Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jan 27, 2016; 8(1): 41-51
Published online Jan 27, 2016. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v8.i1.41
Published online Jan 27, 2016. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v8.i1.41
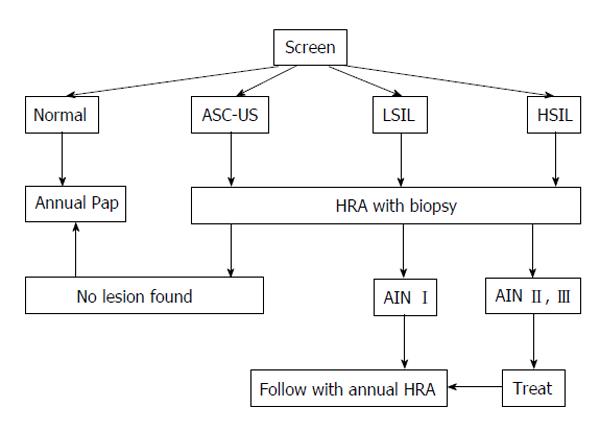
Figure 1 San Francisco algorithm for anal cancer screening of high-risk patients.
ASC-US: Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance; LSIL: Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions; HSIL: High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions; Pap: Papanicolaou; HRA: High-resolution anoscopy; AIN: Anal intraepithelial neoplasia (adopted from Chin Hong, Palefsky. Clin Inf Dis 2002).
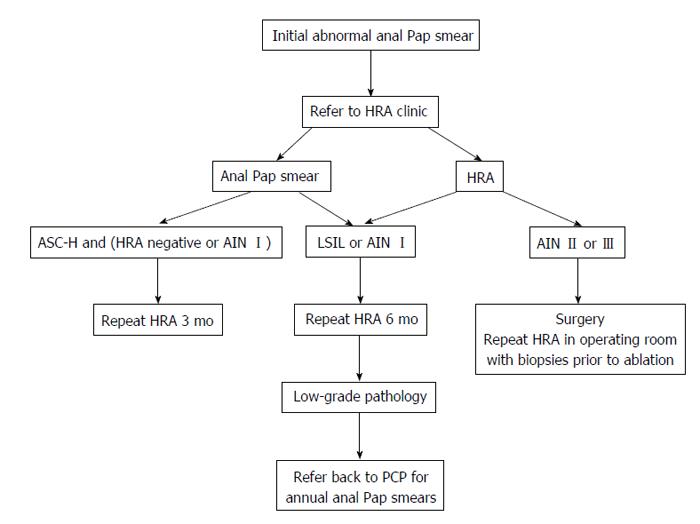
Figure 2 Johns Hopkins Hospital algorithm for anal cancer screening of high-risk patients.
Pap: Papanicolaou; HRA: High-resolution anoscopy; ASC-H: Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance, cannot rule-out high-grade dysplasia; AIN I: Anal intraepithelial neoplasia I; PCP: Primary care physician; LSIL: Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; AIN II: Anal intraepithelial neoplasia II; AIN III: Anal intraepithelial neoplasia III.
- Citation: Leeds IL, Fang SH. Anal cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia screening: A review. World J Gastrointest Surg 2016; 8(1): 41-51
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v8/i1/41.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v8.i1.41