Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jan 27, 2025; 17(1): 99495
Published online Jan 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.99495
Published online Jan 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.99495
Figure 1 Judging bile duct position in laparoscopic.
A: The bile ducts’ course and delineation can be clearly visualized; B: Detecting potential bile leakage after T-tube placement; C: Placing T-tube.
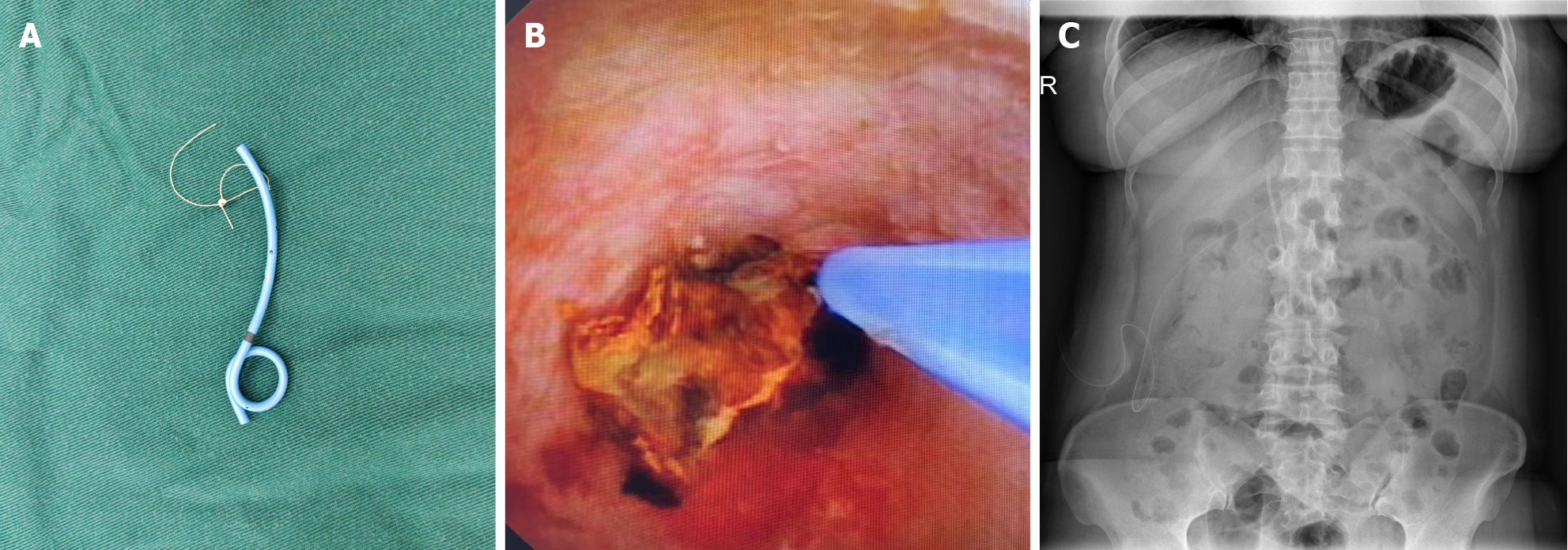
Figure 2 Placement and Positioning of the J Tube.
A: Homemade J-tube with a size 7 ureteral stent; B: Under the guidance of cholangioscopy, the J-tube is placed into the common bile duct; C: Postoperative review with drainage confirms the J-tube is in place.
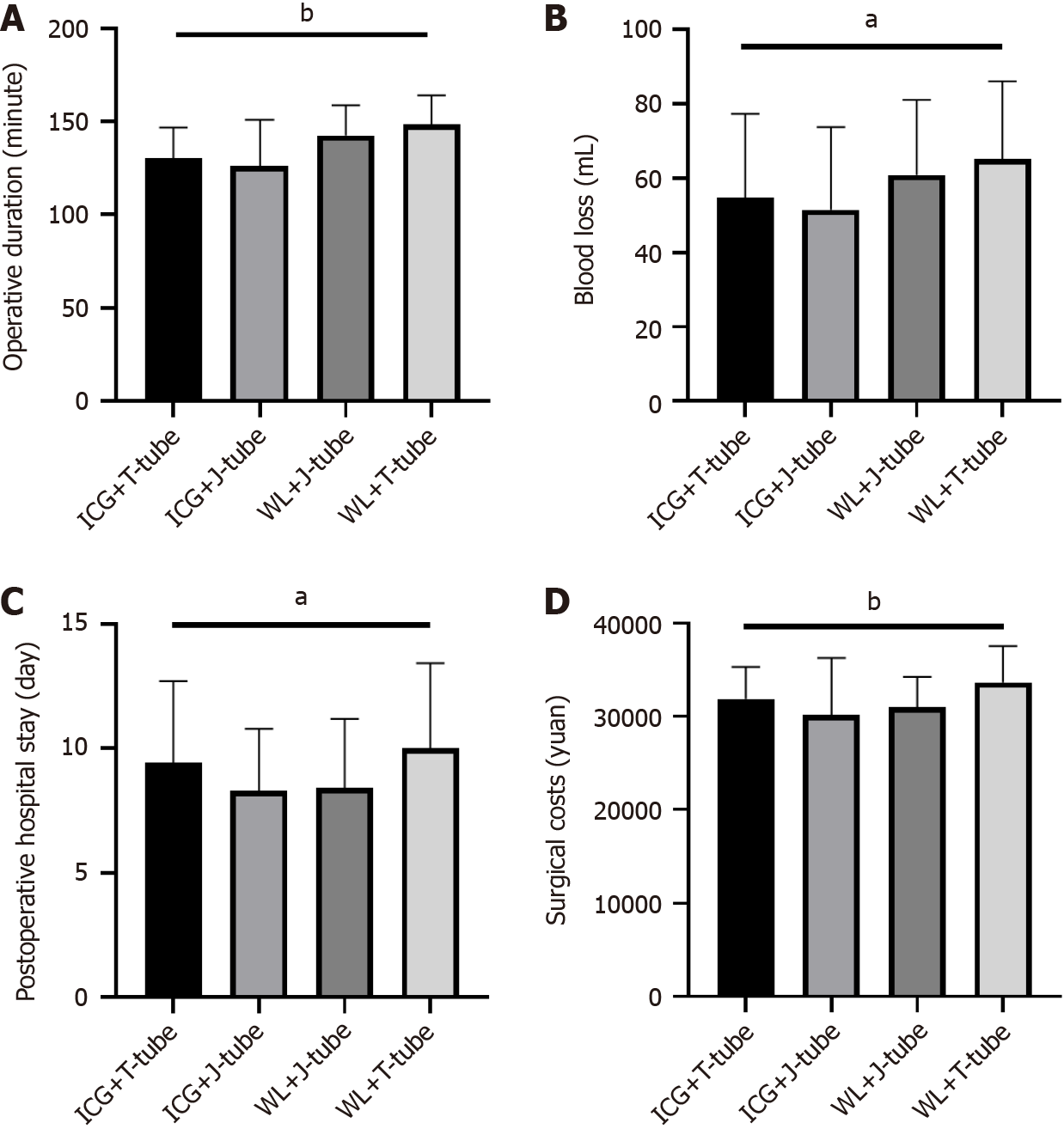
Figure 3 Comparison of surgery-related factors among four groups of patients.
A: Comparison of differences in surgery duration among four groups of patients; B: Comparison of differences in intraoperative blood loss among four groups of patients; C: The total surgery-related costs incurred during hospitalization among four groups of patients; D: The time elapsed from surgery completion to discharge among four groups of patients. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.005. WL: White light laparoscope; ICG: Indocyanine green.
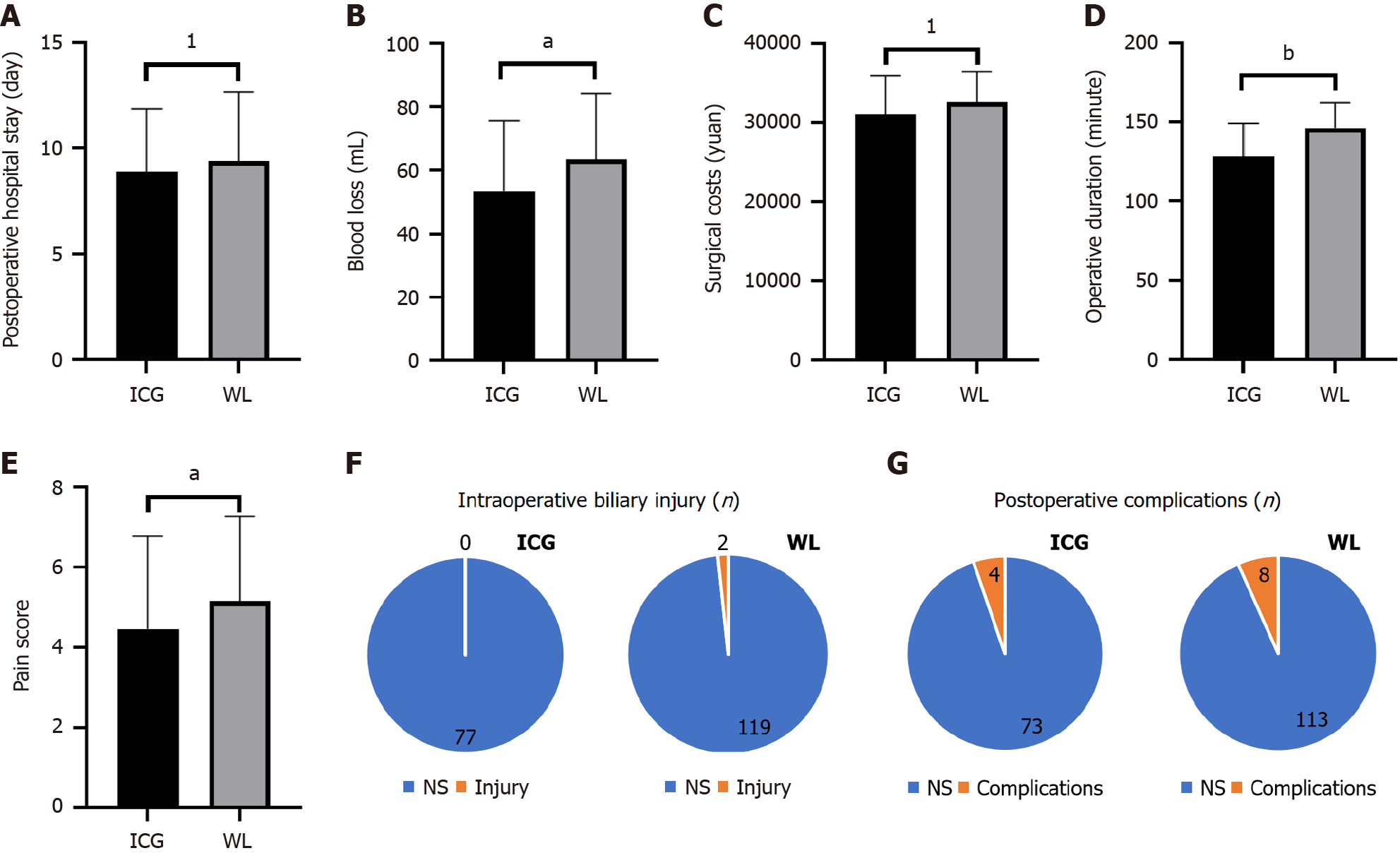
Figure 4 Comparison of intraoperative and postoperative factors between the indocyanine green and white light laparoscope groups.
A: Comparison of intraoperative blood loss between the two groups of patients; B: Comparison of surgical duration between the two groups of patients; C: Numerical rating scale pain scores on the first postoperative day; D: The time experienced by the two groups of patients from the end of surgery to discharge; E: Total costs incurred due to surgery during hospitalization for the two groups of patients; F: Statistics of intraoperative bile duct injuries in the two groups of patients; G: Statistics of postoperative complications in two groups of patients. 1P > 0.05. aP < 0.05. bP < 0.005. WL: White light laparoscope; ICG: Indocyanine green.
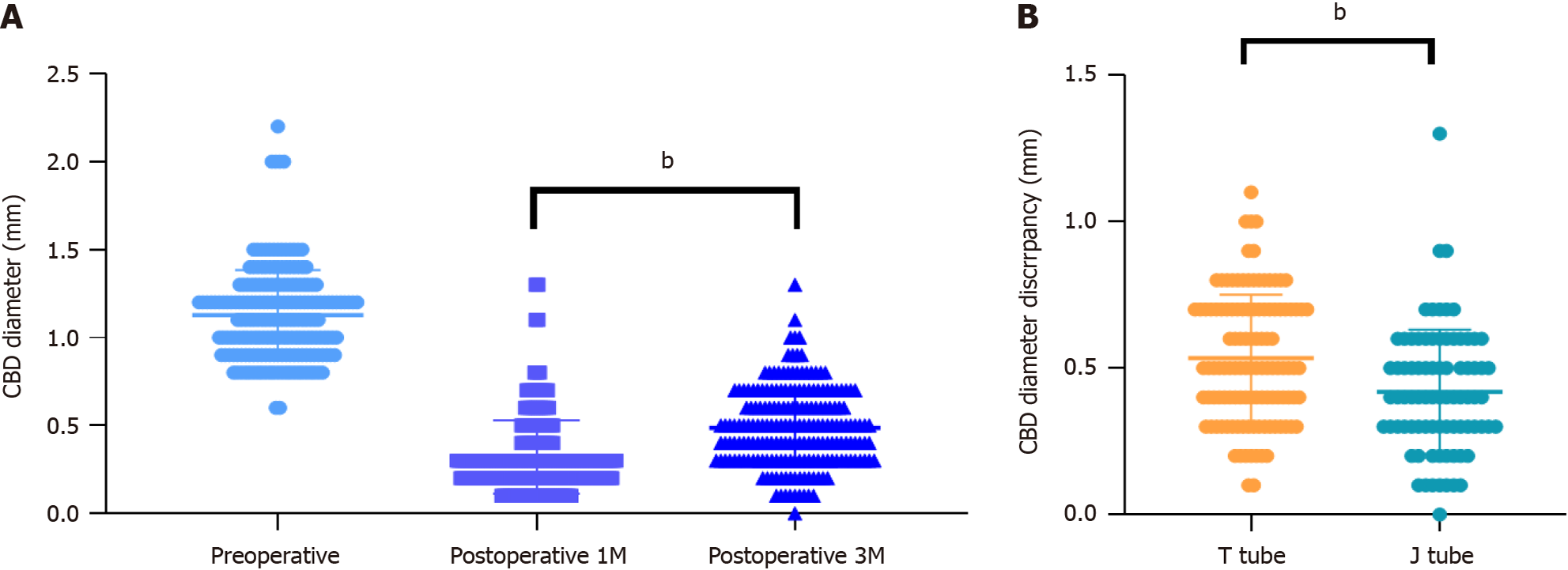
Figure 5 Advise the patient to regularly follow up on the degree of bile duct stricture after discharge.
A: Instruct the patient to come for an ultrasound follow-up in the first and third months after discharge, and compare the common bile duct diameter with the preoperative measurements to determine the changes in the diameter; B: The degree of common bile duct diameter change at the third month post-surgery is significantly different between the T-tube group and the J-tube group. bP < 0.005. M: Month; CBD: Common bile duct.
- Citation: Wang ZH, Yan S, Wang R, Chen L, Wu JZ, Cai WH. Clinical application of indocyanine green fluorescence imaging in laparoscopic cholecystectomy with common bile duct exploration and J-Tube drainage. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(1): 99495
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i1/99495.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.99495