Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jan 27, 2025; 17(1): 98891
Published online Jan 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.98891
Published online Jan 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.98891
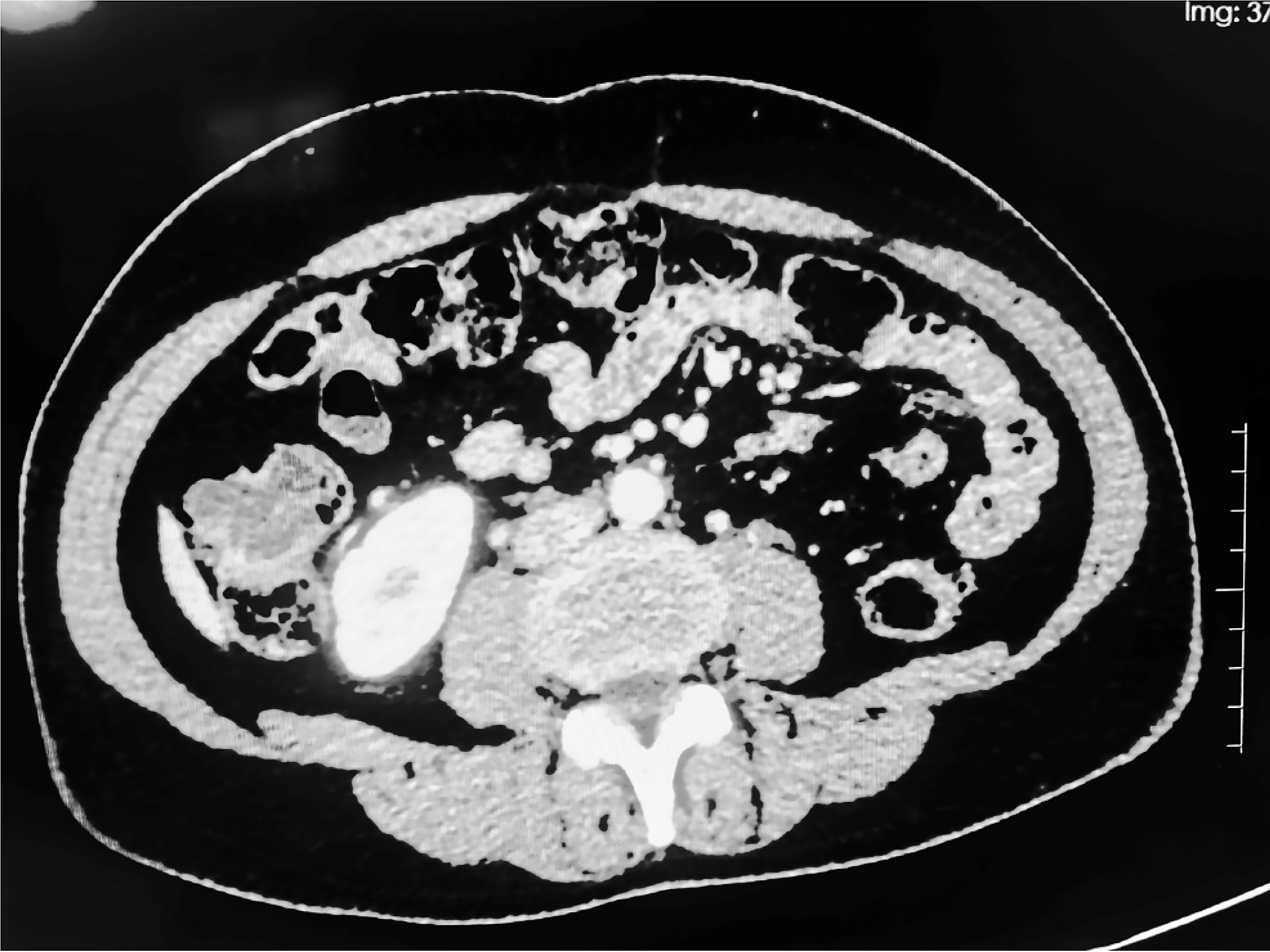
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography revealed localized cystic fluid low-density shadows in the ascending colon that were irregular in shape, with a maximum plane size of 2.
6 cm × 2.1 cm.
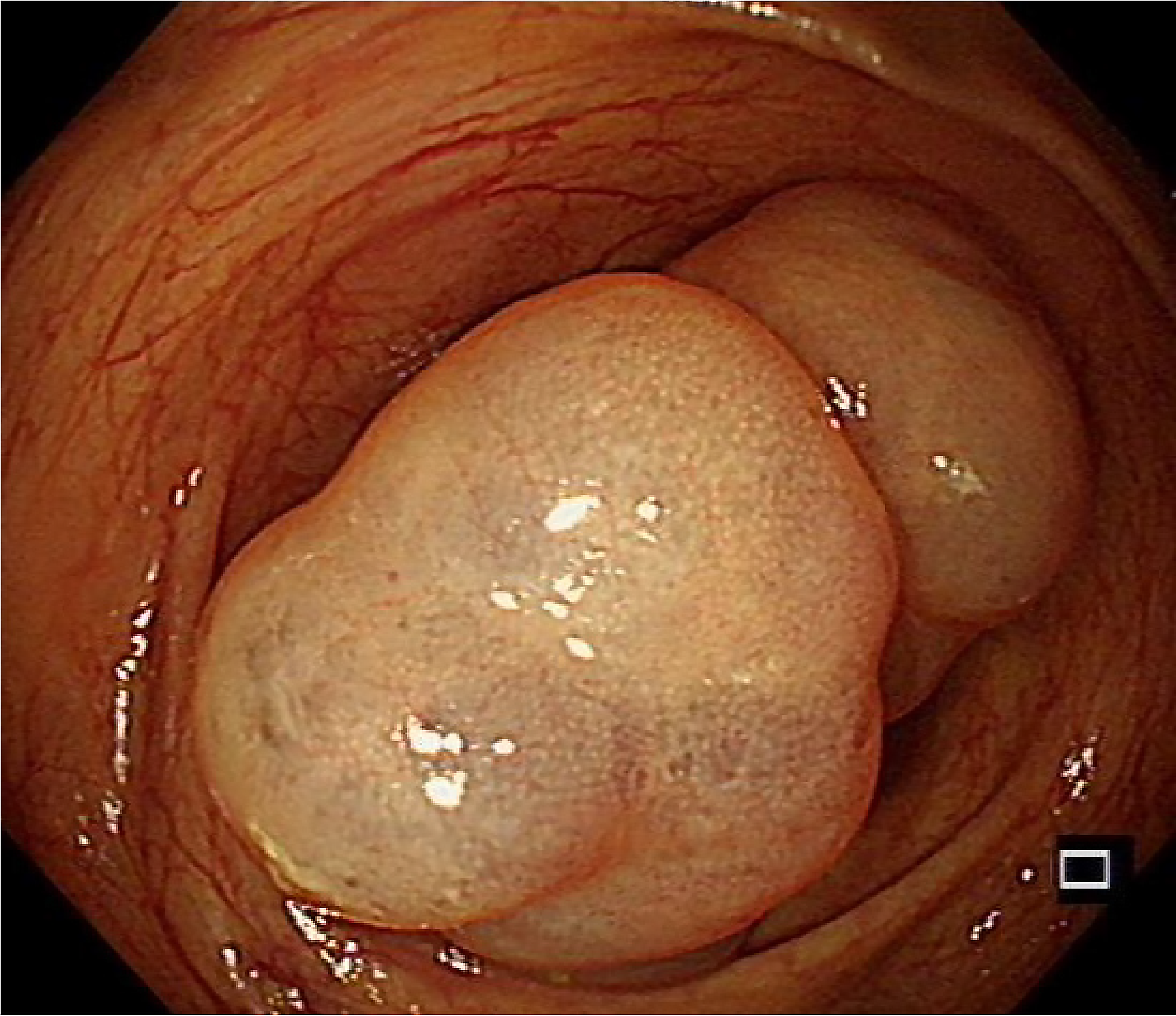
Figure 2
Two translucent ridges at the ascending colon under endoscopy.
Figure 3 The resection process and reexamination results of the lesion.
A-C: After the periphery of the lesion was marked with a dual knife, the edge was cut along the lateral side of the marker. The submucosal tissue was dissected and the lesion was completely dissected; D: No recurrence was observed during colonoscopy re-examination after 1 year.
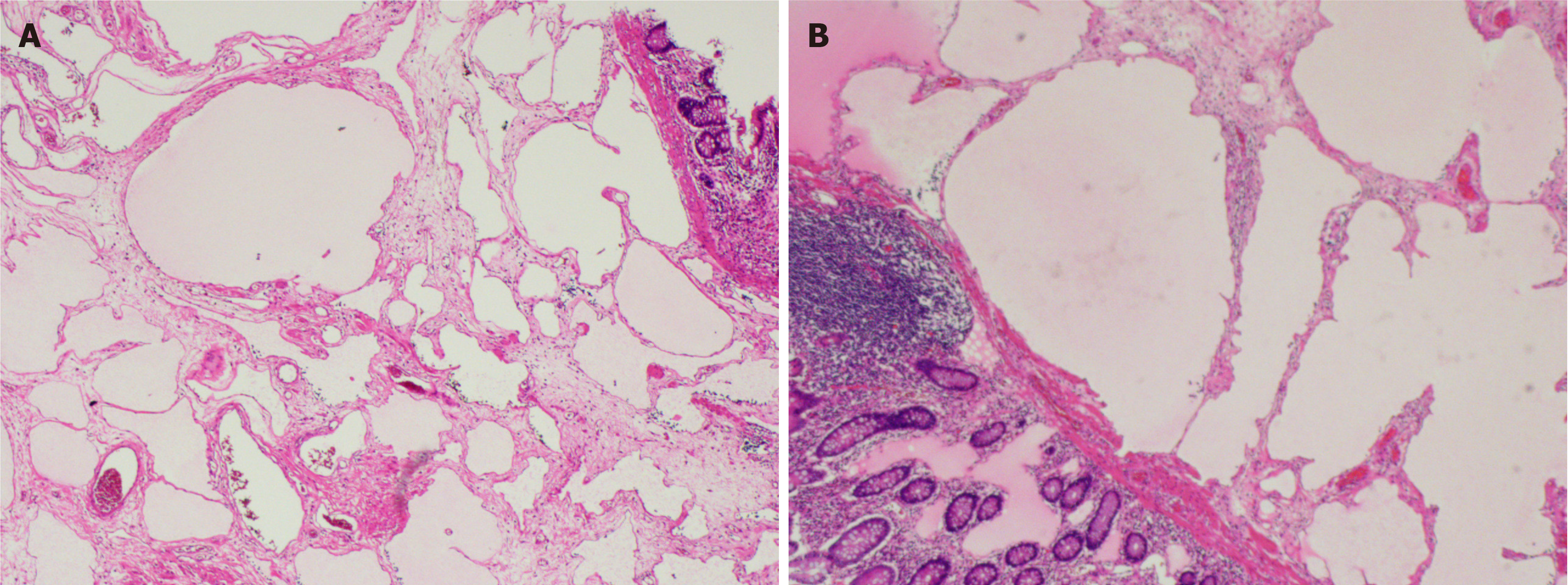
Figure 4 Histopathological results.
A and B: Pathological examination revealed multiple lymphatic cavities of different sizes lined with flat endothelial cells (hematoxylin and eosin × 100).
- Citation: Qu LW, Li QX, Zhu WY, Kang M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection in the treatment of adult cystic lymphangioma: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(1): 98891
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i1/98891.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i1.98891