Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jun 27, 2024; 16(6): 1926-1932
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1926
Published online Jun 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1926
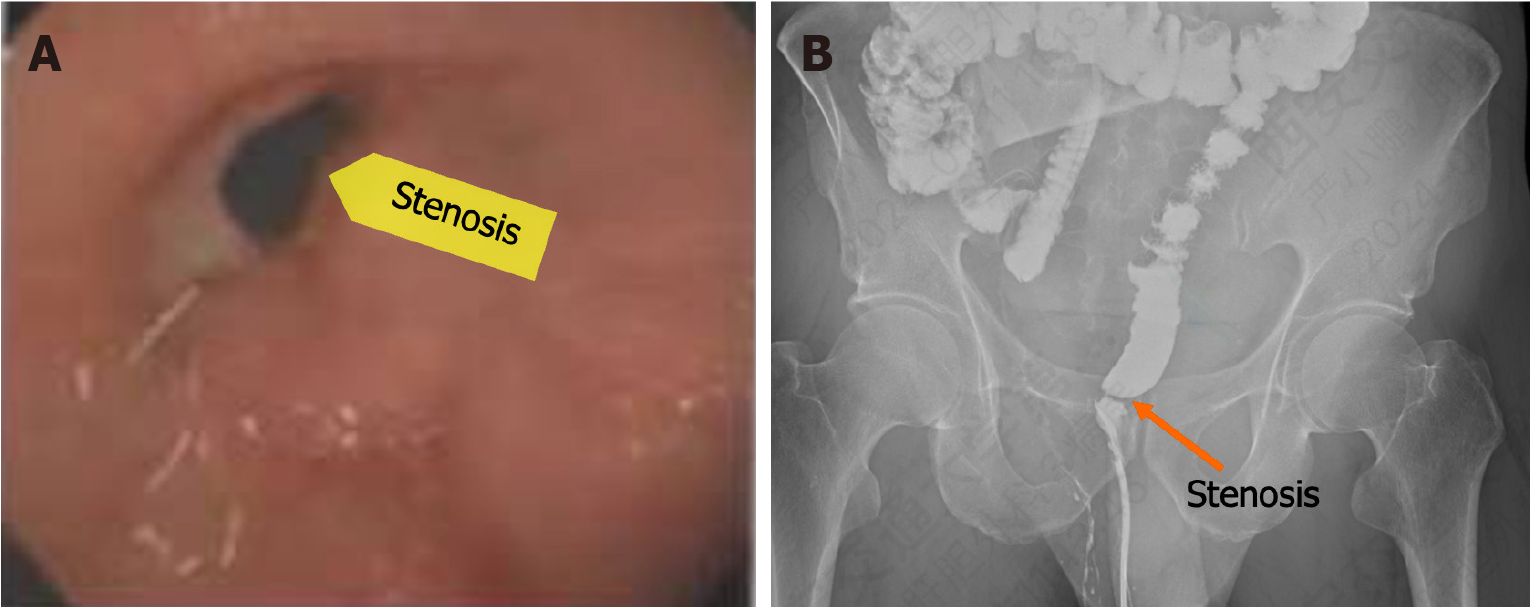
Figure 1 Preoperative examination.
A: Colonoscopy image showing the stenosis; B: Colonography.
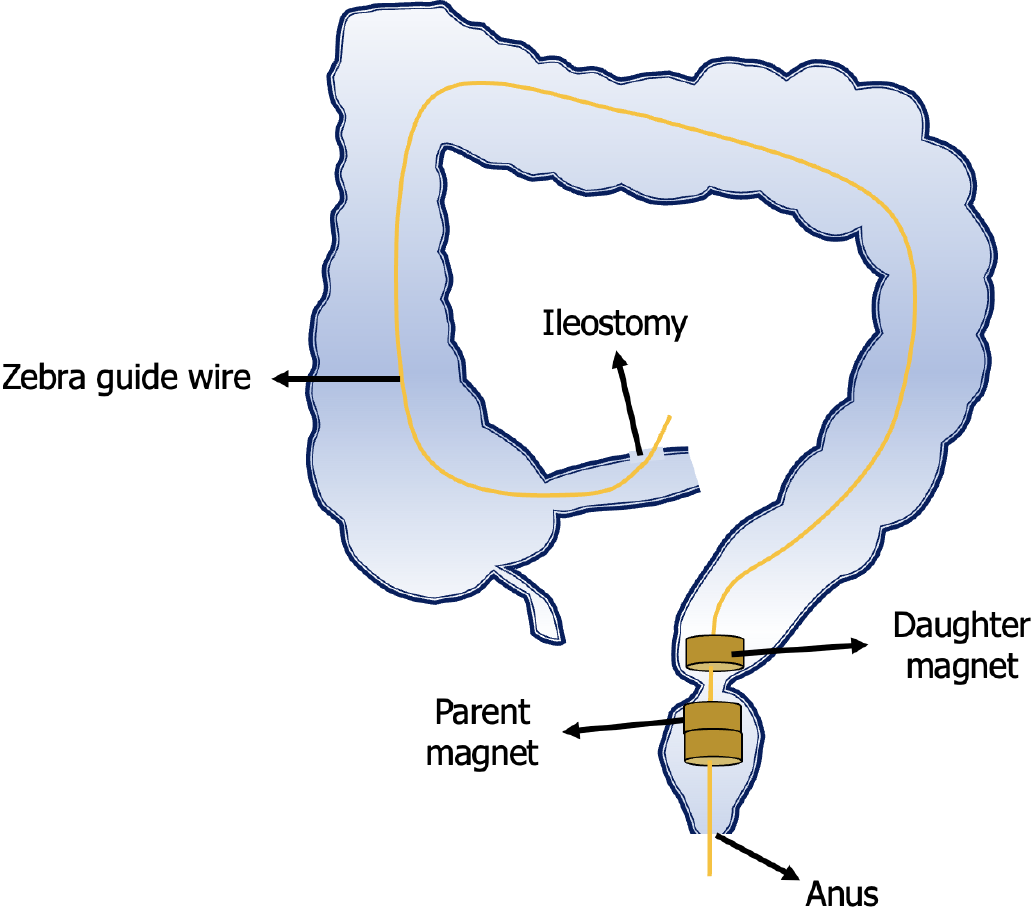
Figure 2 Schematic illustration of the surgical plan.
Zebra guide wire was inserted through the ileostomy and pulled out through the anus with the assistance of colonoscopy. The daughter magnet and parent magnets were inserted into the two sides of the rectum stenosis along the zebra guide wire through the ileostomy and the anus, respectively.
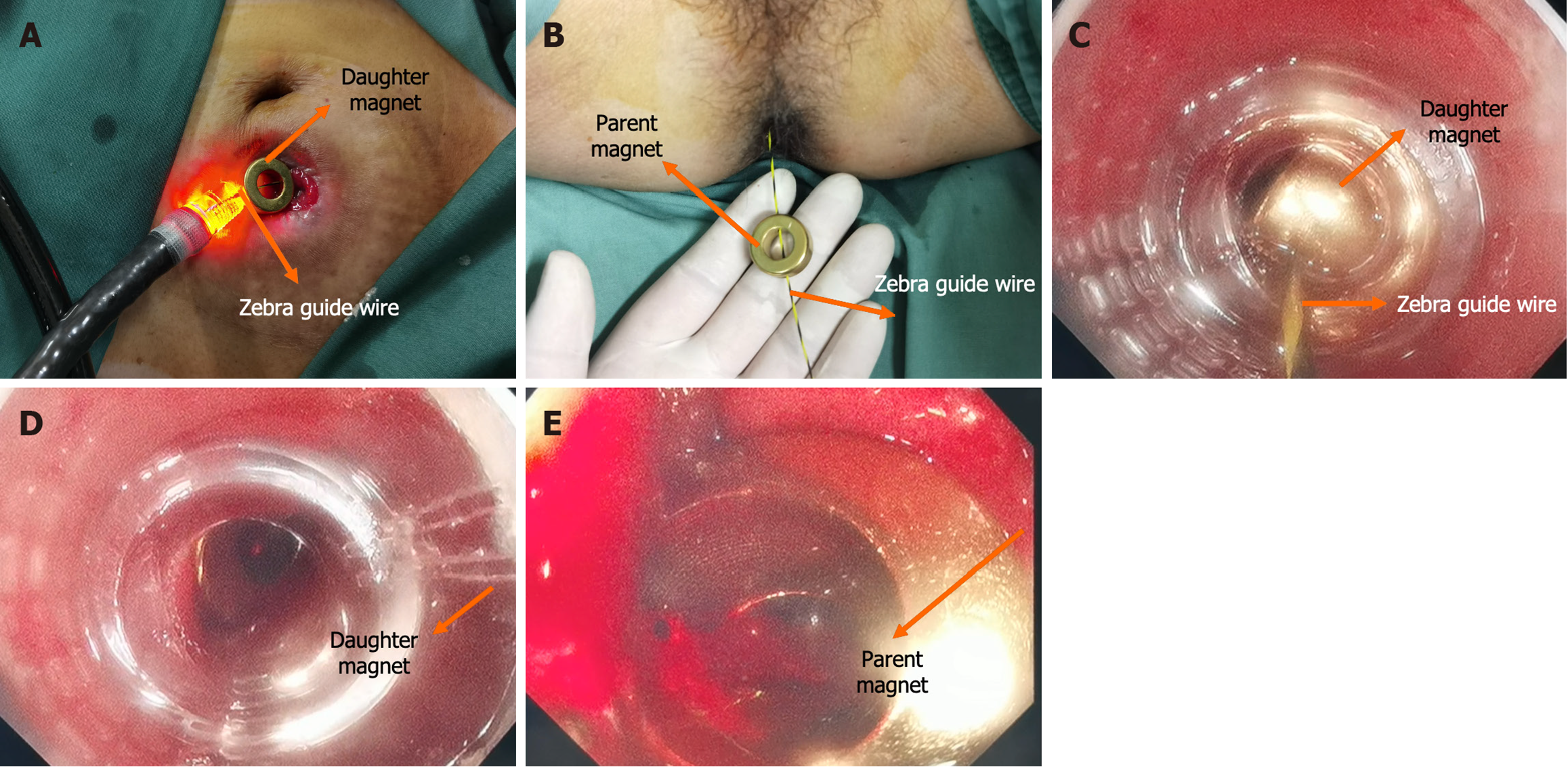
Figure 3 Surgical procedure.
A: The daughter magnet was inserted along the zebra guide wire through the ileostomy; B: The parent magnet was inserted along the zebra guide wire through the anus; C: The push process of the daughter magnet; D: The state of the daughter magnet after attraction; E: The state of the parent magnet after attraction.
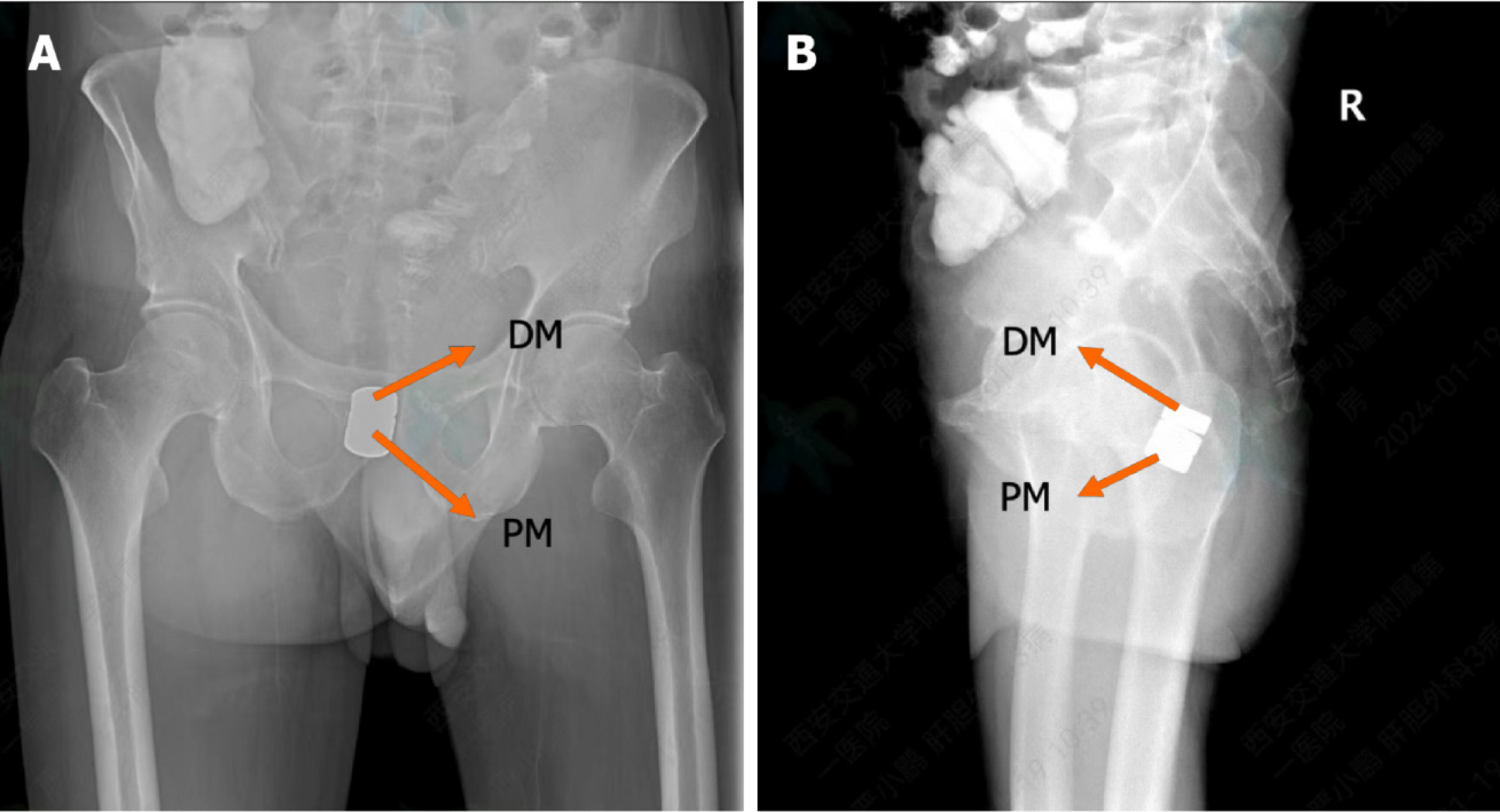
Figure 4 Postoperative x-ray examination.
A: Pelvic anteroposterior radiograph showing the attraction state of the daughter and the parent magnets; B: Pelvic lateral radiograph showing the attraction state of the daughter and the parent magnets. DM: Daughter magnet; PM: Parent magnet.
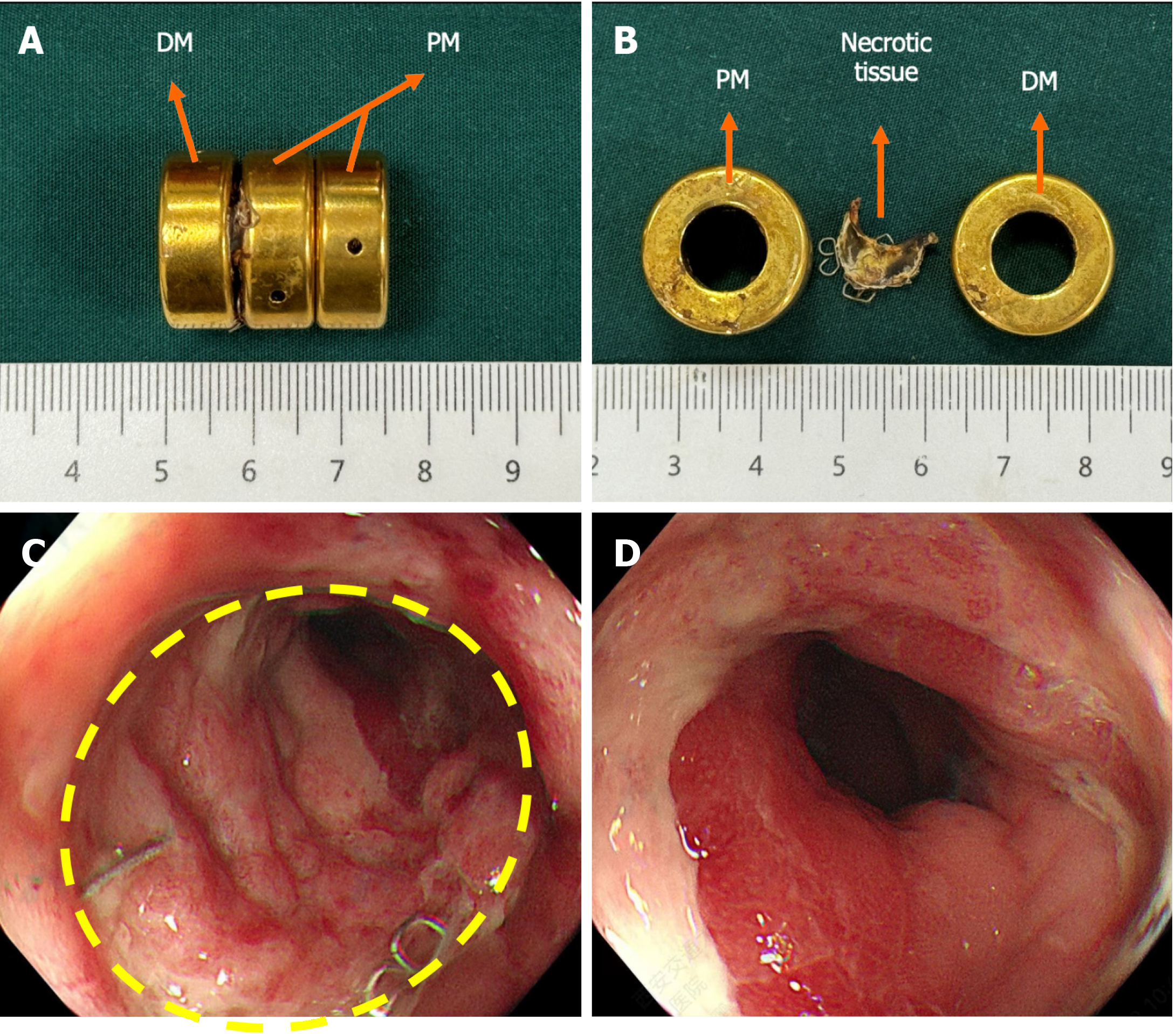
Figure 5 Postoperative colonoscopy.
A: The daughter and parent magnets were discharged on the 16th day after surgery; B: The necrotic tissue between the daughter and the parent magnets; C and D: Colonoscopy image showing good patency of magnetic anastomosis. DM: Daughter magnet; PM: Parent magnet.
- Citation: Zhang MM, Sha HC, Xue HR, Qin YF, Song XG, Li Y, Li Y, Deng ZW, Gao YL, Dong FF, Lyu Y, Yan XP. Novel magnetic compression technique for the treatment of postoperative anastomotic stenosis in rectal cancer: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(6): 1926-1932
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i6/1926.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1926