Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Aug 27, 2022; 14(8): 731-742
Published online Aug 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i8.731
Published online Aug 27, 2022. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i8.731
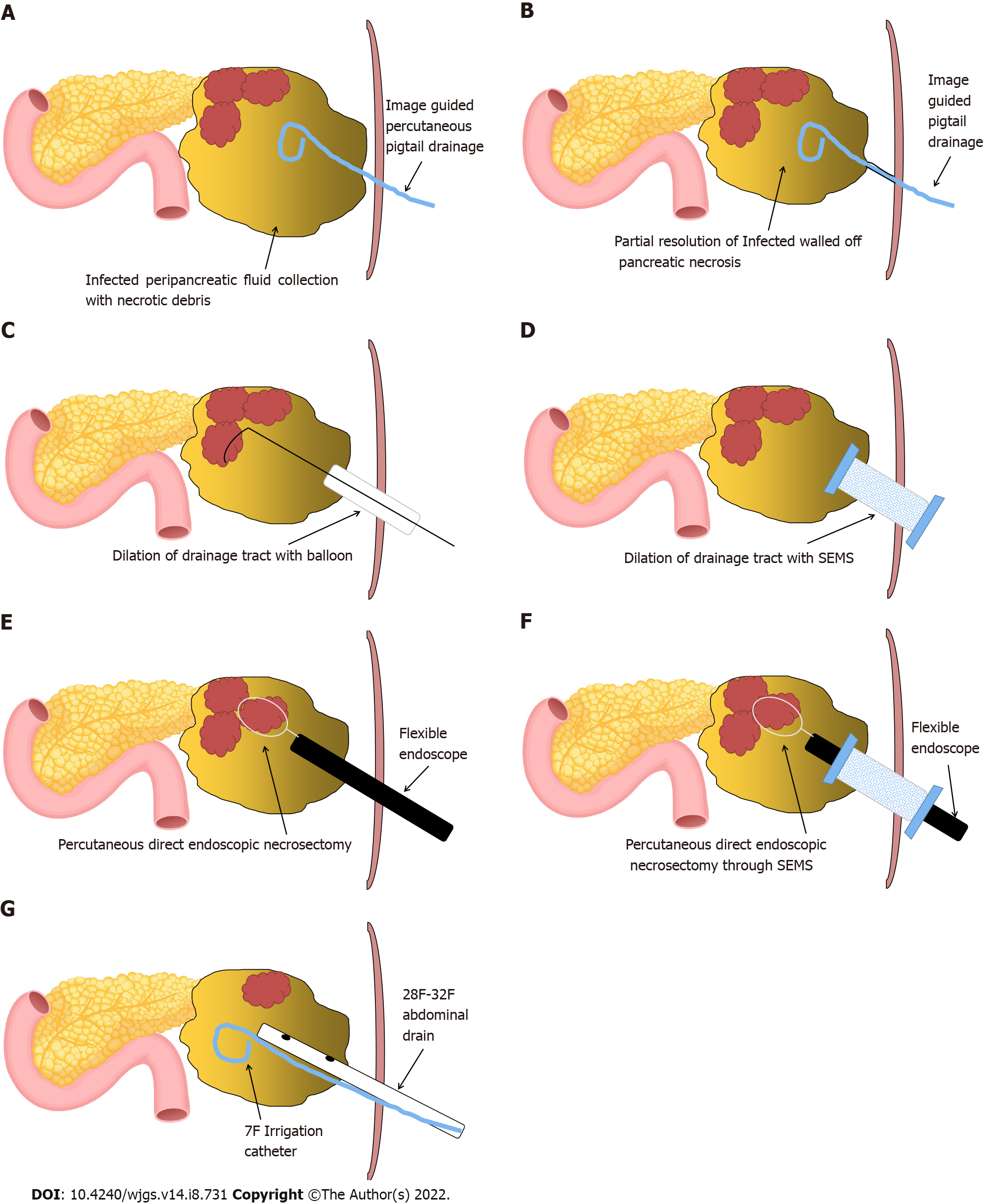
Figure 1 Schematic representation of steps involved in percutaneous direct endoscopic necrosectomy.
A: Image-guided pigtail drainage of infected pancreatic/peripancreatic collection; B: Partial resolution of infected walled off pancreatic necrosis (WOPN) with maturation of drainage tract between the skin and WOPN (usually 7-10 d approximately); C and D: Drainage tract dilation with (C) wire-guided controlled radial expansion balloon or (D) an esophageal fully covered self-expandable metal stent (SEMS); E and F: Percutaneous direct endoscopic necrosectomy with flexible endoscope through (E) the dilated tract or (F) a fully covered SEMS; G: Placement of large bore abdominal drain and irrigation catheter for drainage and irrigation of WOPN cavity, respectively.
- Citation: Vyawahare MA, Gulghane S, Titarmare R, Bawankar T, Mudaliar P, Naikwade R, Timane JM. Percutaneous direct endoscopic pancreatic necrosectomy. World J Gastrointest Surg 2022; 14(8): 731-742
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v14/i8/731.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v14.i8.731