], 2013 | ACP[17], 2022 | ASCRS[18], 2020 | SAGES[45], 2019 | WSES[15], 2020 | ||
| Diagnosis and medical management | |||||||
| Triage to outpatient | - | Recommend outpatient if uncomplicated and mild (level C) | Outpatient in uncomplicated disease as outpatients in absence of SIRS (conditional, low certainty) | - | Selective outpatient in immunocompetent host with uncomplicated diverticulitis (weak, moderate-quality) | Outpatient if uncomplicated without comorbidity, re-evaluate at 7 d (weak, moderate-quality) | |
| Antibiotics | |||||||
| Use | Selective use in uncomplicated disease (conditional, low-quality) | Enteric coverage if inpatient. Use outpatient if persistent or worsening symptoms (level B) | Omit in healthy, immunocompetent outpatients with uncomplicated disease and no SIRS (conditional, low certainty) | Healthy patients with uncomplicated disease should not be treated with antibiotics (strong, high-quality). May use in non-operative strategies (strong, low-quality) | Selective use in immunocompetent patients with uncomplicated disease (weak, high-quality) | Advise against antibiotics in healthy patients with uncomplicated disease and no SIRS (strong, high-quality) | |
| Duration | - | - | Insufficient data | - | - | - | |
| Percutaneous drainage | - | Consider in presence of abscess. No size recommendation (level C) | Insufficient outcomes data with percutaneous drain | Recommend when abscess > 3 cm (strong, moderate-quality) | Abscess < 4 cm: Trial antibiotics, drain for failure. Abscess > 4 cm: Drain upfront (weak, low-quality) | Abscess 4-5 cm: Trial antibiotics, drain for failure (weak, low-quality). Abscess > 5 cm: Drain upfront (weak, low-quality) | |
| Prevention | Fiber, physical activity (conditional, very low-quality) | Fiber intake, weight loss, smoking cessation | - | Tobacco cessation, limit red meat, physical activity weight loss (strong, low-quality) | - | - | |
| Surgical management | |||||||
| Emergency surgery | |||||||
| Indications | - | - | - | Diffuse peritonitis, non-operative treatment failure (strong, low-quality) | Peritonitis - Hinchey class III and IV (strong, low-quality) | ||
| Stoma or no stoma | - | - | - | Restoration of continuity preferred, when possible, based on patient/OR factors, surgeon preference (strong, moderate-quality) | Hartmann’s if unstable, or immunocompromise. Sigmoid resection with primary anastomosis and proximal diversion over Hartmann’s (weak, moderate-quality) | Critically-ill or major comorbidities: Hartmann’s procedure (strong, low-quality). Stable without comorbidities: Primary resection ± diversion (weak, low-quality) | |
| Laparoscopic lavage | - | - | - | Advise against in feculent peritonitis (strong, high-quality). Not preferred in purulent peritonitis (strong, high-quality) | Consider in select Hinchey III with appropriate expertise and intensive monitoring (weak, high-quality) | Reserve for highly selected patients with generalized peritonitis (weak, high-quality) | |
| Elective surgery | |||||||
| Uncomplicated | Recommends against after single episode of acute diverticulitis, individualize (conditional, very low-quality) | - | - | Individualize, do not based on age or episodes (strong, moderate-quality) | Resect when symptomatic disease decreases-quality of life (strong, moderate-quality) | Recommend elective resection in high-risk patients (weak, very low-quality). Individualize, do not base on episodes (weak, low-quality) | |
| Complicated | - | - | - | Consider when diverticular abscess resolved (strong, moderate-quality). Recommend for fistula, obstruction, or structure (strong, moderate-quality) | Minimum six weeks after complicated episode (weak, low-quality) | - | |
Similarly, there has been insight that early surgical intervention in acute, uncomplicated diverticulitis does not prevent future complications. In their 1995 guidelines, the ASCRS recommended elective resection after two episodes of uncomplicated diverticulitis, or one episode of diverticulitis in patients < 50 years or complicated disease at presentation[23]. However, the rate of emergency surgery in uncomplicated disease is low (1 in 2000 patient-years), and only 1.8%-7% of patients with recurrent disease will require emergency surgery[52,53]. Contemporary studies showing similar rates of emergency surgery and recurrence-related hospitalization in patients who underwent colectomy (5%-11%) compared to those who did not (4%-13%) further questioned the utility of “prophylactic” colectomy[10,14]. Complications of elective colectomy are rare, but significant, with a “rescue colostomy” rate of 1%-3% for anastomotic leak[54,55]. On the other hand, the DIRECT trial showed that patients with recurrent diverticulitis had improved quality of life (QoL) scores at six months after randomization to sigmoid colectomy. A criticism of this landmark trial is that the non-operative group had a high risk of surgery (23%) and was underpowered. This raised questions about the criteria for patients included in the study, and generalizability of ‘early surgery’ across a spectrum of diverticulitis presentations[56]. Collectively, these data prompted the CPGs to pivot from recommending surgery based on number of episodes toward “individualized” decisions about surgery. The ongoing Comparison of Surgery and Medicine on the Impact of Diverticulitis trial hopes to address this gap in the literature by evaluating whether elective colectomy is more effective than best medical management at improving patients’ QoL in diverticular disease[57].
The management of acute complicated diverticulitis has undergone a similar evolution. While emergency colectomy remains non-controversial in feculent or purulent peritonitis, the routine use of Hartmann’s procedure has been increasingly challenged in the past decade. Multiple clinical trials and meta-analyses have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of sigmoid colectomy with primary anastomosis (with or without diverting ostomy) in the short- and long-term[58-65]. In the short-term, morbidity and mortality were equivalent or decreased after resection with primary anastomosis vs Hartmann procedure. Despite similar recurrence rates, notable differences between the procedures were seen at follow-up[58-61,63-65]. Specifically, rates of stoma non-reversal were lower and complication rates were higher after reversal in patients who underwent Hartmann procedures, compared to primarily anastomosed patients[29,58,60,62]. The practical implication of these data is that anastomosis should be considered in most emergent cases, rather than defaulting to the traditional Hartmann’s. This is particularly important, as Hartmann procedures are associated with a decrease in general QoL compared to primary anastomosis for perforated diverticulitis, and the presence of a stoma was shown to be an independent predictor of lower QoL in one study[62,66]. In the modern era, most CPGs advise against routine use of the Hartmann procedure in stable patients, favoring primary anastomosis with or without proximal diversion. However, data showing whether the practice of routine anastomosis in emergent diverticulitis has been meaningfully implemented is lacking.
The incidence of diverticulitis has increased dramatically in the United States over the past several decades, and hospitalizations for acute diverticulitis rose by 25%-41% from 2000 to 2010[3,67]. Similarly, the rate of elective colectomy for uncomplicated disease has increased[10,14,20,22]. These increases in healthcare utilization are occurring as data and guidelines are urging a shift away from inpatient care and surgery. One explanation may be that more cases of diverticulitis are driving hospitalization and operations, outpacing the recommendations of CPGs. This argument is supported by two observations: (1) The prevalence of diverticulitis is highest in patients aged 65 years and older, a group whose numbers are predicted to increase by 48% in the United States by 2030[47]. CPGs reserve outpatient management for healthy patients, potentially excluding many older diverticulitis patients from receiving outpatient treatment[15,16,19,44]; and (2) The age-adjusted rate of diverticulitis is also increasing, particularly in adults under 50 years of age wherein the incidence of diverticulitis increased by 132% from 1980 to 2007[3]. Conceptualizing diverticulitis as a progressive disease, rather than relapsing-remitting, may prompt some surgeons to operate on younger patients more frequently; however, the magnitude of this effect on rates of surgery are unknown[22]. Studies evaluating the fundamental epidemiology of diverticular disease are dated, and updated studies are needed to better characterize changes in diverticular disease incidence and distribution. Understanding the interplay between this evolving epidemiology and how diverticulitis is treated across healthcare settings and disease severity is important to contextualizing and optimizing patient care in the modern era.
In addition, better data are needed to assess impact of CPGs on diverticulitis care. Contemporary research shows it takes 17 years to incorporate only 14% of published literature into clinical practice, highlighting the role of CPGs in synthesizing vast bodies of literature, and modernizing practice[68]. When implemented, CPGs have the potential to improve the processes of care and patient outcomes, but are infrequently followed[69-72]. For diverticulitis care, the rising rates of hospitalization and surgery may indicate a delay or disconnect in guideline concordant care. In a recent joint consensus statement by the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery (EAES) and Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES), only 65% of providers offered outpatient treatment to low risk patients with uncomplicated disease[44]. When measured about a decade ago, approximately 1 in 3 patients undergoing elective colectomy in Washington State did not meet CPG criteria for resection and it is unclear whether these data reflect regional practice or larger trends in surgical management of diverticulitis[73]. As such, larger scale studies are needed to assess national trends in diverticulitis surgery, but thus far have been limited by a lack of granularity needed to identify the indication for surgery and, therefore, appropriateness of operation and outcome. Furthermore, when emergent diverticulitis surgery is performed by general surgeons, there is a high, and increasing, rate of ostomy, despite CPG suggesting primary anastomosis is safe[18,74]. Yet, another state-level study suggests that mortality after emergency surgery for perforated diverticulitis (particularly in resection with primary anastomosis) may be higher when performed by general compared to colorectal surgeons. Jointly, these studies offer insight into disconnect with CPGs, but incompletely describe the practice patterns for diverticulitis care and are not generalizable to other clinicians or non-surgical patients. These findings may be explained also by selection bias, isolated regional trends in clinical practice, or standard of care. Indeed, diverticulitis remains a clinical challenge for physicians across specialties, including general practitioners, emergency room physicians, gastroenterologists, and surgeons. Said otherwise, there is a lacking in the definition of “guideline concordant care” for diverticulitis and measures thereof across the spectrum of clinical contexts.
One challenge is many diverticulitis CPGs offer conflicting or vague recommendations, and clinicians are less likely to implement CPGs when they are perceived as lacking clarity or sufficient evidence, offer many weak/conditional recommendations, or are too rigid[71,72,75]. For example, while several studies have indicated that outpatient management for uncomplicated disease in select patients is safe, the incorporation of these findings into modern guidelines is inconsistent (Table 1). The decision whether to operate and what operation to perform is similarly fraught with a lack of consensus, shifting guidelines, and behavioral inertia. No professional society offers discrete indications for elective resection, nor specifies which factors to incorporate into such individualized care. There are also no guidelines for managing chronic manifestations of diverticulitis, such as smoldering disease or chronic pain. The ambiguity of these recommendations likely reflects the complexity of decision-making in diverticulitis and a lack of quality population-level studies that address the fundamental epidemiology of disease. Additionally, it has been long recognized that the staging system for diverticulitis is inaccurate and poorly suited to clinical decision making. For example, the term “complicated disease” spans the spectrum of complex disease, ranging from chronic, QoL-limiting conditions requiring elective surgery (e.g., fistula) and acute, life-threatening disease requiring emergency surgery (e.g., feculent peritonitis). This absence of a clinically relevant classification system could contribute to ambiguous guidelines. Collectively, these factors may contribute to inappropriately heterogeneous and potentially low-value care, particularly considering the persistently high rate of elective colectomy in the United States compared to other Western countries[76].
The absence of clear guidance from professional societies may also explain regional variations in clinical practice that can be driven by patient, hospital, and market factors. For example, referral patterns to surgeons could influence the rate of colectomy via physician-induced demand[77]. In this phenomenon, information asymmetry leads to undue physician influence on patient decision making, thereby increasing demand for health services like surgery. Perhaps patients who might not otherwise undergo an operation choose to do so electively because surgery is offered more often than if they never saw a surgeon. Indeed, one study showed the rate of elective colectomy increased linearly with surgeon density, but the observational nature of the study precludes conclusions about causation[78]. This same study showed patients receiving diverticulitis care in large (> 500 beds) metropolitan for-profit hospitals are more likely to undergo elective colectomy compared to smaller, suburban, or rural hospitals[78]. Importantly, these studies do not differentiate the indication for surgery (e.g., stricture/fistula vs QoL indication) and thus should be interpreted with caution. These data could reflect national referral patterns of complex patients to metropolitan centers or differences in reginal practice patterns, and whether one practice is more ‘guideline concordant’ or not is unknown.
Reframing diverticulitis as a relapsing-remitting disease has the potential to inform systems-level practices to improve the quality, efficiency, and effectiveness of diverticulitis care. To start, the ubiquity of diverticulitis in the general population coupled with the complexity of medical decision-making raises the question of where patients currently do and/or should receive care. It is well established that medical and surgical outcomes are improved and less costly (via economies of scale) when patients with colorectal cancer and inflammatory bowel disease are treated at specialized centers[69,70]. As a result, resources and structures for treating these diseases are concentrated at a few high-volume hospitals, a process called regionalization. To date, no studies have explicitly addressed whether regionalization would produce similar outcomes in diverticulitis, though there is some suggestion that diverticulitis patients may benefit from specialized care. Two separate studies showed that patients undergoing emergent colectomy for complicated diverticulitis undergo fewer Hartmann’s procedures when operated on by fellowship-trained colorectal surgeons compared to general surgeons after controlling for comorbidities and disease severity[74,79]. In one of these studies, patients in the colorectal surgeon group also experienced fewer post-operative complications and had their ostomies reversed sooner[74]. Yet another study suggests patients undergoing a Hartmann’s reversal experienced fewer complications when performed by a colorectal surgeon[80]. While it is possible regionalizing care could increase surgeon volume, expertise, and outcomes, there is no agreed upon definition of “high-volume” at the clinician or systems level. Referral patterns, hospital resources, on-call responsibilities, eligible patient population, and numerous other factors may also explain current practice for diverticulitis care. It is, therefore, critical to characterize who is currently providing care across a spectrum of disease and healthcare settings, particularly when considering potential drawbacks of regionalization such as economic cost, travel burden, and healthcare disparities[81]. Importantly, attempts to regionalize diverticulitis care would require a radical shift in the distribution of diverticular disease burden, a sharp transition that brings into question whether any individual or collection of hospital systems can function as high-volume centers. Even if these centers had sufficient capacity, economic and travel burden are significant costs, which if incurred by rural and underserved patients could significantly limit access to care. Given the lack of supporting data and potential challenges of regionalization, more studies should evaluate the distribution of diverticulitis care focusing beyond single institutions and perhaps at the health system or state level. Characterizing distribution of care allows researchers to explore the association of volume and clinical outcomes in diverticulitis. If diverticulitis care is broadly distributed across institutions, this decentralized model of care has profound implications for how diverticular disease is studied and for implementation of quality improvement initiatives. This work should consider also regional practice patterns to better characterize how diverticular disease is actually treated in the general population.
Expanding the use of telemedicine has the potential to alleviate this burden, but a need for in-person consultation, rescue, and follow-up remains a challenge. Telemedicine also offers little to alleviate the travel burden of 19-42 million Americans without reliable access to fixed broadband services, a new frontier of inequity affecting predominantly poor, racial minority, and rural populations[82-84].
If concordance with CPGs leads to improved patient outcomes across a spectrum of medical and surgical disease, then improving existing CPGs or better adherence to them may result better, more cost-effective care. The decision to “individualize” surgery may arise from a composite assessment of patient/surgeon preferences, disease-specific factors, assessments of the “built environment” (e.g., transportation, social support, etc.), and continuity of care. Yet, CPG recommendations are made without defining what clinical and external factors should be considered before recommending surgery. The SAGES/EAES guidelines advocate for colectomy when symptomatic disease impacts QoL; however, studies evaluating QoL following elective colectomy exhibit mixed results[44,85-89]. Despite technically successful operations, many patients have recurrent or ongoing symptoms after colectomy[86,87]. These studies are often underpowered, lack standardization of QoL, and do not discuss timing of QoL evaluation[85,90]. Presumably, QoL will be lower near a diverticulitis episode, improving overtime as symptoms resolve. In one prospective study, Droullard et al[91] identified four distinct QoL trajectories in diverticulitis patients and found that 40% of patients with unacceptable baseline QoL improved without surgery. These data suggest that phenotyping patient QoL trajectory could aid in the selection of appropriate surgical candidates in diverticulitis, a hypothesis that warrants further study. It is important to note, however, that patients with diverticulosis and no history of diverticulitis may exhibit higher physical and mental QoL scores than patients with symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease and those with a history of diverticulitis. However, differences in QoL scores were small (1-3 points) and whether these findings are clinically meaningful is not established[92]. Making comparisons between studies is challenging due to a lack of standardization in assessing QoL in diverticular disease. Some studies rely on more global assessments, such as the highly-validated and global SF-12, whereas others rely on more specific, but less broadly validated, and potentially convoluted measures, such as the diverticulitis QoL scale[44,66,85,86,89-93]. To date, there is no consensus regarding when or how the impact of diverticulitis on QoL should be assessed, and whether the timing of evaluation could change a surgeons’ propensity to offer surgery. These global and disease specific QoL metrics need to be validated across a spectrum of diverticular disease patients with consideration paid to clinically meaningful changes for each metric. Consolidating these data and providing an actionable tool for clinicians would likely require consensus and multidisciplinary agreement. As an example, the Pelvic Floor Consortium, a multidisciplinary organization that aims to enhance care of patients with pelvic floor disorders, recently modeled how to establish a combined, validated patient reported outcomes tool to standardize QoL assessments across subspecialties[94]. A consortium of colorectal surgeons, general surgeons, gastroenterologists, and primary care providers could offer similar guidance and allow for longitudinal evaluations of QoL in diverticular disease.
Even in the context of clearer CPGs, measuring their implementation is complex and predicated on provision of clear and actional recommendations. Most studies evaluating other programs to improve guideline concordance are often (and appropriately) narrow in scope and lack conceptual clarity, thereby limiting their general applicability. One study implemented benchmarking and a peer-to-peer messaging initiative that increased guideline concordance among surgeons participating in Washington State’s Surgical Care and Outcomes Assessment Program and highlights the potential of regional initiative to improve guideline concordance[73]. However, this was limited to those patients having surgery, and the appropriateness of ‘non-operative’ management was not included. Ongoing research by the Expert Recommendations for Implementation Project seeks to define and evaluate discrete generalizable and comprehensive implementation strategies to improve guideline conformity. These research efforts are ongoing and may provide discrete implementation strategies applicable to diverticulitis care[95].
Awareness of the healthcare burden of diverticulitis and its distribution of inpatient and outpatient care is critical for cost-containment and improving disease management. Population-level studies provide the best reflection of an increasingly common disease that requires complex clinical decision-making that appears discordant with contemporary CPGs. Based on our current understanding of diverticulitis, the biggest challenges include improving population-level data in diverticulitis care, an evaluation of regionalized care for diverticulitis, and development/implementation of CPG-concordance measures.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: United States
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Carabotti M, Italy; Christodoulidis G, Greece; Mutter D, France S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: A P-Editor: Yu HG
| 1. | Strate LL, Morris AM. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Treatment of Diverticulitis. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:1282-1298.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 244] [Cited by in RCA: 272] [Article Influence: 45.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Weizman AV, Nguyen GC. Diverticular disease: epidemiology and management. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011;25:385-389. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 207] [Cited by in RCA: 188] [Article Influence: 13.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Bharucha AE, Parthasarathy G, Ditah I, Fletcher JG, Ewelukwa O, Pendlimari R, Yawn BP, Melton LJ, Schleck C, Zinsmeister AR. Temporal Trends in the Incidence and Natural History of Diverticulitis: A Population-Based Study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015;110:1589-1596. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 153] [Cited by in RCA: 238] [Article Influence: 23.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Shahedi K, Fuller G, Bolus R, Cohen E, Vu M, Shah R, Agarwal N, Kaneshiro M, Atia M, Sheen V, Kurzbard N, van Oijen MG, Yen L, Hodgkins P, Erder MH, Spiegel B. Long-term risk of acute diverticulitis among patients with incidental diverticulosis found during colonoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:1609-1613. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 253] [Cited by in RCA: 308] [Article Influence: 25.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Reichert MC, Krawczyk M, Appenrodt B, Casper M, Friesenhahn-Ochs B, Grünhage F, Jüngst C, Zimmer V, Lammert F, Dauer M. Selective association of nonaspirin NSAIDs with risk of diverticulitis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2018;33:423-430. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Strate LL, Keeley BR, Cao Y, Wu K, Giovannucci EL, Chan AT. Western Dietary Pattern Increases, and Prudent Dietary Pattern Decreases, Risk of Incident Diverticulitis in a Prospective Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2017;152:1023-1030.e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 113] [Article Influence: 14.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Strate LL, Liu YL, Aldoori WH, Syngal S, Giovannucci EL. Obesity increases the risks of diverticulitis and diverticular bleeding. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:115-122.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 282] [Cited by in RCA: 261] [Article Influence: 16.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Hjern F, Wolk A, Håkansson N. Obesity, physical inactivity, and colonic diverticular disease requiring hospitalization in women: a prospective cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107:296-302. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Aune D, Sen A, Leitzmann MF, Tonstad S, Norat T, Vatten LJ. Tobacco smoking and the risk of diverticular disease - a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Colorectal Dis. 2017;19:621-633. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Etzioni DA, Mack TM, Beart RW Jr, Kaiser AM. Diverticulitis in the United States: 1998-2005: changing patterns of disease and treatment. Ann Surg. 2009;249:210-217. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 457] [Cited by in RCA: 412] [Article Influence: 25.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Nguyen GC, Sam J, Anand N. Epidemiological trends and geographic variation in hospital admissions for diverticulitis in the United States. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:1600-1605. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (6)] |
| 12. | Peery AF, Crockett SD, Murphy CC, Lund JL, Dellon ES, Williams JL, Jensen ET, Shaheen NJ, Barritt AS, Lieber SR, Kochar B, Barnes EL, Fan YC, Pate V, Galanko J, Baron TH, Sandler RS. Burden and Cost of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States: Update 2018. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:254-272.e11. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 776] [Cited by in RCA: 1075] [Article Influence: 179.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 13. | van Dijk ST, Bos K, de Boer MGJ, Draaisma WA, van Enst WA, Felt RJF, Klarenbeek BR, Otte JA, Puylaert JBCM, van Geloven AAW, Boermeester MA. A systematic review and meta-analysis of outpatient treatment for acute diverticulitis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2018;33:505-512. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 54] [Article Influence: 7.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Simianu VV, Strate LL, Billingham RP, Fichera A, Steele SR, Thirlby RC, Flum DR. The Impact of Elective Colon Resection on Rates of Emergency Surgery for Diverticulitis. Ann Surg. 2016;263:123-129. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Sartelli M, Weber DG, Kluger Y, Ansaloni L, Coccolini F, Abu-Zidan F, Augustin G, Ben-Ishay O, Biffl WL, Bouliaris K, Catena R, Ceresoli M, Chiara O, Chiarugi M, Coimbra R, Cortese F, Cui Y, Damaskos D, De' Angelis GL, Delibegovic S, Demetrashvili Z, De Simone B, Di Marzo F, Di Saverio S, Duane TM, Faro MP, Fraga GP, Gkiokas G, Gomes CA, Hardcastle TC, Hecker A, Karamarkovic A, Kashuk J, Khokha V, Kirkpatrick AW, Kok KYY, Inaba K, Isik A, Labricciosa FM, Latifi R, Leppäniemi A, Litvin A, Mazuski JE, Maier RV, Marwah S, McFarlane M, Moore EE, Moore FA, Negoi I, Pagani L, Rasa K, Rubio-Perez I, Sakakushev B, Sato N, Sganga G, Siquini W, Tarasconi A, Tolonen M, Ulrych J, Zachariah SK, Catena F. 2020 update of the WSES guidelines for the management of acute colonic diverticulitis in the emergency setting. World J Emerg Surg. 2020;15:32. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 224] [Cited by in RCA: 201] [Article Influence: 40.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Wilkins T, Embry K, George R. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Diverticulitis. Am Fam Physician. 2013;87:612-620. |
| 17. | Qaseem A, Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta I, Lin JS, Fitterman N, Shamliyan T, Wilt TJ; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians*, Crandall CJ, Cooney TG, Cross JT Jr, Hicks LA, Maroto M, Mustafa RA, Obley AJ, Owens DK, Tice J, Williams JW Jr; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Diagnosis and Management of Acute Left-Sided Colonic Diverticulitis: A Clinical Guideline From the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2022;175:399-415. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 12.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Hall J, Hardiman K, Lee S, Lightner A, Stocchi L, Paquette IM, Steele SR, Feingold DL; Prepared on behalf of the Clinical Practice Guidelines Committee of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Left-Sided Colonic Diverticulitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2020;63:728-747. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 139] [Cited by in RCA: 279] [Article Influence: 55.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Stollman N, Smalley W, Hirano I; AGA Institute Clinical Guidelines Committee. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on the Management of Acute Diverticulitis. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1944-1949. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 191] [Cited by in RCA: 211] [Article Influence: 21.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Masoomi H, Buchberg BS, Magno C, Mills SD, Stamos MJ. Trends in diverticulitis management in the United States from 2002 to 2007. Arch Surg. 2011;146:400-406. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 103] [Cited by in RCA: 111] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Yen L, Davis K, Hodgkins P, Loftus EVJr, Erder MH. Direct medical costs of diverticulitis in a US managed care population. Am J Manag Care. 2012;4:e118-e129. |
| 22. | Etzioni DA, Cannom RR, Ault GT, Beart RW Jr, Kaiser AM. Diverticulitis in California from 1995 to 2006: increased rates of treatment for younger patients. Am Surg. 2009;75:981-985. [PubMed] |
| 23. | Roberts P, Abel M, Rosen L, Cirocco W, Fleshman J, Leff E, Levien D, Pritchard T, Wexner S, Hicks T. Practice parameters for sigmoid diverticulitis. The Standards Task Force American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. Dis Colon Rectum. 1995;38:125-132. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 77] [Cited by in RCA: 90] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Wong WD, Wexner SD, Lowry A, Vernava A 3rd, Burnstein M, Denstman F, Fazio V, Kerner B, Moore R, Oliver G, Peters W, Ross T, Senatore P, Simmang C. Practice parameters for the treatment of sigmoid diverticulitis--supporting documentation. The Standards Task Force. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000;43:290-297. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 317] [Cited by in RCA: 299] [Article Influence: 12.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Sawyer RG, Claridge JA, Nathens AB, Rotstein OD, Duane TM, Evans HL, Cook CH, O'Neill PJ, Mazuski JE, Askari R, Wilson MA, Napolitano LM, Namias N, Miller PR, Dellinger EP, Watson CM, Coimbra R, Dent DL, Lowry SF, Cocanour CS, West MA, Banton KL, Cheadle WG, Lipsett PA, Guidry CA, Popovsky K; STOP-IT Trial Investigators. Trial of short-course antimicrobial therapy for intraabdominal infection. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1996-2005. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 438] [Cited by in RCA: 484] [Article Influence: 48.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Strate LL, Liu YL, Syngal S, Aldoori WH, Giovannucci EL. Nut, corn, and popcorn consumption and the incidence of diverticular disease. JAMA. 2008;300:907-914. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 193] [Cited by in RCA: 171] [Article Influence: 10.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Stam MA, Draaisma WA, van de Wall BJ, Bolkenstein HE, Consten EC, Broeders IA. An unrestricted diet for uncomplicated diverticulitis is safe: results of a prospective diverticulitis diet study. Colorectal Dis. 2017;19:372-377. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Marik PE, Zaloga GP. Early enteral nutrition in acutely ill patients: a systematic review. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:2264-2270. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 649] [Cited by in RCA: 519] [Article Influence: 21.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Gregersen R, Andresen K, Burcharth J, Pommergaard HC, Rosenberg J. Long-term mortality and recurrence in patients treated for colonic diverticulitis with abscess formation: a nationwide register-based cohort study. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2018;33:431-440. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Aquina CT, Becerra AZ, Xu Z, Justiniano CF, Noyes K, Monson JRT, Fleming FJ. Population-based study of outcomes following an initial acute diverticular abscess. Br J Surg. 2019;106:467-476. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Humes DJ, West J. Role of acute diverticulitis in the development of complicated colonic diverticular disease and 1-year mortality after diagnosis in the UK: population-based cohort study. Gut. 2012;61:95-100. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Boostrom SY, Wolff BG, Cima RR, Merchea A, Dozois EJ, Larson DW. Uncomplicated diverticulitis, more complicated than we thought. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012;16:1744-1749. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Kishnani S, Ottaviano K, Rosenberg L, Arker SH, Lee H, Schuster M, Tadros M, Valerian B. Diverticular Disease-An Updated Management Review. Gastroenterol Insights. 2022;13:326-339. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Granlund J, Svensson T, Olén O, Hjern F, Pedersen NL, Magnusson PK, Schmidt PT. The genetic influence on diverticular disease--a twin study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;35:1103-1107. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 71] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Strate LL, Erichsen R, Baron JA, Mortensen J, Pedersen JK, Riis AH, Christensen K, Sørensen HT. Heritability and familial aggregation of diverticular disease: a population-based study of twins and siblings. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:736-742.e1; quiz e14. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 97] [Cited by in RCA: 117] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Peery AF, Keku TO, Martin CF, Eluri S, Runge T, Galanko JA, Sandler RS. Distribution and Characteristics of Colonic Diverticula in a United States Screening Population. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:980-985.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 130] [Article Influence: 14.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Schieffer KM, Sabey K, Wright JR, Toole DR, Drucker R, Tokarev V, Harris LR, Deiling S, Eshelman MA, Hegarty JP, Yochum GS, Koltun WA, Lamendella R, Stewart DB Sr. The Microbial Ecosystem Distinguishes Chronically Diseased Tissue from Adjacent Tissue in the Sigmoid Colon of Chronic, Recurrent Diverticulitis Patients. Sci Rep. 2017;7:8467. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Whiteway J, Morson BC. Elastosis in diverticular disease of the sigmoid colon. Gut. 1985;26:258-266. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 138] [Cited by in RCA: 114] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Wess L, Eastwood MA, Wess TJ, Busuttil A, Miller A. Cross linking of collagen is increased in colonic diverticulosis. Gut. 1995;37:91-94. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 124] [Cited by in RCA: 109] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Schieffer KM, Kline BP, Yochum GS, Koltun WA. Pathophysiology of diverticular disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;12:683-692. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Bassotti G, Battaglia E, Bellone G, Dughera L, Fisogni S, Zambelli C, Morelli A, Mioli P, Emanuelli G, Villanacci V. Interstitial cells of Cajal, enteric nerves, and glial cells in colonic diverticular disease. J Clin Pathol. 2005;58:973-977. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 114] [Cited by in RCA: 110] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Bassotti G, Villanacci V, Bernardini N, Dore MP. Diverticular Disease of the Colon: Neuromuscular Function Abnormalities. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2016;50 Suppl 1:S6-S8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Bassotti G, Battaglia E, Spinozzi F, Pelli MA, Tonini M. Twenty-four hour recordings of colonic motility in patients with diverticular disease: evidence for abnormal motility and propulsive activity. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001;44:1814-1820. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 96] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Francis NK, Sylla P, Abou-Khalil M, Arolfo S, Berler D, Curtis NJ, Dolejs SC, Garfinkle R, Gorter-Stam M, Hashimoto DA, Hassinger TE, Molenaar CJL, Pucher PH, Schuermans V, Arezzo A, Agresta F, Antoniou SA, Arulampalam T, Boutros M, Bouvy N, Campbell K, Francone T, Haggerty SP, Hedrick TL, Stefanidis D, Truitt MS, Kelly J, Ket H, Dunkin BJ, Pietrabissa A. EAES and SAGES 2018 consensus conference on acute diverticulitis management: evidence-based recommendations for clinical practice. Surg Endosc. 2019;33:2726-2741. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 140] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 45. | Isacson D, Smedh K, Nikberg M, Chabok A. Long-term follow-up of the AVOD randomized trial of antibiotic avoidance in uncomplicated diverticulitis. Br J Surg. 2019;106:1542-1548. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 62] [Article Influence: 10.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Daniels L, Ünlü Ç, de Korte N, van Dieren S, Stockmann HB, Vrouenraets BC, Consten EC, van der Hoeven JA, Eijsbouts QA, Faneyte IF, Bemelman WA, Dijkgraaf MG, Boermeester MA; Dutch Diverticular Disease (3D) Collaborative Study Group. Randomized clinical trial of observational versus antibiotic treatment for a first episode of CT-proven uncomplicated acute diverticulitis. Br J Surg. 2017;104:52-61. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 166] [Cited by in RCA: 214] [Article Influence: 23.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Jaung R, Nisbet S, Gosselink MP, Di Re A, Keane C, Lin A, Milne T, Su'a B, Rajaratnam S, Ctercteko G, Hsee L, Rowbotham D, Hill A, Bissett I. Antibiotics Do Not Reduce Length of Hospital Stay for Uncomplicated Diverticulitis in a Pragmatic Double-Blind Randomized Trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;19:503-510.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 48. | Desai M, Fathallah J, Nutalapati V, Saligram S. Antibiotics Versus No Antibiotics for Acute Uncomplicated Diverticulitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2019;62:1005-1012. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 49. | Mocanu V, Dang JT, Switzer N, Tavakoli I, Tian C, de Gara C, Birch DW, Karmali S. The role of antibiotics in acute uncomplicated diverticulitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Surg. 2018;216:604-609. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 50. | Mora-López L, Ruiz-Edo N, Estrada-Ferrer O, Piñana-Campón ML, Labró-Ciurans M, Escuder-Perez J, Sales-Mallafré R, Rebasa-Cladera P, Navarro-Soto S, Serra-Aracil X; DINAMO-study Group. Efficacy and Safety of Nonantibiotic Outpatient Treatment in Mild Acute Diverticulitis (DINAMO-study): A Multicentre, Randomised, Open-label, Noninferiority Trial. Ann Surg. 2021;274:e435-e442. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 11.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 51. | O'Connor ES, Leverson G, Kennedy G, Heise CP. The diagnosis of diverticulitis in outpatients: on what evidence? J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14:303-308. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 52. | Morris AM, Regenbogen SE, Hardiman KM, Hendren S. Sigmoid diverticulitis: a systematic review. JAMA. 2014;311:287-297. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 153] [Cited by in RCA: 128] [Article Influence: 11.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 53. | Li D, Baxter NN, McLeod RS, Moineddin R, Nathens AB. The Decline of Elective Colectomy Following Diverticulitis: A Population-Based Analysis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2016;59:332-339. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 54. | Andersen JC, Bundgaard L, Elbrønd H, Laurberg S, Walker LR, Støvring J; Danish Surgical Society. Danish national guidelines for treatment of diverticular disease. Dan Med J. 2012;59:C4453. [PubMed] |
| 55. | Collins D, Winter DC. Elective resection for diverticular disease: an evidence-based review. World J Surg. 2008;32:2429-2433. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 66] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 56. | van de Wall BJM, Stam MAW, Draaisma WA, Stellato R, Bemelman WA, Boermeester MA, Broeders IAMJ, Belgers EJ, Toorenvliet BR, Prins HA, Consten ECJ; DIRECT trial collaborators. Surgery versus conservative management for recurrent and ongoing left-sided diverticulitis (DIRECT trial): an open-label, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;2:13-22. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 79] [Cited by in RCA: 106] [Article Influence: 13.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 57. | Flum D, Davidson G. Comparison of Surgery and Medicine on the Impact of Diverticulitis (COSMID) Trial. [accessed 2022 Oct 25]. In: ClinicalTrials.gov [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): U.S. National Library of Medicine. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04095663 ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04095663. |
| 58. | Acuna SA, Wood T, Chesney TR, Dossa F, Wexner SD, Quereshy FA, Chadi SA, Baxter NN. Operative Strategies for Perforated Diverticulitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2018;61:1442-1453. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 6.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 59. | Halim H, Askari A, Nunn R, Hollingshead J. Primary resection anastomosis versus Hartmann's procedure in Hinchey III and IV diverticulitis. World J Emerg Surg. 2019;14:32. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 60. | Gachabayov M, Oberkofler CE, Tuech JJ, Hahnloser D, Bergamaschi R. Resection with primary anastomosis vs nonrestorative resection for perforated diverticulitis with peritonitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Colorectal Dis. 2018;20:753-770. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 61. | Lambrichts DPV, Vennix S, Musters GD, Mulder IM, Swank HA, Hoofwijk AGM, Belgers EHJ, Stockmann HBAC, Eijsbouts QAJ, Gerhards MF, van Wagensveld BA, van Geloven AAW, Crolla RMPH, Nienhuijs SW, Govaert MJPM, di Saverio S, D'Hoore AJL, Consten ECJ, van Grevenstein WMU, Pierik REGJM, Kruyt PM, van der Hoeven JAB, Steup WH, Catena F, Konsten JLM, Vermeulen J, van Dieren S, Bemelman WA, Lange JF; LADIES trial collaborators. Hartmann's procedure versus sigmoidectomy with primary anastomosis for perforated diverticulitis with purulent or faecal peritonitis (LADIES): a multicentre, parallel-group, randomised, open-label, superiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4:599-610. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 135] [Cited by in RCA: 121] [Article Influence: 20.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 62. | Loire M, Bridoux V, Mege D, Mathonnet M, Mauvais F, Massonnaud C, Regimbeau JM, Tuech JJ. Long-term outcomes of Hartmann's procedure versus primary anastomosis for generalized peritonitis due to perforated diverticulitis: follow-up of a prospective multicenter randomized trial (DIVERTI). Int J Colorectal Dis. 2021;36:2159-2164. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 63. | Bridoux V, Regimbeau JM, Ouaissi M, Mathonnet M, Mauvais F, Houivet E, Schwarz L, Mege D, Sielezneff I, Sabbagh C, Tuech JJ. Hartmann's Procedure or Primary Anastomosis for Generalized Peritonitis due to Perforated Diverticulitis: A Prospective Multicenter Randomized Trial (DIVERTI). J Am Coll Surg. 2017;225:798-805. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 113] [Cited by in RCA: 149] [Article Influence: 18.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 64. | Oberkofler CE, Rickenbacher A, Raptis DA, Lehmann K, Villiger P, Buchli C, Grieder F, Gelpke H, Decurtins M, Tempia-Caliera AA, Demartines N, Hahnloser D, Clavien PA, Breitenstein S. A multicenter randomized clinical trial of primary anastomosis or Hartmann's procedure for perforated left colonic diverticulitis with purulent or fecal peritonitis. Ann Surg. 2012;256:819-26; discussion 826. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 251] [Cited by in RCA: 248] [Article Influence: 20.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 65. | Binda GA, Karas JR, Serventi A, Sokmen S, Amato A, Hydo L, Bergamaschi R; Study Group on Diverticulitis. Primary anastomosis vs nonrestorative resection for perforated diverticulitis with peritonitis: a prematurely terminated randomized controlled trial. Colorectal Dis. 2012;14:1403-1410. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 114] [Cited by in RCA: 127] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 66. | Vermeulen J, Gosselink MP, Busschbach JJ, Lange JF. Avoiding or reversing Hartmann's procedure provides improved quality of life after perforated diverticulitis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14:651-657. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 89] [Cited by in RCA: 87] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 67. | Wheat CL, Strate LL. Trends in Hospitalization for Diverticulitis and Diverticular Bleeding in the United States From 2000 to 2010. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:96-103.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 123] [Cited by in RCA: 131] [Article Influence: 14.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 68. | Beauchemin M, Cohn E, Shelton RC. Implementation of Clinical Practice Guidelines in the Health Care Setting: A Concept Analysis. ANS Adv Nurs Sci. 2019;42:307-324. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 38] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 13.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 69. | Dimick JB, Cowan JA Jr, Upchurch GR Jr, Colletti LM. Hospital volume and surgical outcomes for elderly patients with colorectal cancer in the United States. J Surg Res. 2003;114:50-56. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 87] [Cited by in RCA: 86] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 70. | Nguyen GC, Steinhart AH. The impact of surgeon volume on postoperative outcomes after surgery for Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2014;20:301-306. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 29] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 71. | Qumseya B, Goddard A, Qumseya A, Estores D, Draganov PV, Forsmark C. Barriers to Clinical Practice Guideline Implementation Among Physicians: A Physician Survey. Int J Gen Med. 2021;14:7591-7598. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 55] [Article Influence: 13.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 72. | Cabana MD, Rand CS, Powe NR, Wu AW, Wilson MH, Abboud PA, Rubin HR. Why don't physicians follow clinical practice guidelines? A framework for improvement. JAMA. 1999;282:1458-1465. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4499] [Cited by in RCA: 4609] [Article Influence: 177.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 73. | Simianu VV, Bastawrous AL, Billingham RP, Farrokhi ET, Fichera A, Herzig DO, Johnson E, Steele SR, Thirlby RC, Flum DR. Addressing the appropriateness of elective colon resection for diverticulitis: a report from the SCOAP CERTAIN collaborative. Ann Surg. 2014;260:533-8; discussion 538. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 74. | Jafferji MS, Hyman N. Surgeon, not disease severity, often determines the operation for acute complicated diverticulitis. J Am Coll Surg. 2014;218:1156-1161. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 75. | Gransjøen AM, Wiig S, Lysdahl KB, Hofmann BM. Barriers and facilitators for guideline adherence in diagnostic imaging: an explorative study of GPs' and radiologists' perspectives. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18:556. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 76. | Flum DR, Read TE. Evidence-Based Management of Diverticular Disease: What's New and What's Missing? Dis Colon Rectum. 2020;63:715-717. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 77. | Mohammadshahi M, Yazdani S, Olyaeemanesh A, Akbari Sari A, Yaseri M, Emamgholipour Sefiddashti S. A Scoping Review of Components of Physician-induced Demand for Designing a Conceptual Framework. J Prev Med Public Health. 2019;52:72-81. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 78. | Hawkins AT, Samuels LR, Rothman RL, Geiger TM, Penson DF, Resnick MJ. National Variation in Elective Colon Resection for Diverticular Disease. Ann Surg. 2022;275:363-370. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 79. | Aquina CT, Probst CP, Becerra AZ, Hensley BJ, Iannuzzi JC, Noyes K, Monson JR, Fleming FJ. The impact of surgeon volume on colostomy reversal outcomes after Hartmann's procedure for diverticulitis. Surgery. 2016;160:1309-1317. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 80. | Duverseau MO, O'Neill AM, Sulzer JK, Darden M, Parker G, Buell JF. Comparison of surgical outcomes for colostomy closure performed by acute care surgeons versus a dedicated colorectal surgery service. Surgery. 2022;171:635-640. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 81. | Syed ST, Gerber BS, Sharp LK. Traveling towards disease: transportation barriers to health care access. J Community Health. 2013;38:976-993. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 654] [Cited by in RCA: 977] [Article Influence: 88.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 82. | Julien HM, Eberly LA, Adusumalli S. Telemedicine and the Forgotten America. Circulation. 2020;142:312-314. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 9.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 83. | Busby J, Tanberk J. FCC Reports Broadband Unavailable to 21.3 Million Americans, BroadbandNow Study Indicates 42 Million Do Not Have Access. [cited 25 October 2022]. Available from: https://broadbandnow.com/research/fcc-underestimates-unserved-by-50-percent. |
| 84. | Federal Communications Commission. 2020 Broadband Deployment Report. [cited 29 October 2022]. Available from: https://www.fcc.gov/reports-research/reports/broadband-progress-reports/2020-broadband-deployment-report. |
| 85. | Andeweg CS, Berg R, Staal JB, ten Broek RP, van Goor H. Patient-reported Outcomes After Conservative or Surgical Management of Recurrent and Chronic Complaints of Diverticulitis: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:183-190. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 86. | Janes S, Meagher A, Frizelle FA. Elective surgery after acute diverticulitis. Br J Surg. 2005;92:133-142. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 229] [Cited by in RCA: 200] [Article Influence: 10.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 87. | Egger B, Peter MK, Candinas D. Persistent symptoms after elective sigmoid resection for diverticulitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2008;51:1044-1048. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 77] [Cited by in RCA: 86] [Article Influence: 5.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 88. | Forgione A, Leroy J, Cahill RA, Bailey C, Simone M, Mutter D, Marescaux J. Prospective evaluation of functional outcome after laparoscopic sigmoid colectomy. Ann Surg. 2009;249:218-224. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 91] [Cited by in RCA: 92] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 89. | Pasternak I, Wiedemann N, Basilicata G, Melcher GA. Gastrointestinal quality of life after laparoscopic-assisted sigmoidectomy for diverticular disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012;27:781-787. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 90. | Lin M, Raman SR. Evaluation of Quality of Life and Surgical Outcomes for Treatment of Diverticular Disease. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2018;31:251-257. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 91. | Droullard DJ, Khor S, Hantouli M, Strate LL, Lange EO, Chen F, Flum DR, Davidson GH. Assessing the Impact of Diverticulitis on Quality of Life over Time. J Am Coll Surg. 2021;233:552. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 92. | Carabotti M, Cuomo R, Barbara G, Pace F, Andreozzi P, Cremon C, Annibale B. Demographic and clinical features distinguish subgroups of diverticular disease patients: Results from an Italian nationwide registry. United European Gastroenterol J. 2018;6:926-934. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 93. | Spiegel BM, Reid MW, Bolus R, Whitman CB, Talley J, Dea S, Shahedi K, Karsan H, Teal C, Melmed GY, Cohen E, Fuller G, Yen L, Hodgkins P, Erder MH. Development and validation of a disease-targeted quality of life instrument for chronic diverticular disease: the DV-QOL. Qual Life Res. 2015;24:163-179. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 94. | Bordeianou LG, Anger JT, Boutros M, Birnbaum E, Carmichael JC, Connell KA, De EJB, Mellgren A, Staller K, Vogler SA, Weinstein MM, Yafi FA, Hull TL; Members of the Pelvic Floor Disorders Consortium Working Groups on Patient-Reported Outcomes. Measuring Pelvic Floor Disorder Symptoms Using Patient-Reported Instruments: Proceedings of the Consensus Meeting of the Pelvic Floor Consortium of the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons, the International Continence Society, the American Urogynecologic Society, and the Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine and Urogenital Reconstruction. Dis Colon Rectum. 2020;63:6-23. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 95. | Powell BJ, Waltz TJ, Chinman MJ, Damschroder LJ, Smith JL, Matthieu MM, Proctor EK, Kirchner JE. A refined compilation of implementation strategies: results from the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change (ERIC) project. Implement Sci. 2015;10:21. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1969] [Cited by in RCA: 2669] [Article Influence: 266.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |