Published online Oct 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i10.2123
Peer-review started: July 4, 2023
First decision: July 19, 2023
Revised: August 1, 2023
Accepted: August 15, 2023
Article in press: August 15, 2023
Published online: October 27, 2023
Processing time: 115 Days and 0.1 Hours
Low anterior resection syndrome (LARS) is a common complication of anus-preserving surgery in patients with colorectal cancer, which significantly affects patients' quality of life.
To determine the relationship between the incidence of LARS and patient quality of life after colorectal cancer surgery and to establish a LARS prediction model to allow perioperative precision nursing.
We reviewed the data from patients who underwent elective radical resection for colorectal cancer at our institution from April 2013 to June 2020 and completed the LARS score questionnaire and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Core Quality of Life and Colorectal Cancer Module questionnaires. According to the LARS score results, the patients were divided into no LARS, mild LARS, and severe LARS groups. The incidence of LARS and the effects of this condition on patient quality of life were determined. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify independent risk factors for the occurrence of LARS. Based on these factors, we established a risk prediction model for LARS and evaluated its performance.
Among the 223 patients included, 51 did not develop LARS and 171 had mild or severe LARS. The following quality of life indicators showed significant di
The quality of life of patients with LARS after colorectal cancer surgery is significantly reduced.
Core Tip: Low anterior resection syndrome (LARS) is a common complication of anus-preserving surgery in patients with colorectal cancer. In this study, we found that LARS significantly affected patients’ quality of life after colorectal cancer surgery, and that perioperative precision nursing could significantly reduce the incidence of LARS and improve patients’ quality of life. Furthermore, we established a LARS prediction model, which showed excellent performance in predicting the occurrence of LARS after colorectal cancer surgery. This prediction model can enable implementation of perioperative precision nursing to improve the quality of life of patients with LARS.
- Citation: Jin DA, Gu FP, Meng TL, Zhang XX. Effect of low anterior resection syndrome on quality of life in colorectal cancer patients: A retrospective observational study. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(10): 2123-2132
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i10/2123.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i10.2123
Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer worldwide[1], with a global incidence of 7.7 per 100000 population[2] and more than 1 million affected patients in the United States[3]. According to the National Cancer Institute’s Sur
Colorectal cancer treatment is based on a comprehensive multidisciplinary approach, and includes a variety of treatment methods, such as surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and traditional Chinese medicine[8-11]. With the vigorous development of scientific research and the continuous exploration of approaches in clinical practice, the surgery-based multidisciplinary treatment strategy has played a significant role in improving the prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer[12,13].
With the continuous improvement of surgical techniques and equipment, the survival rates of patients with colorectal cancer have significantly improved[13,14]. According to the latest data from the American Cancer Society, the 5-year overall survival rate is 65%, with patients in local areas and hospitals having a better prognosis, with rates of up to 90% and 71%, respectively[15]. However, in patients with advanced colorectal cancer, the effect of surgical treatment is far from ideal. For these patients, current guidelines recommend the use of chemotherapy drugs, including 5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and irinotecan[15].
Advancement in treatment methods has allowed colorectal cancer surgery to effectively improve patient symptoms in addition to providing good disease control and prolonging patient survival[16]. Retention of the anal canal, urinary function, and sexual function while ensuring radical resection has become the surgical objective. However, some patients develop low anterior resection syndrome (LARS) after anus-preserving surgery[17,18].
LARS is a subjective discomfort syndrome with common symptoms including incontinence, increased frequency and urgency of defecation, difficulty in emptying, and other symptoms, which brings great inconvenience to patients[9,19]. The incidence of LARS has been reported to range from 17.8% to 80.0%. Nonetheless, to date, there have been no population-based cohort studies to determine the incidence of LARS and its relationship with patient quality of life[20,21].
The accelerated development of rehabilitation surgery has shortened the overall length of hospital stay of patients with colorectal cancer[22]. However, a shorter hospitalization stay reduces the time for patients to acquire anal rehabilitation skills prior to being discharged from the hospital, which may lead to an increase in the incidence of LARS[23].
This was a longitudinal observational retrospective cohort study with a hospital-based survey that included patients surgically treated for colorectal cancer. Postoperatively, patients were provided with the LARS score questionnaire, the third edition of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Core Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC QLQ-C30), and the Colorectal Cancer Module (EORTC QLQ-CR29) questionnaire[24]. To ensure patient compliance, each hospital assigned a responsible person to supervise and inspect the completion of the questionnaires. Researchers from the three hospitals met once a week to discuss the content of the study and the completion of the questionnaires.
Perioperative clinicopathological characteristics of patients and tumors were extracted from the medical records. Data were analyzed to determine the incidence of LARS and its effects on patient quality of life and to identify independent risk factors for the occurrence of LARS. Based on these factors, we established a risk prediction model for LARS and evaluated its performance.
LARS score: The LARS score questionnaire evaluates defecation frequency, occasional uncontrollable exhaust (flatulence), occasional anal leakage, stool properties, and urgency. Based on the findings of this questionnaire, patients were divided into three groups as follows: No LARS (0-20 points), mild LARS (21-29 points), and severe LARS (30-42 points).
EORTC QLQ-C30: The EORTC QLQ-C30 contains the following domains: Physical, role, emotional, and cognitive function, total health status, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, pain, shortness of breath, insomnia, loss of appetite, constipation, diarrhea, and economic difficulties. Body function was scored based on the ability of the patient to engage in strenuous activities and long- or short-distance walks outdoors, the necessity to stay in bed or a chair during the day, and the ability to eat, dress, bathe, or go to the toilet. Role function was scored based on restrictions in work and daily activities and hobby or leisure activities (physical strength). Emotional function was scored based on feelings of nervousness, worry, irritability, and depression. Cognitive function was scored based on the ability to concentrate and remember. Total health status was scored based on general health status and life quality, as assessed over one week. Fatigue was scored based on the requirement for rest and the presence of weakness and tiredness. The total QLQ-C30 score was obtained by summing the total percentile scores of each domain.
EORTC QLQ-CR29: The EORTC QLQ-CR29 contains the following domains: Urinary frequency, stool blood/mucus, body image, ostomy, male sexual function, impotence, female sexual function, pain, incontinence, urinary pain, abdominal pain, hip pain, abdominal distension, dry mouth, hair loss, taste abnormalities, anxiety, and obesity. The total QLQ-CR29 score was obtained by summing the total percentile scores of each domain.
The study population included patients who underwent elective radical resection for colorectal cancer at our institution from April 2013 to June 2020 and completed the LARS score and the EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaires.
The perioperative management and treatment of patients were in full compliance with current guidelines. All surgeries were performed by surgeons with more than 5 years of experience in performing primary surgery. Histopathological analysis was performed by the pathologists of our hospital.
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Completed preoperative colonoscopy and postoperative pathological confirmation of colorectal cancer; (2) elective colorectal cancer surgery with definite indications and without contraindications; (3) age ≥ 18 years; and (4) ability to complete the questionnaires.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Palliative colorectal resection; (2) history of immune system disorders, uremia, or severe preoperative renal impairment; (3) concurrent other primary malignant tumors, except for gastric cancer; (4) emergency surgery due to ileus; and (5) incomplete or otherwise disqualified questionnaire data.
Relevant clinical, surgical, and pathological data were extracted from the patient medical records, which included age, sex, preoperative radiotherapy, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, tumor size, length, resection margin (cm), tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage, degree of differentiation (01/23), total/partial mesorectal excision (TME/PME), anal distance (cm), presence of stoma, lymphatic dissection, and surgery type (open or endoscopic).
For analyses, patients were divided into no-LARS and LARS groups based on the LARS score results. The LARS group included patients with mild and severe LARS. The above clinicopathological factors were compared between the groups. Continuous variables are expressed as the mean with standard deviation or median with interquartile range and were compared using Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney’s U test, as appropriate. Categorical variables are expressed as frequencies with percentages and were compared using the Chi-square test.
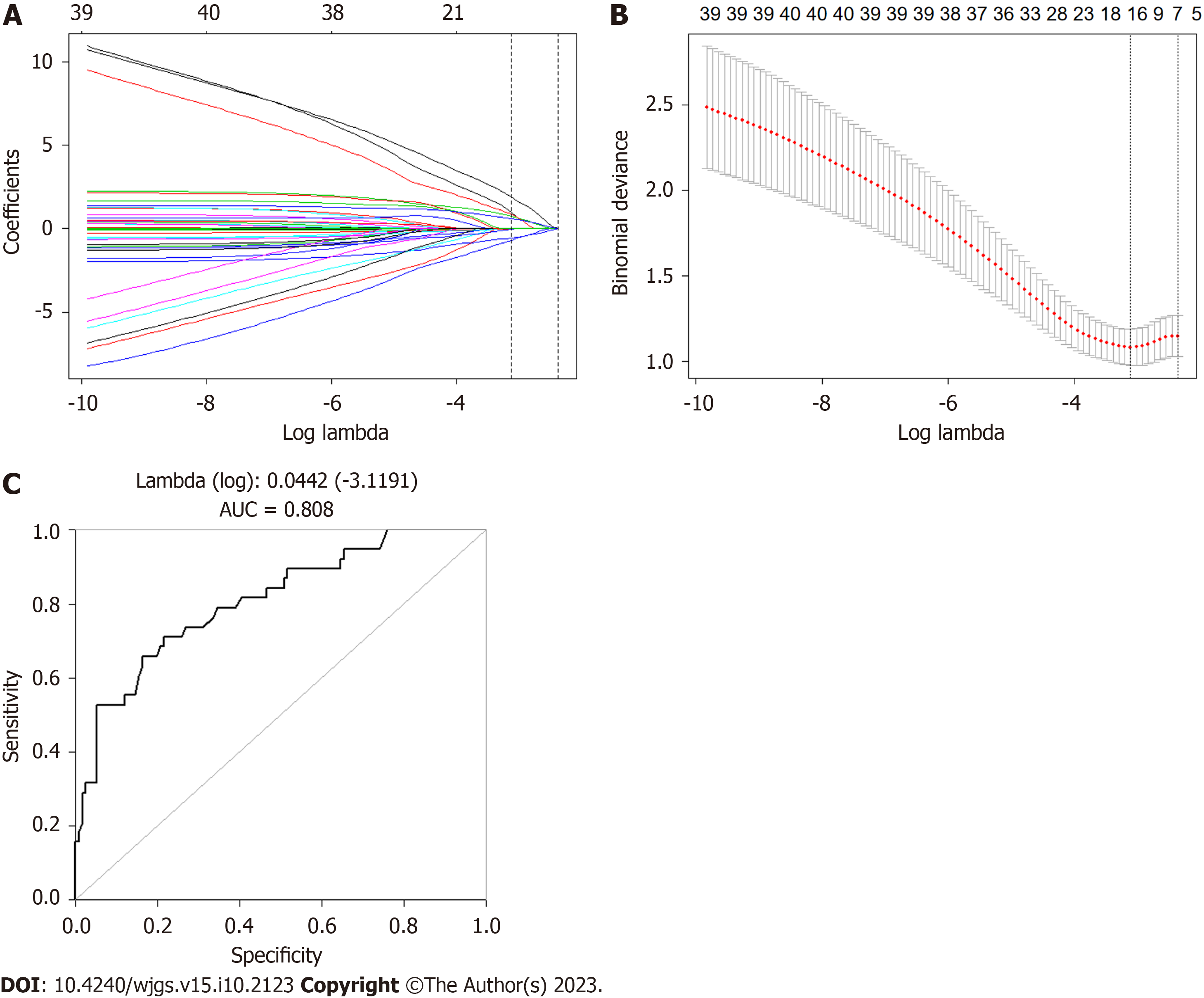
The Chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests were used for univariate analysis to identify factors associated with LARS. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed based on the univariate analysis results, and odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals were calculated. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was employed to select significant clinicopathological factors associated with LARS. Based on the selected independent risk factors, a visual prediction model of LARS risk and survival line chart were constructed.
IBM SPSS Statistics version 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, United States) was used for statistical analyses. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. All P values were two-tailed.
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of our institution.
Of the 312 patients who underwent colorectal surgery during the study period, 19 were excluded for the following reasons: Seven due to preoperative metastasis to other sites and palliative surgical treatment, three due to preoperative diagnosis of severe renal failure, and nine due to discrepancy between the pre- and postoperative diagnosis. Therefore, a total of 293 patients received questionnaires, of whom 265 (90.4%) returned completed questionnaires. Among them, 42 patients who completed the questionnaires in less than 300 s were excluded. Finally, 223 (84.15%) patients with qualified questionnaires were included in the analysis.
There were 65 women (25.12%) and 158 men (74.88%), with an average age of 59.21 (range, 52-68) years. According to the LARS score results, 51 (22.86%) patients did not have LARS, 47 (121.07%) had mild LARS, and 125 (56.05%) had severe LARS.
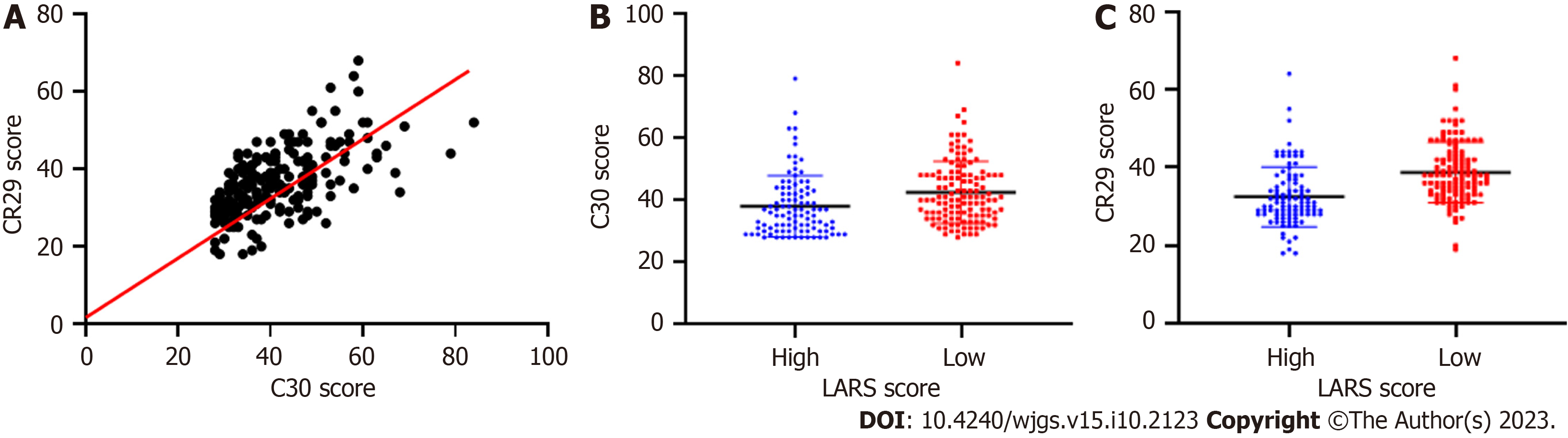
Compared with those without LARS, patients with LARS had significantly lower scores for physical, emotional, and cognitive function and total health status and higher scores for fatigue, nausea and vomiting, pain, shortness of breath, insomnia, constipation, and diarrhea. The relationship between LARS and quality of life assessed using the EORTC QLQ-C30 and EORTC QLQ-CR29 questionnaires is shown in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. The scatterplot correlation analysis showed good consistency between the two quality of life assessment methods (Figure 1).
| No LARS (n = 51) | LARS (n = 171) | P value | |
| Physical function: High/low | 36 (70.6%)/15 (29.4%) | 87 (50.6%)/85 (49.4%) | 0.0081 |
| Role function: High/low | 33 (64.7%)/18 (35.3%) | 88 (51.5%)/84 (48.5%) | 0.06 |
| Emotional function: High/low | 38 (74.5%)/13 (25.5%) | 98 (56.9%)/74 (43.1%0 | 0.0172 |
| Cognitive function: High/low | 36 (70.6%)/15 (29.4%) | 75 (43.8%)/97 (56.2%) | 0.0011 |
| Total health status: High/low | 29 (56.9%)/22 (43.1%) | 69 (40.3%)/103 (59.7%) | 0.0262 |
| Fatigue: High/low | 33 (64.7%)/18 (35.3%) | 86 (50%)/86 (50%) | 0.0452 |
| Nausea and vomiting: High/low | 45 (88.2%)/6 (11.8%) | 146 (84.9%)/26 (15.1%) | 0.365 |
| Pain: High/low | 44 (86.3%)/7 (13.7%) | 109 (63.4%)/63 (36.6%) | 0.0011 |
| Polypnea: High/low | 46 (90.2%)/5 (9.8%) | 129 (75.0%)/43 (25%) | 0.0132 |
| Sleeplessness: High/low | 40 (78.4%)/11 (21.6%) | 93 (54.1%)/79 (45.9%) | 0.0011 |
| Appetite loss: High/low | 42 (82.3%)/9 (17.6%) | 126 (73.3%)/46 (26.7%) | 0.126 |
| Constipation: High/low | 35 (68.6%)/16 (31.4%) | 71 (41.3%)/101 (58.7%) | 0.0011 |
| Diarrhea: High/low | 41 (80.4%)/10 (19.6%) | 77 (44.8%)/95 (57.2%) | 0.0011 |
| Financial difficulty: High/low | 46 (90.2%)/5 (9.8%) | 142 (82.5%)/30 (17.5%) | 0.135 |
| Without LARS (n = 51) | With LARS (n = 171) | P value | |
| Frequent micturition: With/without | 27 (52.3%)/24 (47.9%) | 74 (43.0%)/98 (56.9%) | 0.138 |
| Blood in stool: With/without | 41 (80/4%)/10 (19.6%) | 106 (61.6%)/66 (38.4%) | 0.0091 |
| Body image: With/without | 41 (80/4%)/10 (19.6%) | 88 (51.2%)/84 (48.8%) | 0.0011 |
| Male sexual function: With/without | 16 (44.4%)/20 (55.6%) | 60 (53.6%)/52 (46.4%) | 0.223 |
| Impotence: With/without | 21 (61.7%)/13 (38.3%) | 52 (50%)/52 (50%) | 0.160 |
| Female sexual function: With/without | 9 (81.8%)/2 (18.2%) | 37 (80.4%)/9 (19.6%) | 0.644 |
| Pain: With/without | 8 (88.8%)/1 (11.1%) | 33 (78.6%)/9 (21.4%) | 0.429 |
| Uroclepsia: With/without | 49 (96.1%)/2 (3.9%) | 149 (86.6%)/23 (13.3%) | 0.061 |
| Odynuria: With/without | 47 (92.1%)/4 (7.8%) | 157 (91.3%)/15 (8.7%) | 0.816 |
| Stomachache: With/without | 44 (86.3%)/7 (13.7%) | 129 (75.0%)/43 (25.0%) | 0.062 |
| Pygalgia: With/without | 48 (94.1%)/3 (5.9%) | 128 (74.4%)/44 (25.6%) | 0.0011 |
| Ventosity: With/without | 44 (86.3%)/7 (13.7%) | 110 (63.9%)/62 (36.1%) | 0.0011 |
| Thirst: With/without | 32 (19.6%)/19 (37.2%) | 83 (48.3%)/89 (51.2%) | 0.0481 |
| Alopecia: With/without | 47 (92.2%)/4 (7.8%) | 118 (68.6%)/54 (31.4%) | 0.0011 |
| Allotriogeustia: With/without | 46 (90.2%)/5 (9.8%) | 114 (66.3%)/28 (33.8%) | 0.180 |
| Anxiety: With/without | 29 (56.9%)/22 (43.1%) | 54 (31.3%)/118 (68.6%) | 0.0011 |
| Obesity: With/without | 35 (68.6%)/16 (31.3%) | 97 (56.4%)/75 (43.6%) | 0.081 |
According to the findings of the LARS score assessment, 99 patients received low LARS scores and 124 received high scores. A comparison of clinicopathological factors between the groups showed that TME/PME, ostomy, preoperative radiotherapy, and neoadjuvant chemotherapy were significantly correlated with LARS scores (P < 0.05, Table 3).
| Low LARS score (n = 99) | High LARS score (n = 124) | P value | |
| Age (yr): < 59/≥ 60 | 49 (49.5%)/50 (50.5%) | 62 (50.0%)/62 (50.0%) | 0.524 |
| Sex: Male/female | 73 (73.4%)/26 (26.3%) | 81 (65.3%)/43 (34.6%) | 0.114 |
| Tumor size (cm): < 4/≥ 4 | 44 (44.4%)/52 (55.6%) | 69 (55.6%)/49 (44.4%) | 0.044 |
| Length (cm): < 12/≥ 12 | 25 (25.3%)/63 (74.7%) | 25 (23.1%)/83 (76.8%) | 0.249 |
| Length of distal margin (cm): < 3/≥ 3 | 43 (52.4%)/39 (47.6%) | 52 (57.1%)/39 (42.8%) | 0.32 |
| T: 0, 1/2, 3 | 10 (15.1%)/56 (84.8%) | 13 (17.6%)61 (82.4%) | 0.439 |
| N: < 17/≥ 17 | 60 (61.8%)/37 (38.1%) | 77 (63.1%)/45 (36.9%0 | 0.479 |
| M: No/yes | 86 (92.5%)/7 (7.5%) | 86 (89.6%)/10 (10.4%) | 0.331 |
| Differentiated degree: 0, 1/2, 3 | 31 (31.9%)/66 (68.1%0 | 45 (37.8%)/74 (62.2%) | 0.264 |
| TME/PME | 59 (62.1%)/39 (37.9%) | 58 (47.5%)/64 (52.4%) | 0.041 |
| Anal distance: < 9/≥ 9(cm) | 41 (41.8%)/57 (58.2%) | 62 (51%)/60 (49%) | 0.117 |
| Fistulation: No/yes | 53 (53.5%)/46 (46.5%) | 50 (41.3%)/71 (58.7%) | 0.005 |
| Preoperation radiotherapy: No/yes | 79 (81.4%)/18 (18.6%) | 79 (64.7%)/43 (35.1%) | 0.0211 |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy: No/yes | 84 (85.7%)/14 (24.3%) | 84 (68.3%)/39 (31.7%) | 0.0072 |
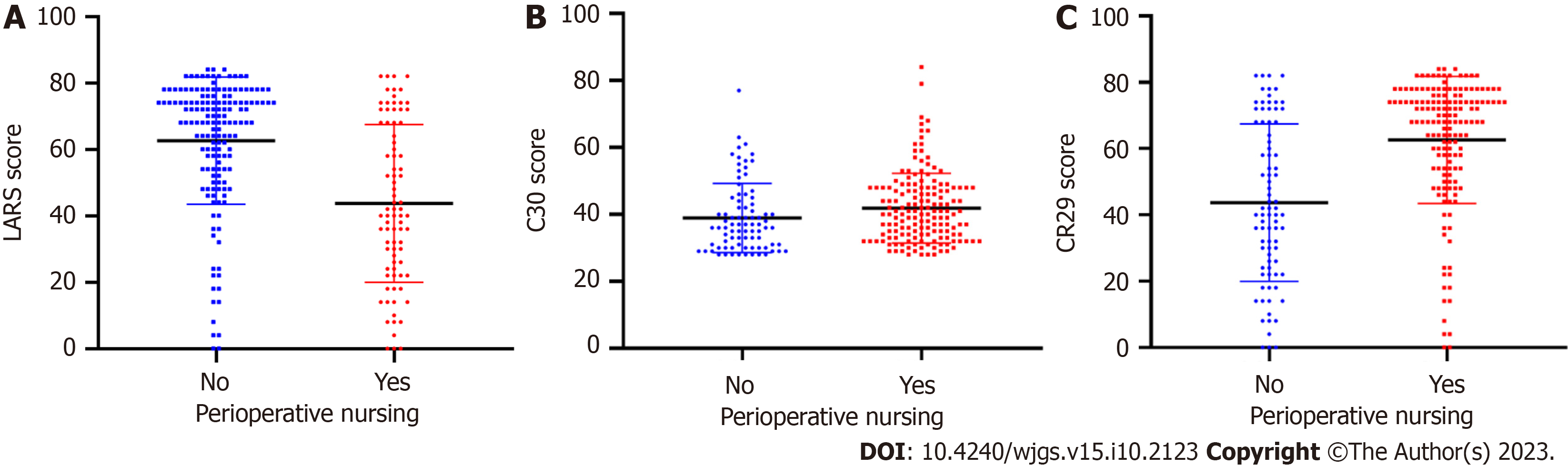
According to the perioperative nursing method and patient clinical course, patients were divided into precision and routine nursing groups. The two groups were compared based on the LARS, QLQ-C30, and QLQ-CR29 scores (Figure 2). Perioperative precision nursing was associated with lower LARS scores and higher QLQ-C30 and QLQ-CR29 scores (P < 0.05). These results indicate that perioperative precision nursing is of great significance for reducing the incidence of LARS and improving patient quality of life.
LASSO regression analysis showed that TME/PME, ostomy, preoperative radiotherapy, and neoadjuvant chemotherapy were independent risk factors for the occurrence of LARS after colorectal surgery (P < 0.05). These factors were used to establish a prediction model, which had an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.808 for predicting LARS (Figure 3).
Before the LARS score questionnaire was developed in 2012, most studies on postoperative long-term quality of life focused on the incontinence symptom of defecation dysfunction[25]. This research method formed the misunderstanding that "intestinal dysfunction recovers within 1 year after surgery and the function of long-term survival patients is acceptable”[11]. In this study, we found that LARS significantly affected patient quality of life after colorectal cancer surgery and that perioperative precision nursing has the potential to significantly reduce the incidence of LARS and improve patient quality of life. Furthermore, TME/PME, ostomy, preoperative radiotherapy, and neoadjuvant chemotherapy were identified as independent risk factors for LARS. Based on these clinicopathological factors, we established a LARS prediction model that showed excellent performance in predicting the occurrence of LARS after colorectal cancer surgery.
Surgical resection is the main method for treating colorectal cancer[26]. With the continuous updating of surgical techniques and equipment and the expanding knowledge on neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and colorectal cancer pathology and molecular pathology, postoperative survival rates continue to increase[27]. LARS is a common com
Although most LARS symptoms disappear within 1 year after surgery, the occurrence greatly inconveniences patients. In this study, patients with LARS had a significantly poorer quality of life than those without, and the quality of life decreased with the aggravation of LARS symptoms. To assess patient quality of life, we used the EORTC QLQ-C30 and EORTC QLQ-CR29 questionnaires. Our analysis showed good consistency between the scores of these two questionnaires, confirming that both reflect the quality of life of patients well[30].
In the present study, we found that TME/PME, ostomy, preoperative radiotherapy, and neoadjuvant chemotherapy were independent risk factors for LARS. This is consistent with the results of a prior study that identified the anastomotic site-anal edge distance, anastomotic leakage, radiotherapy, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, TNM stage, and sex as risk factors for LARS after surgery for low rectal cancer[31]. Furthermore, we established a LARS risk prediction model, which had an accuracy of over 80%.
Most prior studies on LARS have focused on the causes and risk factors for LARS without exploring factors that may help reduce LARS incidence and severity[32]. In the current study, we found that personalized precision nursing during the perioperative period could help reduce LARS scores and improve patient quality of life. Therefore, perioperative precision nursing is an important protective factor for LARS. As personalized precision nursing is labor-intensive and requires substantial material resources, patients should undergo LARS risk assessment before surgery, and precision nursing should be applied according to the results, which can improve patient quality of life[33].
The findings of this study are of great significance for predicting the long-term functional prognosis of patients after anal preservation. If the patient has not received radiation and the anastomotic height is high, it is unlikely that severe LARS will occur from a long-term survival perspective. If these patients have more severe LARS symptoms early after surgery, active treatment may result in a good functional prognosis[33].
There are still some limitations in this study. All patients included in this study retrospectively. According to the LARS risk prediction model established in this study, prospective perioperative nursing studies can be conducted, which will be the plan of further research[34].
The LARS risk prediction model established in this study can enable the implementation of perioperative precision nursing for high-risk patients after colorectal cancer surgery. This may result in reduced LARS incidence and severity, which is of great value for improving the quality of life and happiness index of patients undergoing colorectal cancer surgery.
Low anterior resection syndrome (LARS) is a common complication of anus-preserving surgery for colorectal cancer, which seriously affects the daily life of patients.
In order to reduce the incidence and severity of LARS, while improving the quality of life of patients undergoing colorectal cancer surgery.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between LARS and patient quality of life in a large cohort of patients and to identify perioperative clinicopathological factors that can predict the occurrence of LARS.
This was a longitudinal retrospective cohort study using a hospital-based survey. In this study, the LARS score questionnaire and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Core Quality of Life and Colorectal Cancer module questionnaires were completed.
Multiple independent risk factors for LARS were identified in the study. The accuracy of the LARS prediction model established was 0.808.
The LARS prediction model in this study can implement perioperative precision nursing and improve the quality of life of LARS patients.
The LARS prediction model would enable the implementation of perioperative precision nursing interventions to improve patient quality of life.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Rumpold H, Austria; Shinozaki E, Japan S-Editor: Lin C L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Xu ZH
| 1. | Akizuki E, Matsuno H, Satoyoshi T, Ishii M, Usui A, Ueki T, Nishidate T, Okita K, Mizushima T, Mori M, Takemasa I. Validation of the Japanese Version of the Low Anterior Resection Syndrome Score. World J Surg. 2018;42:2660-2667. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Rubinkiewicz M, Zarzycki P, Czerwińska A, Wysocki M, Gajewska N, Torbicz G, Budzyński A, Pędziwiatr M. A quest for sphincter-saving surgery in ultralow rectal tumours-a single-centre cohort study. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16:218. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Altomare DF, Picciariello A, Ferrara C, Digennaro R, Ribas Y, De Fazio M. Short-term outcome of percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation for low anterior resection syndrome: results of a pilot study. Colorectal Dis. 2017;19:851-856. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 4. | Barugola G, Bertocchi E, Gentile I, Cracco N, Sartori CA, Ruffo G. Hostile pelvis: how to avoid permanent stoma. Updates Surg. 2018;70:459-465. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Battersby NJ, Bouliotis G, Emmertsen KJ, Juul T, Glynne-Jones R, Branagan G, Christensen P, Laurberg S, Moran BJ; UK and Danish LARS Study Groups. Development and external validation of a nomogram and online tool to predict bowel dysfunction following restorative rectal cancer resection: the POLARS score. Gut. 2018;67:688-696. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 75] [Article Influence: 10.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Chen TY, Emmertsen KJ, Laurberg S. What Are the Best Questionnaires To Capture Anorectal Function After Surgery in Rectal Cancer? Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2015;11:37-43. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 66] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Hou XT, Pang D, Lu Q, Yang P, Jin SL, Zhou YJ, Tian SH. Validation of the Chinese version of the low anterior resection syndrome score for measuring bowel dysfunction after sphincter-preserving surgery among rectal cancer patients. Eur J Oncol Nurs. 2015;19:495-501. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Hain E, Maggiori L, Zappa M, Prost À la Denise J, Panis Y. Anastomotic leakage after side-to-end anastomosis for rectal cancer: does leakage location matter? Colorectal Dis. 2018;. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Hughes DL, Cornish J, Morris C; LARRIS Trial Management Group. Functional outcome following rectal surgery-predisposing factors for low anterior resection syndrome. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2017;32:691-697. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 109] [Article Influence: 13.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Hupkens BJP, Breukink SO, Olde Reuver Of Briel C, Tanis PJ, de Noo ME, van Duijvendijk P, van Westreenen HL, Dekker JWT, Chen TYT, Juul T. Dutch validation of the low anterior resection syndrome score. Colorectal Dis. 2018;20:881-887. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Ihnát P, Vávra P, Prokop J, Pelikán A, Ihnát Rudinská L, Penka I. Functional outcome of low rectal resection evaluated by anorectal manometry. ANZ J Surg. 2018;88:E512-E516. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | van Heinsbergen M, den Haan N, Maaskant-Braat AJ, Melenhorst J, Belgers EH, Leijtens JW, Bloemen JG, Rutten HJ, Bouvy ND, Janssen-Heijnen ML, Konsten JL. Functional bowel complaints and quality of life after surgery for colon cancer: prevalence and predictive factors. Colorectal Dis. 2020;22:136-145. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 40] [Article Influence: 8.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Bondeven P, Emmertsen KJ, Laurberg S, Pedersen BG. Neoadjuvant therapy abolishes the functional benefits of a larger rectal remnant, as measured by magnetic resonance imaging after restorative rectal cancer surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2015;41:1493-1499. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Chen TY, Wiltink LM, Nout RA, Meershoek-Klein Kranenbarg E, Laurberg S, Marijnen CA, van de Velde CJ. Bowel function 14 years after preoperative short-course radiotherapy and total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer: report of a multicenter randomized trial. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2015;14:106-114. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 156] [Cited by in RCA: 222] [Article Influence: 20.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Cura Pales CG, An S, Cruz JP, Kim K, Kim Y. Postoperative Bowel Function After Anal Sphincter-Preserving Rectal Cancer Surgery: Risks Factors, Diagnostic Modalities, and Management. Ann Coloproctol. 2019;35:160-166. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Haak HE, Maas M, Lambregts DMJ, Beets-Tan RGH, Beets GL; Dutch Watch-and-Wait Consortium. Is watch and wait a safe and effective way to treat rectal cancer in older patients? Eur J Surg Oncol. 2020;46:358-362. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | van Heinsbergen M, Leijtens JW, Slooter GD, Janssen-Heijnen ML, Konsten JL. Quality of Life and Bowel Dysfunction after Transanal Endoscopic Microsurgery for Rectal Cancer: One Third of Patients Experience Major Low Anterior Resection Syndrome. Dig Surg. 2020;37:39-46. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Huisman JF, van Westreenen HL, van der Wouden EJ, Vasen HFA, de Graaf EJR, Doornebosch PG, Tang TJ, Schot I, Brohet RM, de Vos Tot Nederveen Cappel WH, Vermaas M. Effectiveness of endosponge therapy for the management of presacral abscesses following rectal surgery. Tech Coloproctol. 2019;23:551-557. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Hupkens BJP, Martens MH, Stoot JH, Berbee M, Melenhorst J, Beets-Tan RG, Beets GL, Breukink SO. Quality of Life in Rectal Cancer Patients After Chemoradiation: Watch-and-Wait Policy Versus Standard Resection - A Matched-Controlled Study. Dis Colon Rectum. 2017;60:1032-1040. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 131] [Cited by in RCA: 185] [Article Influence: 23.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | van der Heijden JAG, Thomas G, Caers F, van Dijk WA, Slooter GD, Maaskant-Braat AJG. What you should know about the low anterior resection syndrome - Clinical recommendations from a patient perspective. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44:1331-1337. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 2.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Ziv Y, Zbar A, Bar-Shavit Y, Igov I. Low anterior resection syndrome (LARS): cause and effect and reconstructive considerations. Tech Coloproctol. 2013;17:151-162. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 80] [Cited by in RCA: 100] [Article Influence: 7.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Błaszkowski T, Kładny J, Al-Amawi T, Kaczmarek K, Kwietniak M, Wojtasik P, Halczak M, Michalak T, Jezierski K, Chmialak M. Factors determining the quality of life in patients undergoing radical surgery due to malignant tumors of the rectum. Pol Przegl Chir. 2021;93:1-5. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Nekliudov NA, Tsarkov PV, Tulina IA. Uni-center, patient-blinded, randomized, 12-month, parallel group, noninferiority study to compare outcomes of 3-row vs 2-row circular staplers for colorectal anastomosis formation after low anterior resection for rectal cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98:e15978. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Ameri H, Yousefi M, Yaseri M, Nahvijou A, Arab M, Akbari Sari A. Mapping EORTC-QLQ-C30 and QLQ-CR29 onto EQ-5D-5L in Colorectal Cancer Patients. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2020;51:196-203. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Janavikula Sankaran R, Kollapalayam Raman D, Raju P, Syed A, Rajkumar A, Aluru JR, Nazeer N, Rajkumar S, Kj J. Laparoscopic Ultra Low Anterior Resection: Single Center, 6-Year Study. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2020;30:284-291. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Foo CC, Kin Ng K, Tsang JS, Siu-Hung Lo O, Wei R, Yip J, Lun Law W. Low Anterior Resection Syndrome After Transanal Total Mesorectal Excision: A Comparison With the Conventional Top-to-Bottom Approach. Dis Colon Rectum. 2020;63:497-503. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Sun G, Lou Z, Zhang H, Yu GY, Zheng K, Gao XH, Meng RG, Gong HF, Furnée EJB, Bai CG, Zhang W. Retrospective study of the functional and oncological outcomes of conformal sphincter preservation operation in the treatment of very low rectal cancer. Tech Coloproctol. 2020;24:1025-1034. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Kadota T, Ikematsu H, Sasaki T, Saito Y, Ito M, Mizutani T, Ogawa G, Shitara K, Ito Y, Kushima R, Kanemitsu Y, Muto M. Protocol for a single-arm confirmatory trial of adjuvant chemoradiation for patients with high-risk rectal submucosal invasive cancer after local resection: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG1612 (RESCUE study). BMJ Open. 2020;10:e034947. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Lee KH, Kim JY, Sul YH. Colorectal Perforation After Anorectal Manometry for Low Anterior Resection Syndrome. Ann Coloproctol. 2017;33:146-149. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Liapi A, Mavrantonis C, Lazaridis P, Kourkouni E, Zevlas A, Zografos G, Theodoropoulos G. Validation and comparative assessment of low anterior resection syndrome questionnaires in Greek rectal cancer patients. Ann Gastroenterol. 2019;32:185-192. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Keane C, Sharma P, Yuan L, Bissett I, O'Grady G. Impact of temporary ileostomy on long-term quality of life and bowel function: a systematic review and meta-analysis. ANZ J Surg. 2020;90:687-692. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 9.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Keller DS, Lawrence JK, Delaney CP. Laparoscopic low anterior resection in a patient with Lynch syndrome and previous right hemicolectomy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2013;56:263. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Sturiale A, Martellucci J, Zurli L, Vaccaro C, Brusciano L, Limongelli P, Docimo L, Valeri A. Long-term functional follow-up after anterior rectal resection for cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2017;32:83-88. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 115] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 12.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Liu F, Guo P, Shen Z, Gao Z, Wang S, Ye Y. [Risk factor analysis of low anterior resection syndrome after anal sphincter preserving surgery for rectal carcinoma]. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017;20:289-294. [PubMed] |