Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Sep 27, 2024; 16(9): 2748-2754
Published online Sep 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i9.2748
Published online Sep 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i9.2748
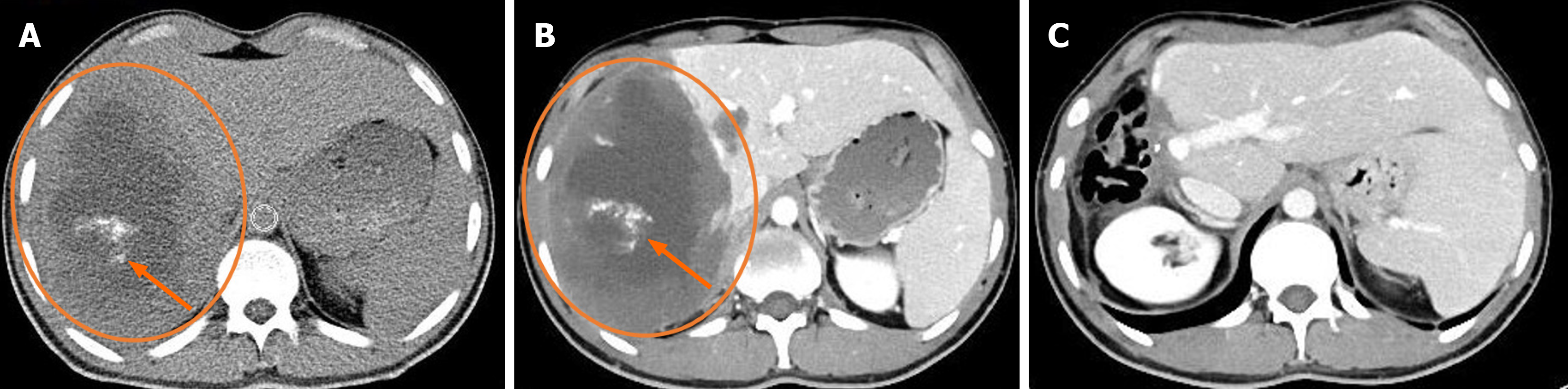
Figure 1 A solid mass lesion in the right lobe of the liver with macro calcification, large cystic-necrotic components and no significant contrast enhancement.
A: Non-contrast computed tomography (CT) (orange arrow); B: Hepatic venous phase CT (orange arrow); C: Treatment of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis with right hepatectomy.
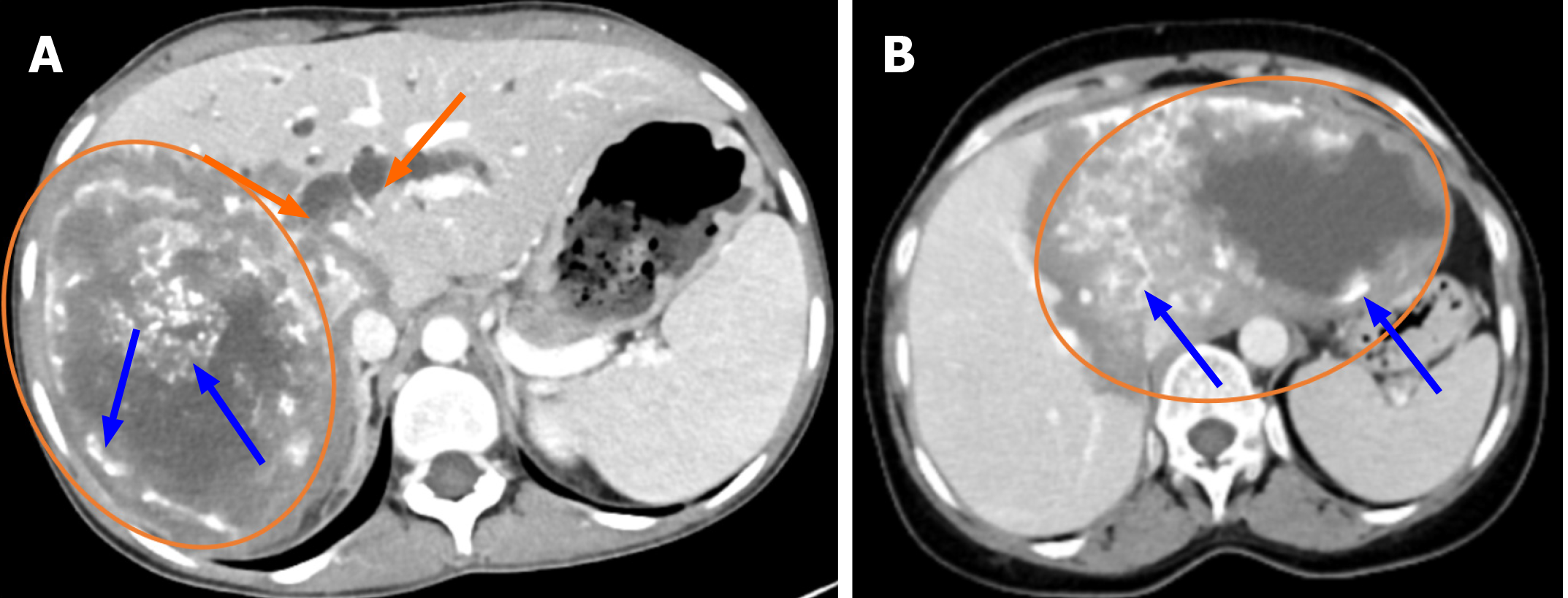
Figure 2 Hepatic venous phase contrast-enhanced computed tomography images.
A: Solid mass lesion in the right lobe of the liver with cystic-necrotic components and peripheral and central calcifications. Dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts is observed (orange arrow, blue arrow); B: Solid mass lesion with cystic-necrotic components, peripheral and central calcifications, filling the left lobe of the liver and extending to the right lobe (orange arrow, blue arrow).
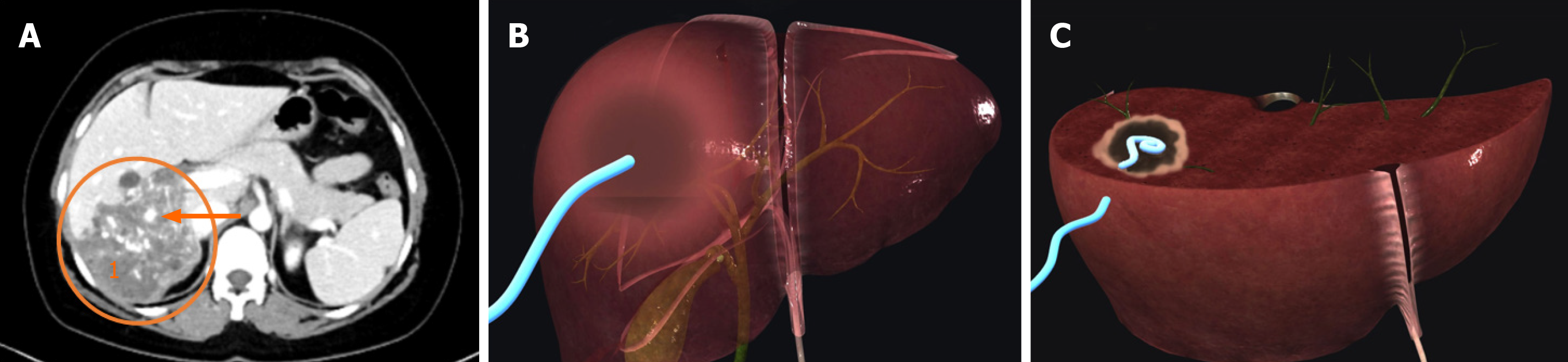
Figure 3 Application of a percutaneous drainage catheter to a lesion in the right lobe of the liver.
A: The right lobe of the liver shows a lesion (circle) with typical peripheral calcifications (arrows) and central necrosis1; B and C: 3D image in the coronal and axial planes showing the position of the percutaneous drainage catheter in the patient.
- Citation: Aydin S, Irgul B, Memis KB, Kızılgoz V, Kantarci M. Characteristics of the imaging diagnosis of alveolar echinococcosis. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(9): 2748-2754
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i9/2748.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i9.2748