Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jun 27, 2024; 16(6): 1939-1947
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1939
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1939
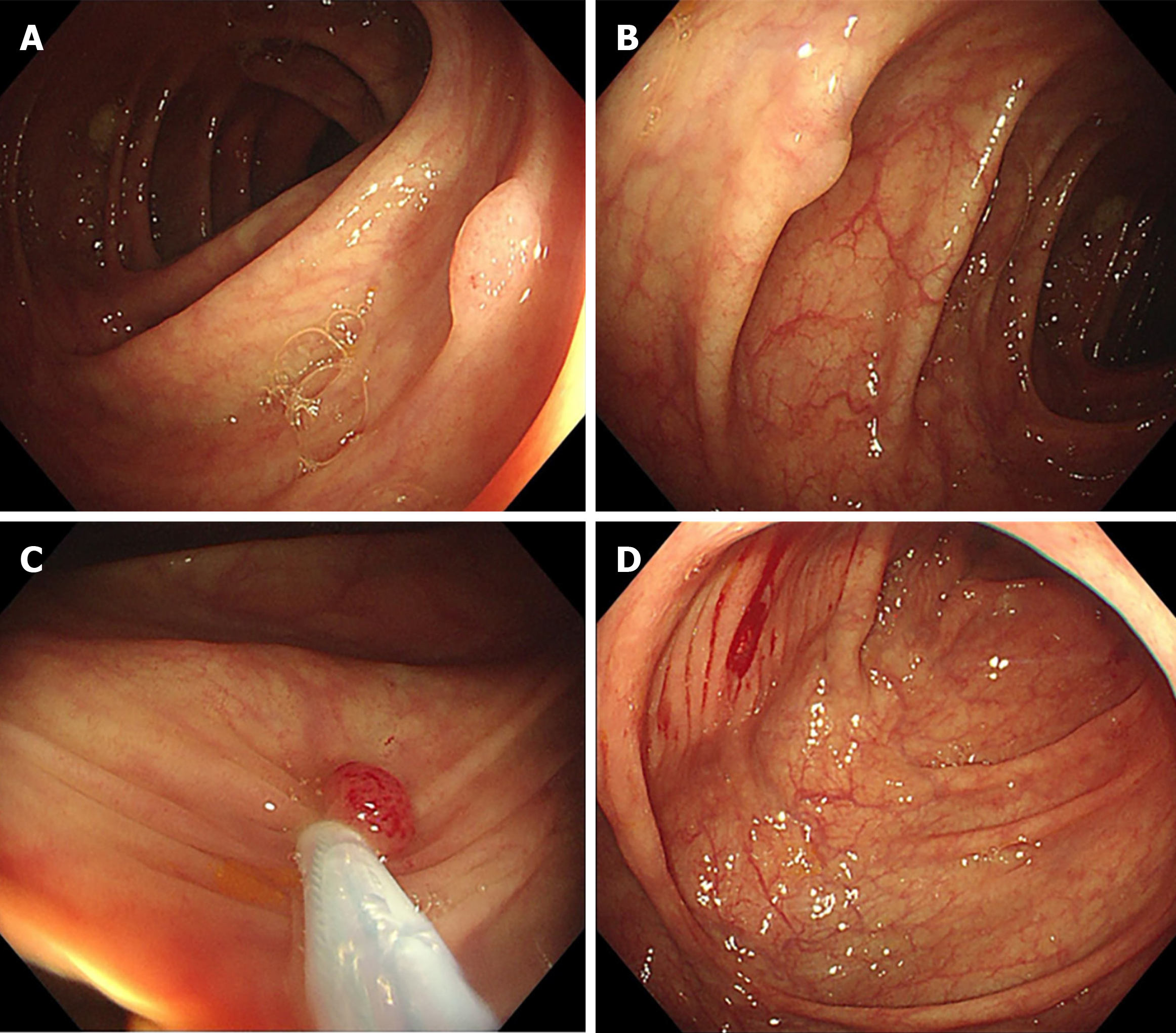
Figure 1 Images of initial colonoscopy of case 1.
A and B: Two polyps measuring 4-5 mm in the ascending colon near the hepatic flexure discovered during withdrawal; C: Polyp in Figure 1A removed by cold snare polypectomy (CSP); D: Post-polypectomy wound after CSP of the polyp in Figure 1B.
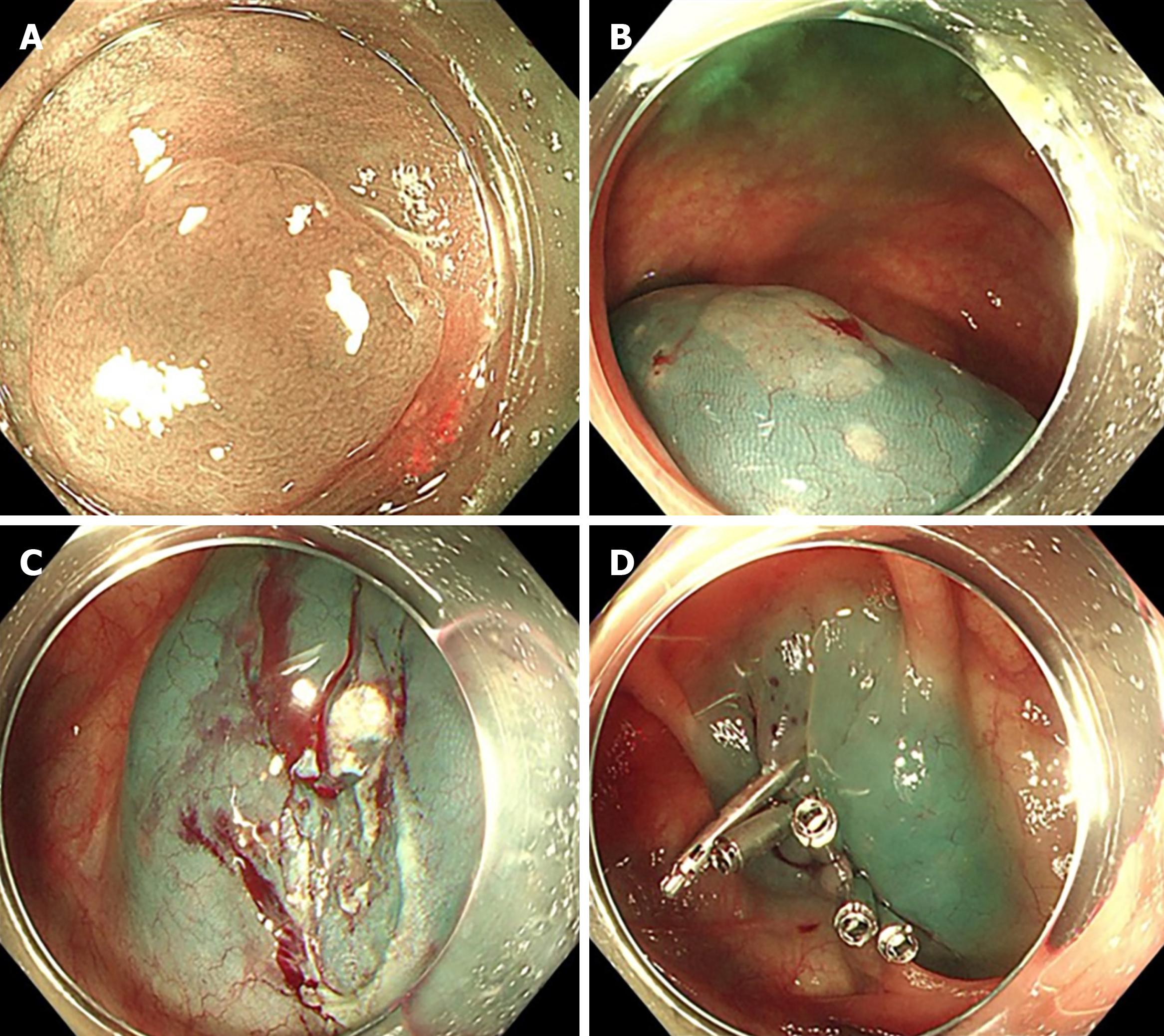
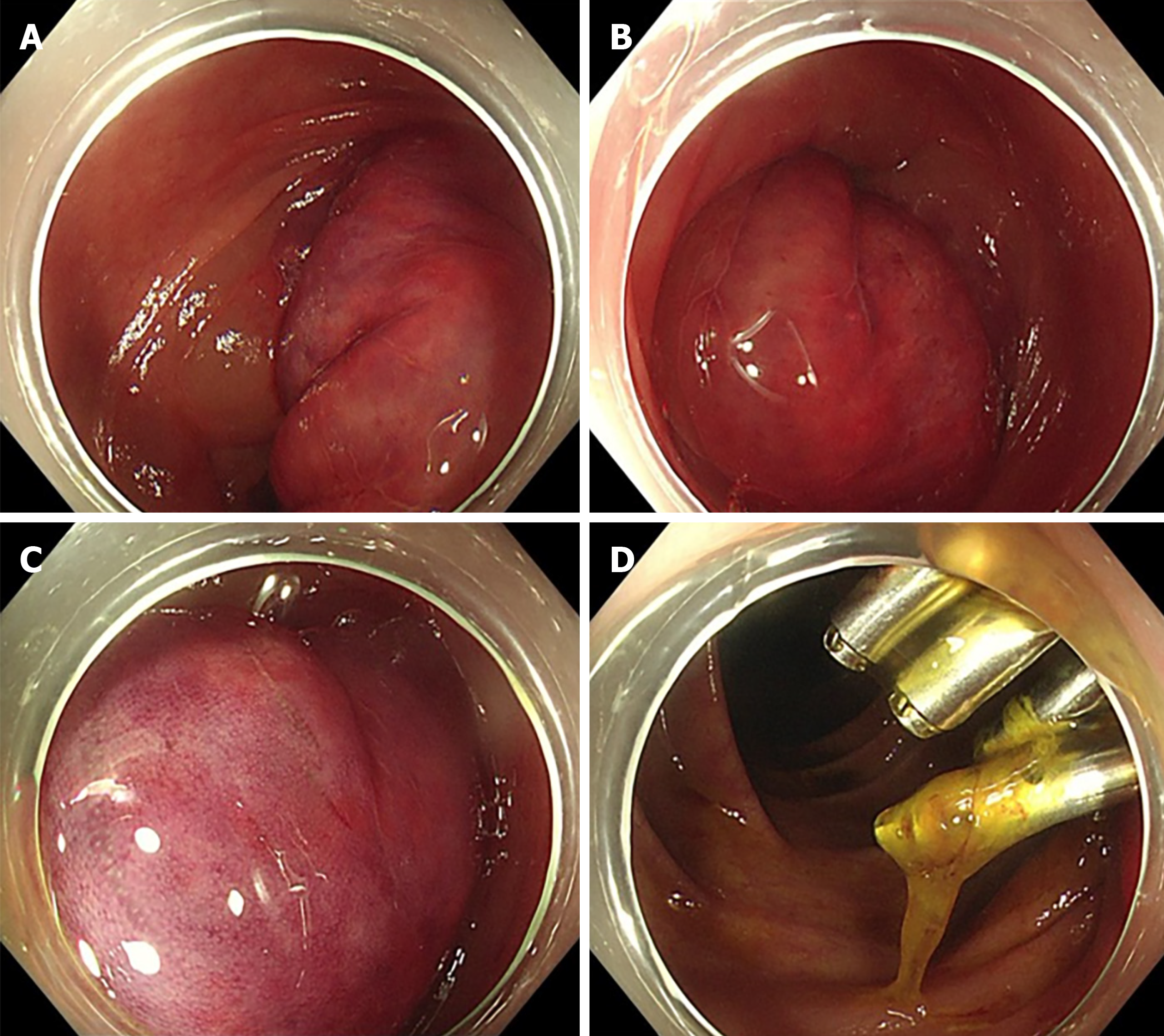
Figure 2 Images of initial colonoscopy of case 2.
A-C: A flat polyp measuring 12 mm discovered in the transverse colon near the hepatic flexure, and removed by endoscopic mucosal resection; D: The mucosal defect closed using five metal clips.
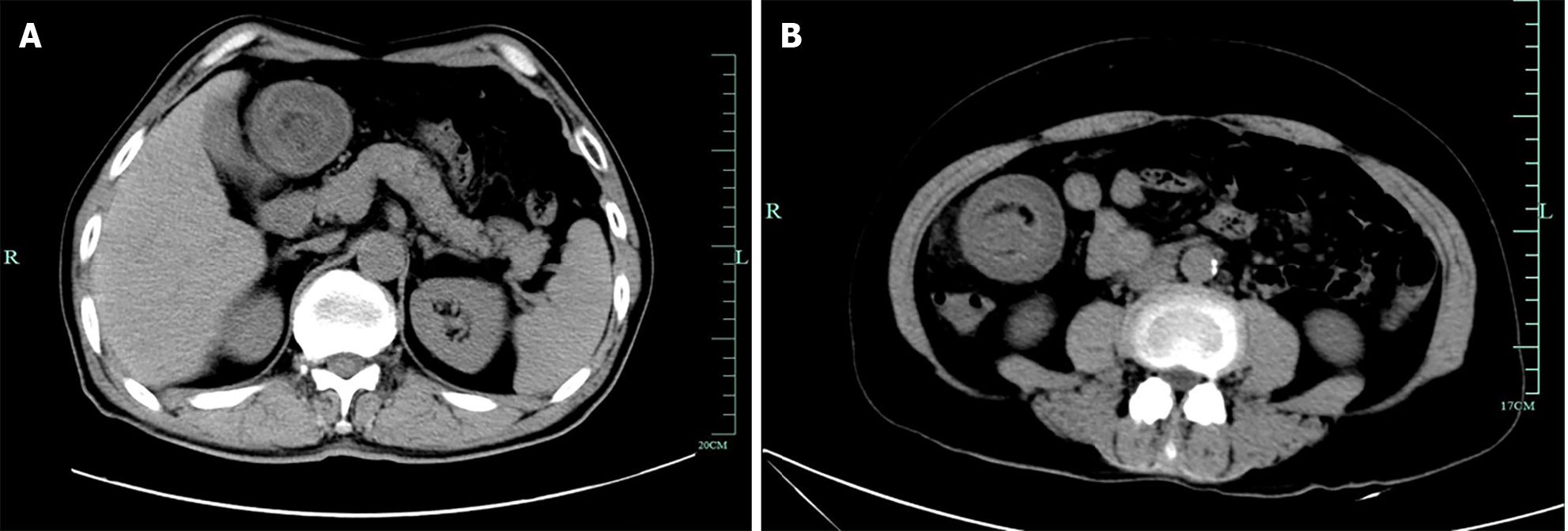
Figure 3 Urgent abdominal computed tomography.
A: Urgent abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealing a colo-colonic intussusception near the hepatic flexure; B: Emergency abdominal CT revealing a target-like lesion with thickened intestinal walls.
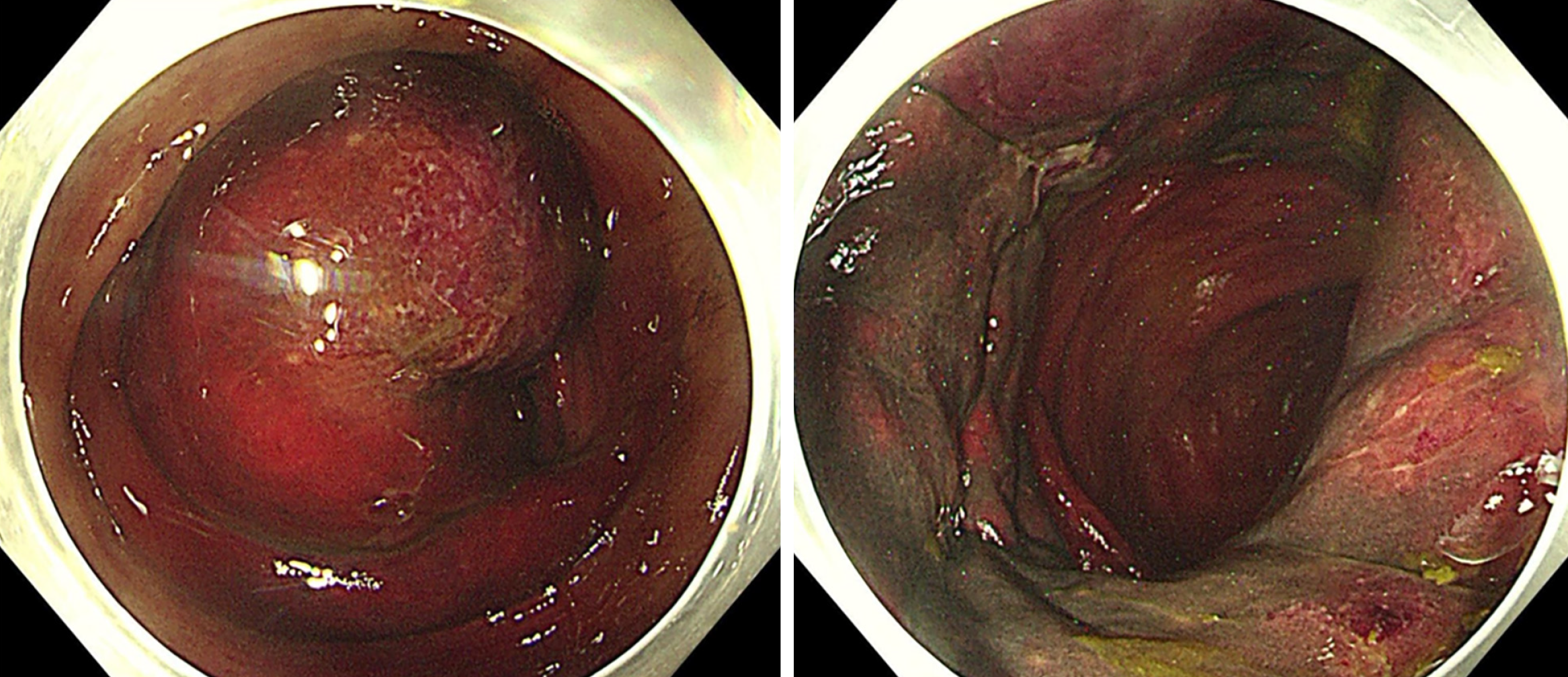
Figure 4 Images of emergency colonoscopy of case 1.
Colonoscopy revealing congested, swollen, purple-red-colored mucosa in the ascending colon near hepatic flexure, invaginating into the distal bowel.
Figure 5 Images of emergency colonoscopy of case 2.
A-C: Colonoscopy revealing congested, swollen, and purple-red-colored mucosa in the transverse colon, invaginating into the distal bowel; D: Post-polypectomy wound with metal clips located approximately 5 cm above the inflamed mucosa and not affected by the intussusception.
- Citation: Xiang SH, Xu GQ. Colo-colonic intussusception as a rare complication of colonoscopy with polypectomy: Two case reports. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(6): 1939-1947
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i6/1939.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1939