Published online Feb 27, 2019. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v11.i2.112
Peer-review started: January 27, 2019
First decision: February 19, 2019
Revised: February 21, 2019
Accepted: February 21, 2019
Article in press: February 22, 2019
Published online: February 27, 2019
Processing time: 31 Days and 8.3 Hours
Esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction (EGJOO) is a rare syndrome, characterized by an elevation of the integrated relaxation pressure of the lower esophageal sphincter, not accompanied by alterations in esophageal motility that may lead to the criteria for achalasia. We were unable to find any prior report of the combination of Heller myotomy with anterior partial fundoplication (Dor) as the treatment for EGJOO. We herein report a case of EGJOO treated with laparoscopic Heller myotomy combined with Dor fundoplication.
A 26-year-old man presented with a 3-year history of solid dysphagia and a 30-kg weight loss. He was treated with oral nifedipine, isosorbide, and omeprazole, without resolution of symptoms. An upper gastrointestinal series (barium swallow) revealed a “bird’s beak” sign. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy was positive for Los Angeles grade A peptic esophagitis. High-resolution esophageal manometry was compatible with EGJOO. Esophageal pH monitoring showed pathological acid reflux both in orthostatic and decubitus position. An 8-cm laparoscopic Heller myotomy combined with an anterior 220° Dor fundoplication was performed. Solid diet was introduced on postoperative day 2, and the patient was discharged home the same day. At 17-mo follow-up, he reported no symptoms. Barium swallow was compatible with complete radiologic resolution. Both esophageal manometry and upper endoscopy showed normal findings 9 mo after the operation.
Surgical treatment with Heller myotomy and Dor fundoplication is a potential treatment option for EGJOO refractory to medical treatment.
Core tip: Esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction (EGJOO) is a rare syndrome, characterized by an elevation of the integrated relaxation pressure of the lower esophageal sphincter, not accompanied by alterations in esophageal motility that may lead to the criteria for achalasia. Surgical treatment of EGJOO is very rarely considered and very few cases have been reported in the medical literature. We herein report the first case of EGJOO successfully treated with laparoscopic Heller myotomy combined with Dor fundoplication.
- Citation: Pereira PF, Rosa AR, Mesquita LA, Anzolch MJ, Branchi RN, Giongo AL, Paixão FC, Chedid MF, Kruel CD. Esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction successfully treated with laparoscopic Heller myotomy and Dor fundoplication: First case report in the literature. World J Gastrointest Surg 2019; 11(2): 112-116
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v11/i2/112.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v11.i2.112
Esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction (EGJOO) is a rare syndrome, characterized by an elevation of the integrated relaxation pressure of the lower esophageal sphincter, not accompanied by alterations in esophageal motility that may lead to the criteria for achalasia[1]. In a recent study, of the 1000 patients meeting the criteria for evaluation by esophageal pressure topography, only 8 were diagnosed with EGJOO[2].
The main clinical manifestations of EGJOO are dysphagia, chest pain, or both. Because the symptoms may resolve without intervention in up to 40% of cases, a waiting period between diagnosis and initiation of treatment is recommended[3]. Oral calcium-channel blockers are the treatment of choice, but botulinum toxin injections may also be employed. Further therapeutic options include endoscopic treatment, such as dilation and endoscopic myotomy[1,3]. In only a minority of patients EGJOO may progress to achalasia[1].
According to a recent expert consensus document on the management of esophageal motility disorders, surgical treatment of EGJOO is not an option.3 Therefore, surgical treatment of EGJOO is very rarely considered and very few cases have been reported in the medical literature[2,4]. Although a few cases using laparoscopic Heller myotomy for the treatment of EGJOO have been reported[1], we did not find any prior report of the combination of Heller myotomy with anterior partial fundoplication (Dor fundoplication) for the treatment of EGJOO[3]. We herein report a case of EGJOO treated with laparoscopic Heller myotomy combined with Dor fundoplication.
A 26-year-old man presented with a 3-year history of solid dysphagia and a 30-kg weight loss. He also complained of heartburn and regurgitation, especially at night.
The patient was referred to the outpatient clinic and treated with oral nifedipine, isosorbide, and omeprazole, without resolution of symptoms.
The history of past illness was unremarkable.
The personal and family history was negative for gastrointestinal and endocrine disease.
The Physical examination upon admission revealed a thin patient. No lumps or abdominal tumors were detected.
Routine blood tests, routine urine tests and urinary sediment examination, routine fecal tests and occult blood test, blood biochemistry, immune indexes, and infection indexes – all were within normal limits.
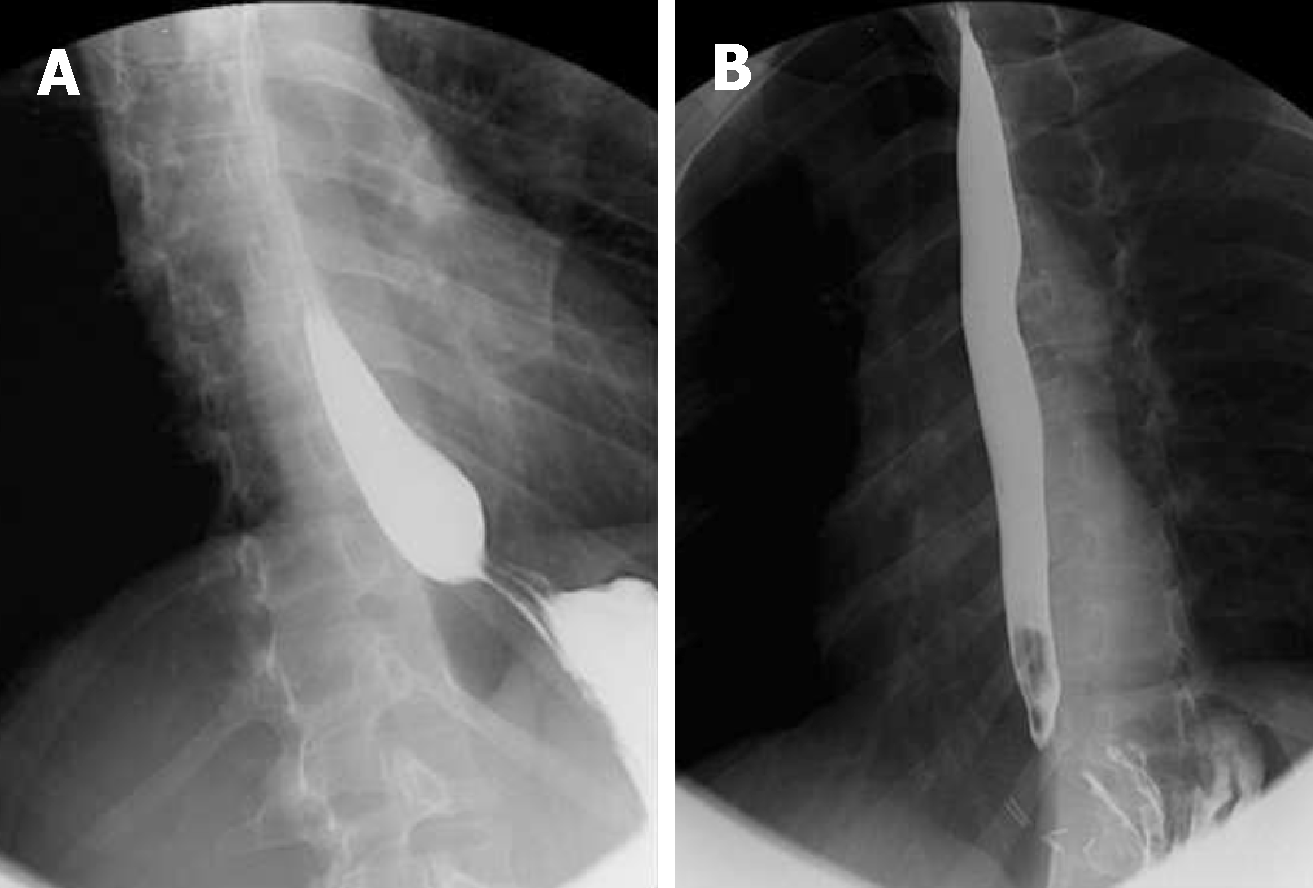
An upper gastrointestinal series (barium swallow) revealed a “bird’s beak” sign (Figure 1A).
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy was positive for Los Angeles grade A peptic esophagitis. High-resolution esophageal manometry revealed an integrated relaxation pressure of 28 mm Hg, with incomplete relaxation and normal esophageal peristalsis (100% peristaltic waves), compatible with EGJOO (Table 1). Esophageal pH monitoring showed pathological acid reflux both in orthostatic and decubitus position.
| Normal values | Patient values | |
| Lower esophageal sphincter | ||
| Localization | 47.1 - 44.1 | |
| Resting pressure (mmHg) | 10-45 | 46.7 |
| Residual pressure (mmHg) | < 8 | 15.4 |
| Integrated relaxation pressure(mmHg) | < 15 | 28 |
| Relaxation | Complete | Incomplete |
| EGJ length (cm) | 3-5 | 3 |
| Esophageal body | ||
| Peristaltic waves (%) | 80 - 100 | 100 |
| Distal latency (s) | > 4.5 | 10.0 |
| Distal contractile Integral (mmHg/s/cm) | 450 – 5000 | 5948 |
An 8-cm laparoscopic Heller myotomy combined with an anterior 220° Dor fundoplication was performed. Liquid diet was introduced on postoperative day 1. The patient was started on a solid diet on postoperative day 2 and discharged home the same day.
At the 17-mo follow-up visit, the patient reported no regurgitation and complete resolution of symptoms. A repeat barium swallow revealed no gastroesophageal obstruction and no esophageal dilation, compatible with complete radiologic resolution (Figure 1B).
Nine months after the operation, both a repeat endoscopy and an esophageal manometry showed normal findings (Table 2).
| Normal values | Patient values | |
| Lower esophageal sphincter | ||
| Localization | 48-44 | |
| Resting pressure (mmHg) | 10-45 | 7.1 |
| Residual pressure (mmHg) | < 8 | - 4 |
| Relaxation | Completo | Complete |
| EGJ length (cm) | 3-5 | 4 |
| Esophageal body | ||
| Peristaltic waves (%) | 80-100 | 100 |
Surgical treatment of EGJOO is controversial[5]. Three cases of successful Heller myotomy were reported by Scherer et al[2]. Recently, Lin et al[4] reported a successful robotic-assisted thoracoscopic esophageal myotomy and Belsey-Mark IV fundoplication. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no prior published report of the combination of Heller myotomy with anterior partial fundoplication as the treatment for EGJOO.
Heller myotomy alone appears to be associated with symptomatic acid reflux in patients with achalasia. Conversely, the combination of complete (Nissen) fun-doplication with Heller myotomy may predispose patients to post-fundoplication lower dysphagia. Furthermore, post-fundoplication dysphagia has been shown to resolve in parallel with the reduction of intrabolus pressure following conversion to partial fundoplication[5]. In view of these observations, our Division has used Heller myotomy associated with anterior partial fundoplication as the standard treatment for achalasia refractory to endoscopic treatment. Therefore, the same treatment was employed in this case for the treatment of EGJOO refractory to medical and endoscopic treatment.
Surgical treatment with Heller myotomy and Dor fundoplication provides a potential option for the treatment of EGJOO refractory to medical treatment.
Manuscript source: Invited manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country of origin: Brazil
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P- Reviewer: Arda I, Rubbini M S- Editor: Wang JL L- Editor: A E- Editor: Wu YXJ
| 1. | Kahrilas PJ, Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, Gyawali CP, Roman S, Smout AJ, Pandolfino JE; International High Resolution Manometry Working Group. The Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;27:160-174. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1373] [Cited by in RCA: 1443] [Article Influence: 144.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Scherer JR, Kwiatek MA, Soper NJ, Pandolfino JE, Kahrilas PJ. Functional esophagogastric junction obstruction with intact peristalsis: a heterogeneous syndrome sometimes akin to achalasia. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009;13:2219-2225. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 172] [Cited by in RCA: 147] [Article Influence: 9.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Kahrilas PJ, Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, Gyawali CP, Roman S, Smout AJPM, Pandolfino JE; International Working Group for Disorders of Gastrointestinal Motility and Function. Expert consensus document: Advances in the management of oesophageal motility disorders in the era of high-resolution manometry: a focus on achalasia syndromes. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14:677-688. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 60] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 7.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Lin KH, Lee SC, Huang TW, Huang HK. Esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction-related functional chest pain treated using robotic-assisted thoracoscopic esophageal myotomy. J Thorac Dis. 2017;9:E432-E436. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Teitelbaum EN, Dunst CM, Reavis KM, Sharata AM, Ward MA, DeMeester SR, Swanström LL. Clinical outcomes five years after POEM for treatment of primary esophageal motility disorders. Surg Endosc. 2018;32:421-427. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 91] [Cited by in RCA: 91] [Article Influence: 11.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |