Published online May 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i5.984
Peer-review started: December 25, 2022
First decision: January 10, 2023
Revised: January 22, 2023
Accepted: March 27, 2023
Article in press: March 27, 2023
Published online: May 27, 2023
Processing time: 152 Days and 6.2 Hours
Ganglioneuroblastoma (GNB) is a peripheral neuroblastoma (NB) with malignant degree between highly malignant NB and benign ganglioma (GN). Pathology is the gold standard of diagnosis. Although GNB is not uncommon in children, biopsy alone may lead to an inaccurate diagnosis, especially for giant tumors. However, surgical resection may be associated with significant complications. Here, we report a case of computer-assisted surgical resection of a giant GNB in a child and successful rescue of the inferior mesenteric artery.
A 4-year-old girl was admitted to our department for a giant retroperitoneal lesion, which was considered to be an NB by her local hospital. The symptoms of the girl disappeared spontaneously without treatment. On physical examination, a mass of about 10 cm × 7 cm could be palpated in her abdomen. Ultrasonography and contrast-enhanced computed tomography performed in our hospital also showed an NB, and there was a very thick blood vessel inside the tumor. However, aspiration biopsy revealed GN. Surgical resection is the best treatment option for this giant benign tumor. For precise preoperative evaluation, three-dimensional reconstruction was performed. It was clear that the tumor was close to the abdominal aorta. The superior mesenteric vein was pushed forward, and the inferior mesenteric artery passed through the tumor. Because GN generally does not invade blood vessels, we split the tumor with a CUSA knife during the operation and found that there was indeed a straight and intact vascular sheath. Arterial pulsation was observed in the completely exposed inferior mesenteric artery. The pathologists interpreting the tissue finally diagnosed it as a mixed GNB (GNBi), which is more malignant than GN. However, both GN and GNBi usually have a good prognosis.
This was a case of successful surgical resection of a giant GNB, and aspiration biopsy underestimated the pathological staging of the tumor. Preoperative three-dimensional reconstruction assisted with the radical resection of the tumor and rescue of the inferior mesenteric artery.
Core Tip: The diagnosis and treatment of ganglioneuroblastoma is complex. Sampling errors associated with aspiration biopsy may lead to inaccurate diagnosis, while difficult surgical resection leads to many postoperative complications. Three-dimensional reconstruction and other technologies may contribute to the safety of surgery. Here, we introduce a child who underwent computer-assisted accurately guided surgical excision of a giant ganglioneuroblastoma, and her inferior mesenteric artery was rescued.
- Citation: Xiu WL, Liu J, Zhang JL, Su N, Wang FJ, Hao XW, Wang FF, Dong Q. Computer-assisted rescue of the inferior mesenteric artery in a child with a giant ganglioneuroblastoma: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(5): 984-991
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i5/984.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i5.984
Ganglioneuroblastoma (GNB) derives from primitive neural crest cells of the neuroectoderm[1,2], and its biological behavior and degree of differentiation are between highly malignant neuroblastoma (NB) and benign ganglioneuroma (GN). These three types are difficult to distinguish and can be transformed into each other, which often leads to difficulties in clinical diagnosis and disease progression. GNB can be divided into nodular (GNBn) and mixed (GNBi) based on histological features[3,4]. GN/GNBi commonly has a good prognosis due to good differentiation[5]. However, it is seldom found because it is nonfunctional and without significant clinical symptoms in the early stages. When a tumor is found, it often compresses and even encases blood vessels due to its large volume. In addition, it is insensitive to chemotherapy and easily recurs. The above characteristics increase the difficulty of radical surgical resection and treatment[6,7]. Computer-assisted system (CAS) three-dimensional (3D) image reconstruction can be used to accurately evaluate and preoperatively plan the treatment to optimize surgical modalities by clearly displaying the spatial anatomical relationship between the tumor and surrounding vessels and organs in different colors. This may be beneficial to improve the prognosis of these children[8,9]. Here, we report a child who underwent computer-assisted accurately guided surgical excision of a giant GNB, and her inferior mesenteric artery was rescued.
A 4-year-old girl visited her local hospital due to abdominal pain and vomiting for one day. Then, she was admitted to our department for a giant retroperitoneal lesion, which was considered an NB.
The girl’s abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan showed a giant retroperitoneal lesion, which was considered an NB. For further diagnosis and treatment, she visited our department. Her symptoms such as abdominal pain and vomiting had disappeared spontaneously without treatment after admission.
Previously, she did not have a specific past medical history.
The girl did not have any significant family history. Both her father and mother were healthy.
On physical examination, a mass was found on palpation of abdomen, mainly in the left upper and left lower quadrants, extending to the right lower quadrant, of about 10 cm × 7 cm in size. It was firm mass without tenderness, and had an unclear boundary and limited mobility.
Tumor markers revealed a neuron-specific enolase level of 42.45 ng/mL. All other blood test findings, including other tumor markers, coagulation, liver and renal function tests, were within normal values.
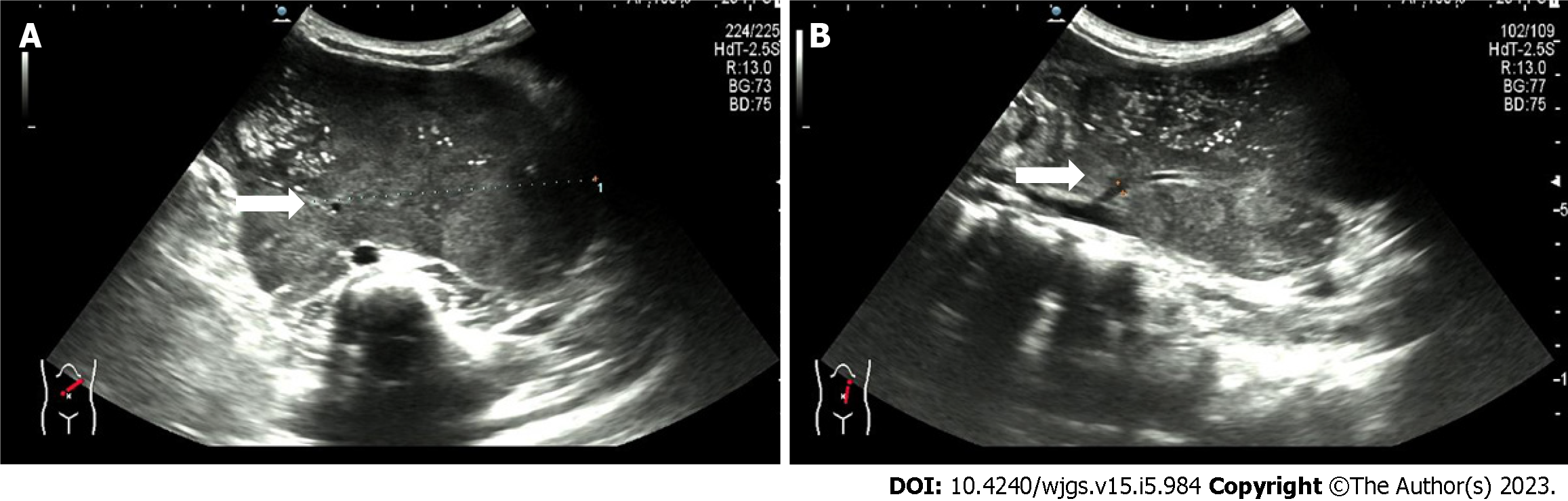
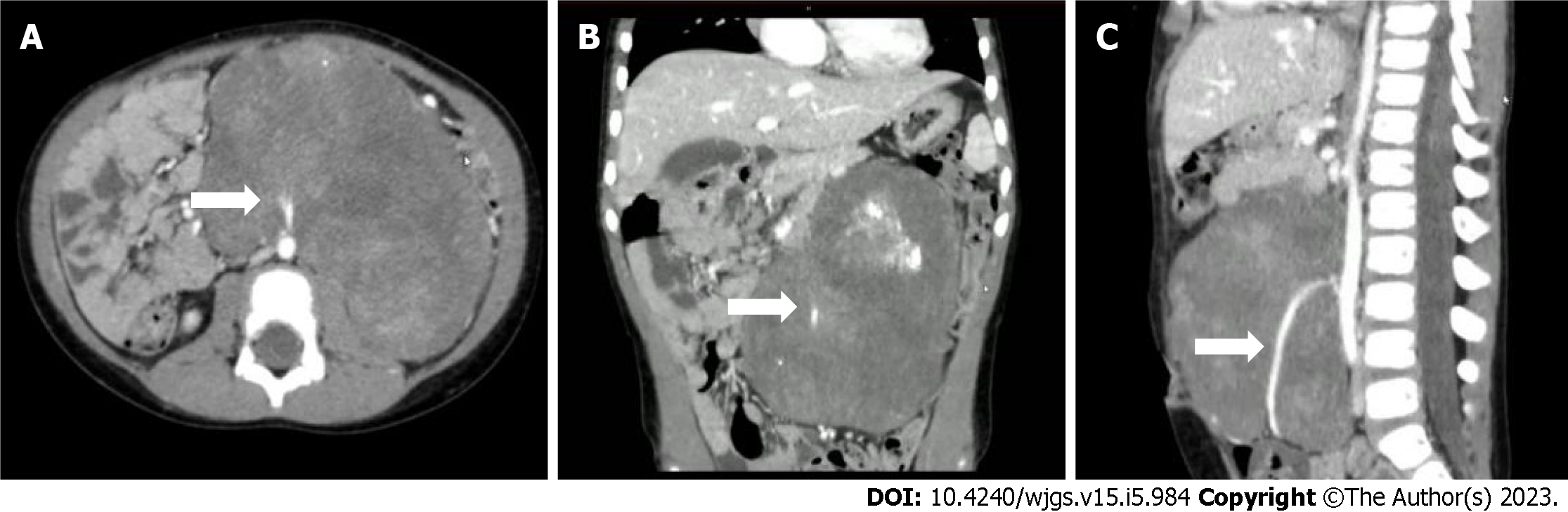
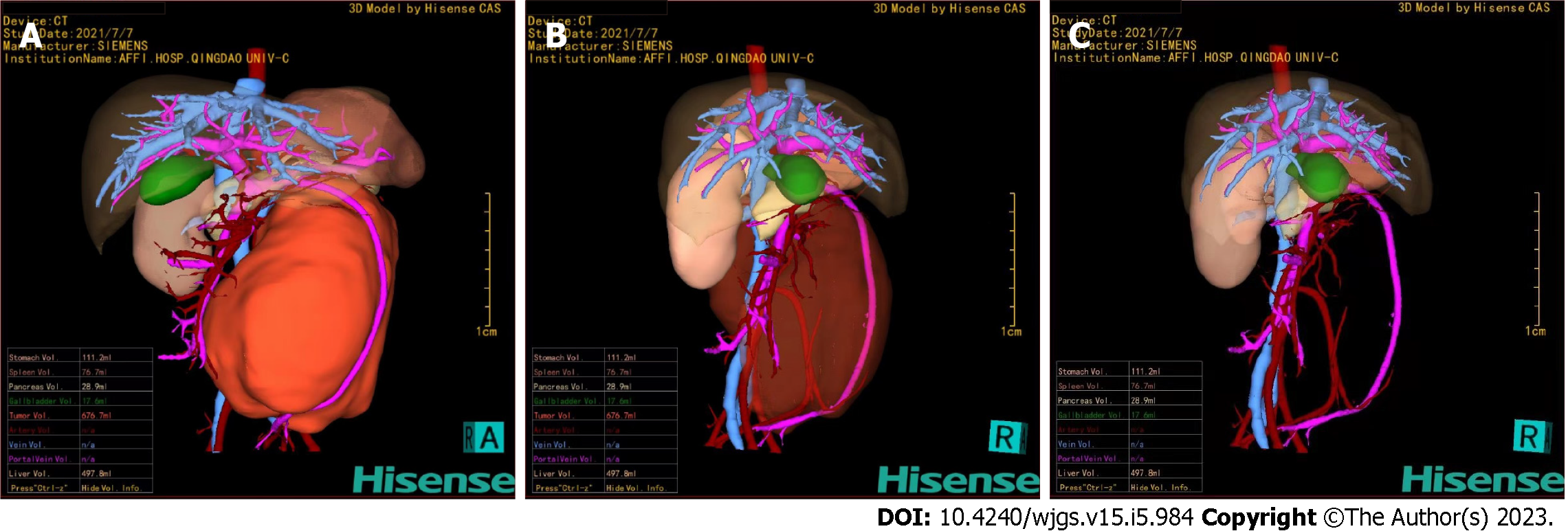
Ultrasonography showed a giant hypoechoic mass in the left retroperitoneal space, and the mass had a patchy strong echogenicity and no obvious cystic area. The lesion size was 12.4 cm × 10.5 cm × 6.3 cm with irregular morphology, and the mass crossed the midline. A tumor blood supply vessel with a diameter of 0.3 cm branched from the abdominal aorta (Figure 1). Contrast-enhanced CT showed that the huge lesion appeared well defined and was 123 mm × 85 mm in maximum cross-section, while the inferior mesenteric artery was fully encased 360°. Mixed density and patchy calcification were seen within the mass, the solid component was significantly enhanced, and adjacent structures were pushed out. The radiologists considered it to be a tumor (NB?) (Figure 2).
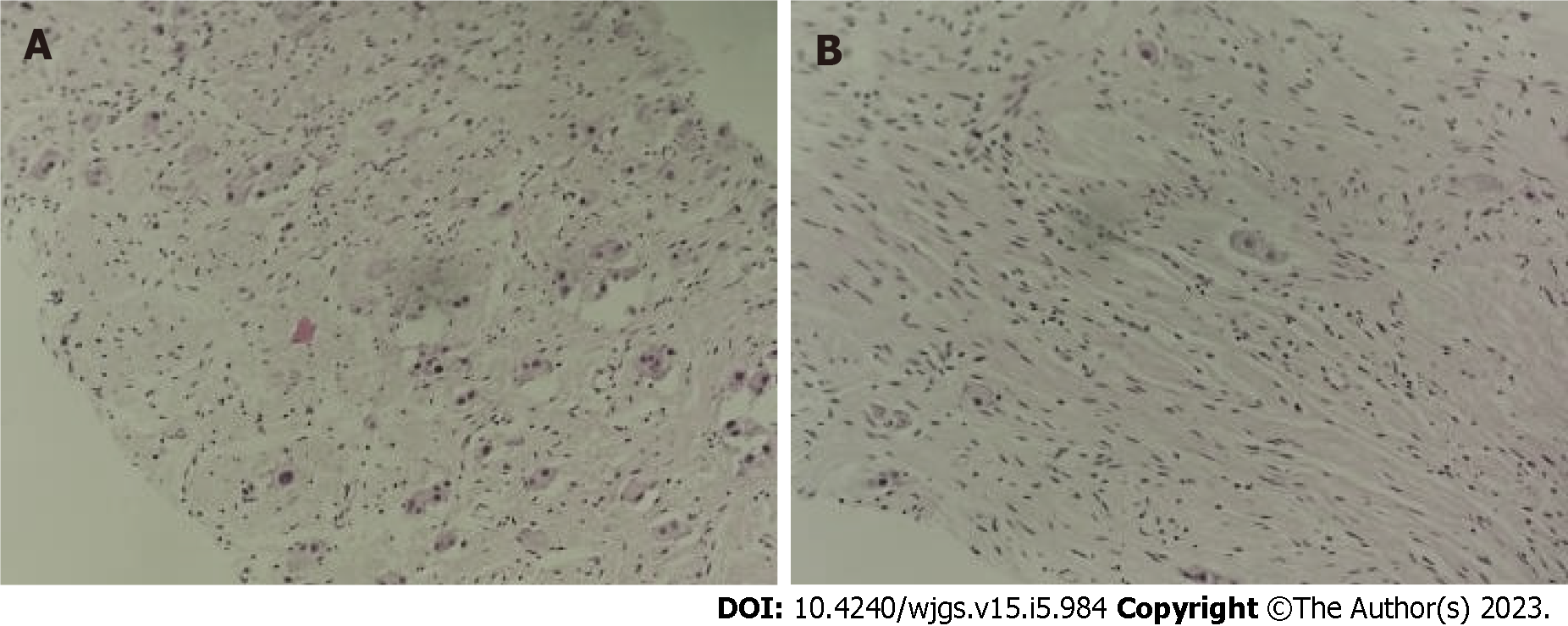
To clarify the diagnosis and decide the next treatment, ultrasound-guided abdominal mass aspiration biopsy was performed. Pathology revealed a retroperitoneal neoplastic lesion, and some cells were spindle-shaped and considered Schwann stroma. As a whole, the tumor was differentiated, while some of the cells were suspected to have undergone ganglion cell differentiation. Some areas appeared to be immature, but no definite NB nesting mass was observed. Immunohistochemical results showed calretinin (+-), Syn (+-), NF (+-), and SOX10 (+-). Therefore, the pathologists first considered it to be a GN (Figure 3).
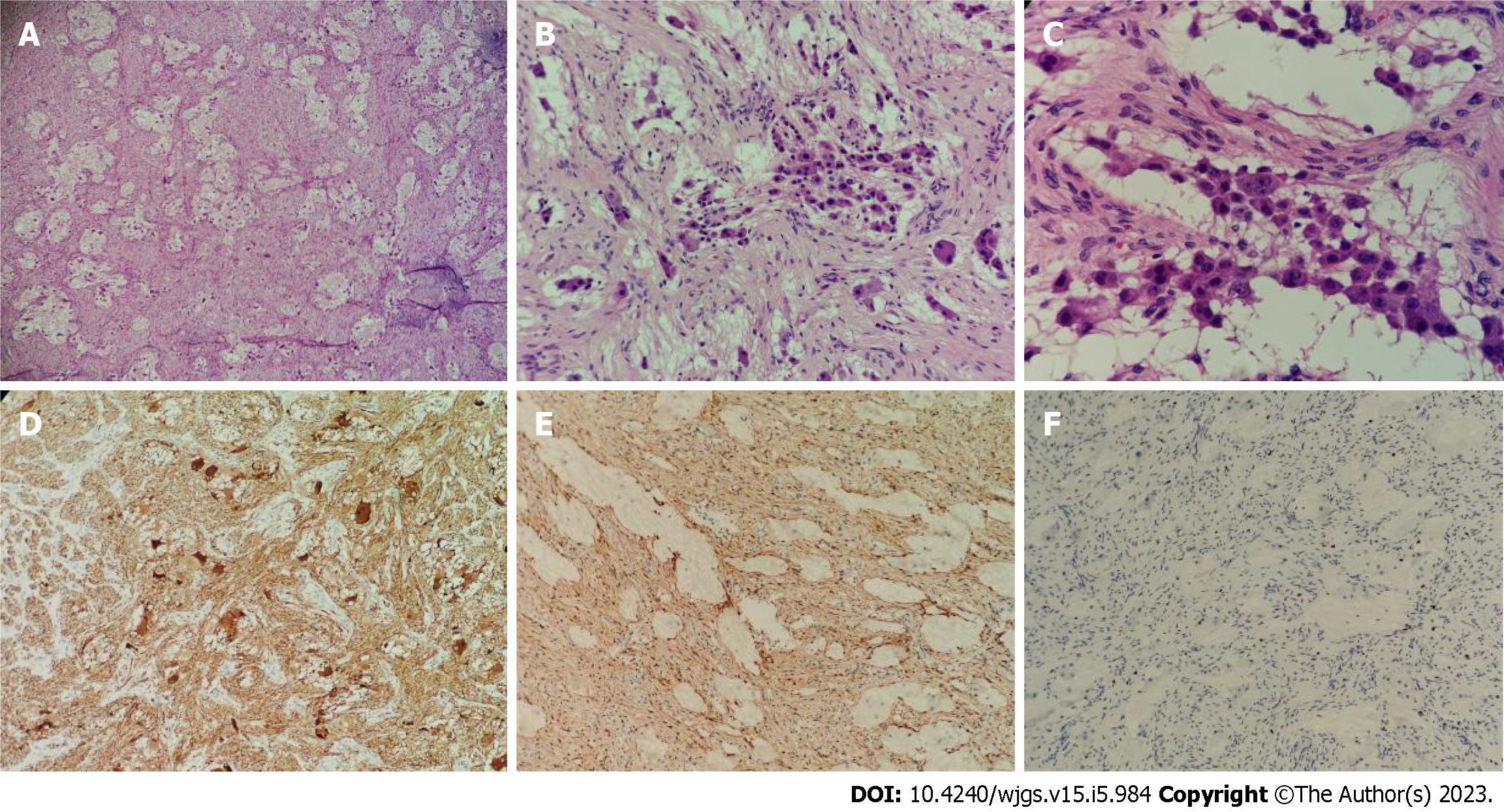
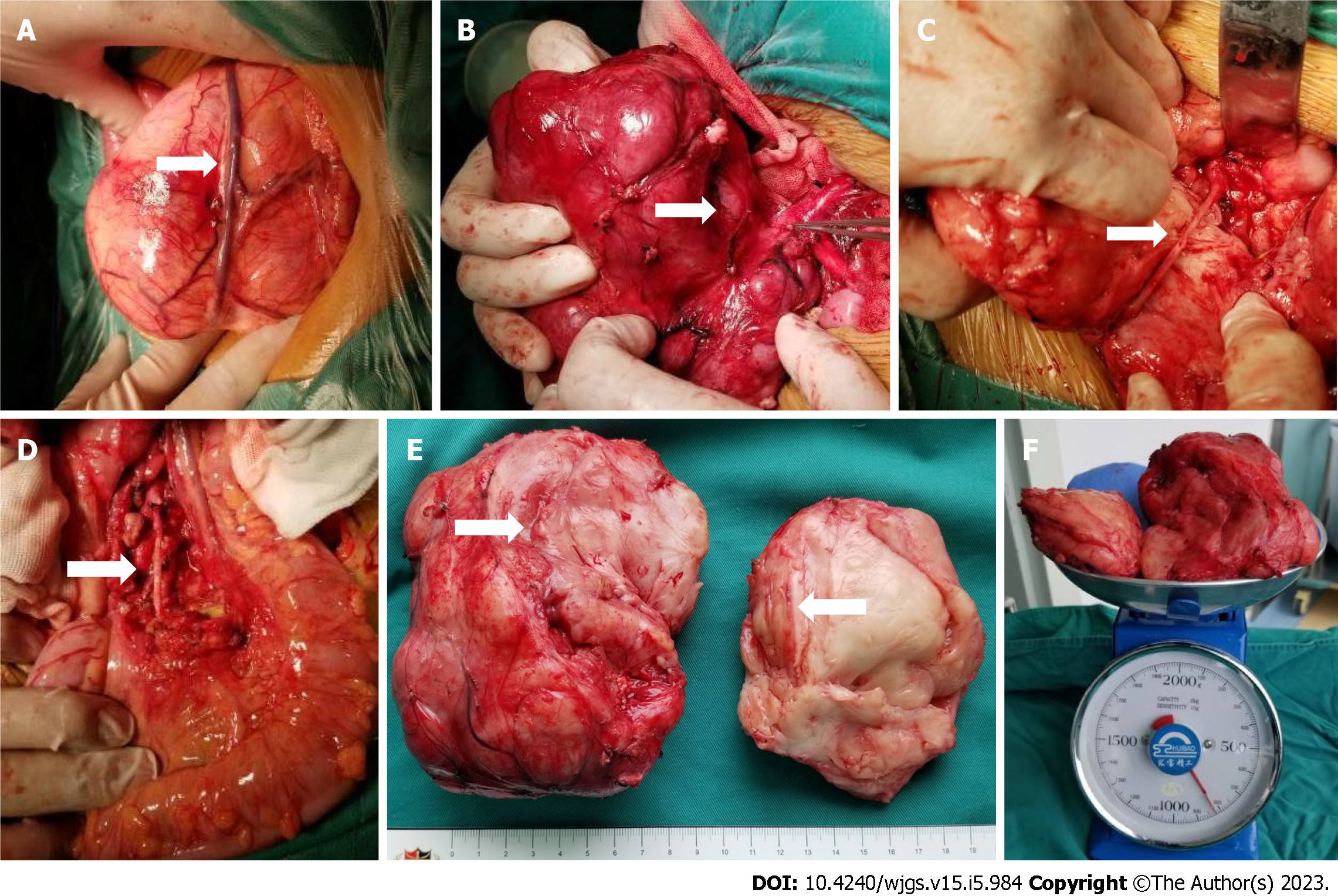
Macroscopically, the two postoperative masses were grayish-white and nodule-like, they were approximately 15 cm × 8 cm and 10 cm × 2 cm in size; and they had soft cut surfaces and fibrous capsules. Microscopically, the tumor was mainly composed of nerve fibers and ganglion cells. However, there were a few scattered small round cells with deeply stained nuclei, and these were considered neuroblasts (less than 10% of the tumor). Immunohistochemistry showed NSE (+), S100 (+), Ki-67 (+, 2%), calretinin (nodal cells +), and NeuN (-). Therefore, the pathologists finally diagnosed it as a GNBi. In addition, metastasis was not observed in the abdominal aortic lymph nodes (Figure 4).
Surgical resection is the best option for this type of benign tumor. Then, for precise preoperative evaluation, 3D reconstruction was performed using CAS. The reconstructed image clearly showed that the tumor was located in the retroperitoneum, and the mass had a volume of 676.7 mL. The mass was extremely close to the abdominal aorta. The superior mesenteric vein was pushed forward, and the inferior mesenteric artery passed through the tumor (Figure 5). In fact, GN mostly grows along the space around the organs and encases blood vessels but does not invade. Also, it generally does not cause occlusion or stenosis of blood vessels. Therefore, we evaluate that surgical treatment would be feasible in this case.
After sufficient preoperative preparation, radical surgical resection was performed (Figure 6). The intraoperative situation was completely consistent with the preoperative CAS evaluation. The giant tumor was located in the retroperitoneum and was completely surrounded by a fibrous capsule. We carefully separated tissues and protected the intestinal canal and mesentery around the tumor, especially the superior mesenteric vein on the surface of the tumor. The vessels supplying the tumor were ligated. Then, the tumor was exposed clearly and was seen to be close to the abdominal aorta, and the inferior mesenteric artery was penetrating the tumor. During the operation, we tried to block the distal inferior mesenteric artery but found that the color of the distal sigmoid colon and rectum became darker. Therefore, we split the tumor with a CUSA knife from the junction of the posterior of the tumor and the abdominal aorta and carefully peeled out the complete inferior mesenteric artery. The tumor section was yellowish-white with a straight vascular sheath. Arterial pulsation was observed in the completely exposed inferior mesenteric artery, and the intestinal canal was ruddy. This operation took 3.5 h, and the bleeding volume was approximately 20 mL.
The child recovered well after surgery without complications such as bleeding and intestinal obstruction. Postoperative positron emission tomography-CT did not show any abnormal increase in metabolism. No tumor cells were found on bone marrow biopsy pathology. We comprehensively considered that she was very low risk, and she did not receive any radiotherapy or chemotherapy. After more than one year of follow-up, no tumor recurrence or metastasis was found in the imaging examinations.
GN/GNBi accounts for approximately 25% of focal NTs. Compared with immature NTs (NB/GNBn), GN/GNBi often has better clinical and biological behavior[6,10]. However, GN/GNBi is generally insensitive to chemotherapy, and surgical resection of suspected GN or GNB can be performed to avoid sampling errors associated with aspiration biopsy. Existing tumor compression symptoms can be relieved by surgery, and surgery can also reduce the possibility of malignant transformation[11,12]. Due to the large volume of the tumor and its impact on important blood vessels, the operation is difficult and highly risky, can lead to numerous surgical complications and affect the short-term and long-term quality of life of children. Therefore, in recent years, some scholars have advocated cytoreductive surgery or follow-up observation for GN/GNBi[13,14]. However, on the premise of minimizing surgical complications, complete radical surgical resection is still the best choice for a definite diagnosis and cure of the disease[6,7,10,14,15]. In this case, the surgery was precisely guided by CAS, resulting in complete resection of the tumor and skeletonization of the vessels without postoperative complications, which may indicate a better clinical prognosis.
Giant GN/GNBi tumors derived from the retroperitoneum often have mesenteric roots at the base of the tumor body. The involvement of either the abdominal aorta, inferior vena cava, or mesenteric arteries or all of them is usually the main factor that affects the complete resection of tumors. At present, traditional ultrasound and two-dimensional CT images can only be displayed along a specific interface and cannot display the anatomical relationship as a whole, especially the origin and shape of curved vessels[16]. CAS is a 3D reconstruction based on CT data that can be used for precise preoperative evaluation and surgical planning by reconstructing organs and tumors and tracking arteries. It can display the adjacent relationship between the tumor and surrounding vascular organs in a 3D, dynamic and overall way[17]. The CAS of this patient clearly showed that the giant retroperitoneal tumor completely encased the inferior mesenteric artery with a clear vessel shape and normal tube wall shape. The tumor also pushed up the superior mesenteric vein and was close to the abdominal aorta. Therefore, the key point of this surgery is to preserve the inferior mesenteric artery and protect the abdominal aorta and the superior mesenteric vein. Thus, it reduces recurrence and prevents complications such as bleeding, intestinal obstruction, and intestinal necrosis[18].
Radical surgical resection is the best choice for the diagnosis and cure of GN/GNBi. CAS can be used to accurately evaluate and plan surgery from the overall perspective, and this planning has great significance to determine the origin and shape of curved blood vessels.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Surgery
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Jain S, India; Kim BJ, South Korea S-Editor: Yan JP L-Editor: A P-Editor: Zhao S
| 1. | Kaatsch P. Epidemiology of childhood cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2010;36:277-285. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 561] [Cited by in RCA: 621] [Article Influence: 41.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Ward E, DeSantis C, Robbins A, Kohler B, Jemal A. Childhood and adolescent cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:83-103. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1416] [Cited by in RCA: 1591] [Article Influence: 144.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 3. | Shimada H, Ambros IM, Dehner LP, Hata J, Joshi VV, Roald B. Terminology and morphologic criteria of neuroblastic tumors: recommendations by the International Neuroblastoma Pathology Committee. Cancer. 1999;86:349-363. [PubMed] |
| 4. | He WG, Yan Y, Tang W, Cai R, Ren G. Clinical and biological features of neuroblastic tumors: A comparison of neuroblastoma and ganglioneuroblastoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8:37730-37739. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 51] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Peuchmaur M, d'Amore ES, Joshi VV, Hata J, Roald B, Dehner LP, Gerbing RB, Stram DO, Lukens JN, Matthay KK, Shimada H. Revision of the International Neuroblastoma Pathology Classification: confirmation of favorable and unfavorable prognostic subsets in ganglioneuroblastoma, nodular. Cancer. 2003;98:2274-2281. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 201] [Cited by in RCA: 171] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Alexander N, Sullivan K, Shaikh F, Irwin MS. Characteristics and management of ganglioneuroma and ganglioneuroblastoma-intermixed in children and adolescents. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2018;65:e26964. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Yang T, Huang Y, Xu T, Tan T, Yang J, Pan J, Hu C, Li J, Zou Y. Surgical management and outcomes of ganglioneuroma and ganglioneuroblastoma-intermixed. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017;33:955-959. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Su L, Dong Q, Zhang H, Zhou X, Chen Y, Hao X, Li X. Clinical application of a three-dimensional imaging technique in infants and young children with complex liver tumors. Pediatr Surg Int. 2016;32:387-395. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Zhao J, Zhou XJ, Zhu CZ, Wu Y, Wei B, Zhang G, Hao XW, Zhang H, Jiang Z, Dong Q. 3D simulation assisted resection of giant hepatic mesenchymal hamartoma in children. Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2017;22:54-59. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Decarolis B, Simon T, Krug B, Leuschner I, Vokuhl C, Kaatsch P, von Schweinitz D, Klingebiel T, Mueller I, Schweigerer L, Berthold F, Hero B. Treatment and outcome of Ganglioneuroma and Ganglioneuroblastoma intermixed. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:542. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 90] [Article Influence: 10.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Whitlock RS, Mehl SC, Larson SK, Foster JH, Hicks J, Nuchtern JG, Sher AC, Vasudevan SA, Naik-Mathuria B. Characteristics of benign neuroblastic tumors: Is surgery always necessary? J Pediatr Surg. 2022;57:1538-1543. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Montante C, Fabozzi F, Villani MF, D'Andrea ML, Stracuzzi A, Natali GL, Del Baldo G, Del Bufalo F, Garganese MC, Serra A, Tomà P, Alaggio R, Vennarini S, Colafati GS, Mastronuzzi A, De Ioris MA. The Pitfall of Ganglioneuroblastoma-Nodular Diagnosis: Clinical and Imaging Considerations over a Rare Bifocal Sporadic Case. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | De Bernardi B, Gambini C, Haupt R, Granata C, Rizzo A, Conte M, Tonini GP, Bianchi M, Giuliano M, Luksch R, Prete A, Viscardi E, Garaventa A, Sementa AR, Bruzzi P, Angelini P. Retrospective study of childhood ganglioneuroma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1710-1716. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 96] [Cited by in RCA: 105] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Sánchez-Galán A, Barrena S, Vilanova-Sánchez A, Martín SH, Lopez-Fernandez S, García P, Lopez-Santamaria M, Martínez L, Tovar JA. Ganglioneuroma: to operate or not to operate. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2014;24:25-30. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Fu Z, Ren J, Zhou J, Shen J. Comparing the diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT scan and bone marrow biopsy in newly diagnosed pediatric neuroblastoma and ganglioneuroblastoma. Front Oncol. 2022;12:1031078. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 16. | Xiu W, Liu J, Li T, Hao X, Liu H, Xia N, Duan Y, Jiang Z, Shang C, Dong Q. Application value of computer-assisted surgery system in pediatric hepatic hemangioma. Pediatr Surg Int. 2021;37:1575-1583. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Liu J, Xiu W, Duan G, Dong Q. Application of 3D Simulation Software in Chemotherapy and Hepatoblastoma Surgery in Children. Front Surg. 2022;9:908381. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Mari GM, Crippa J, Cocozza E, Berselli M, Livraghi L, Carzaniga P, Valenti F, Roscio F, Ferrari G, Mazzola M, Magistro C, Origi M, Forgione A, Zuliani W, Scandroglio I, Pugliese R, Costanzi ATM, Maggioni D. Low Ligation of Inferior Mesenteric Artery in Laparoscopic Anterior Resection for Rectal Cancer Reduces Genitourinary Dysfunction: Results From a Randomized Controlled Trial (HIGHLOW Trial). Ann Surg. 2019;269:1018-1024. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 89] [Article Influence: 14.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |