Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Feb 27, 2024; 16(2): 554-570
Published online Feb 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.554
Published online Feb 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.554
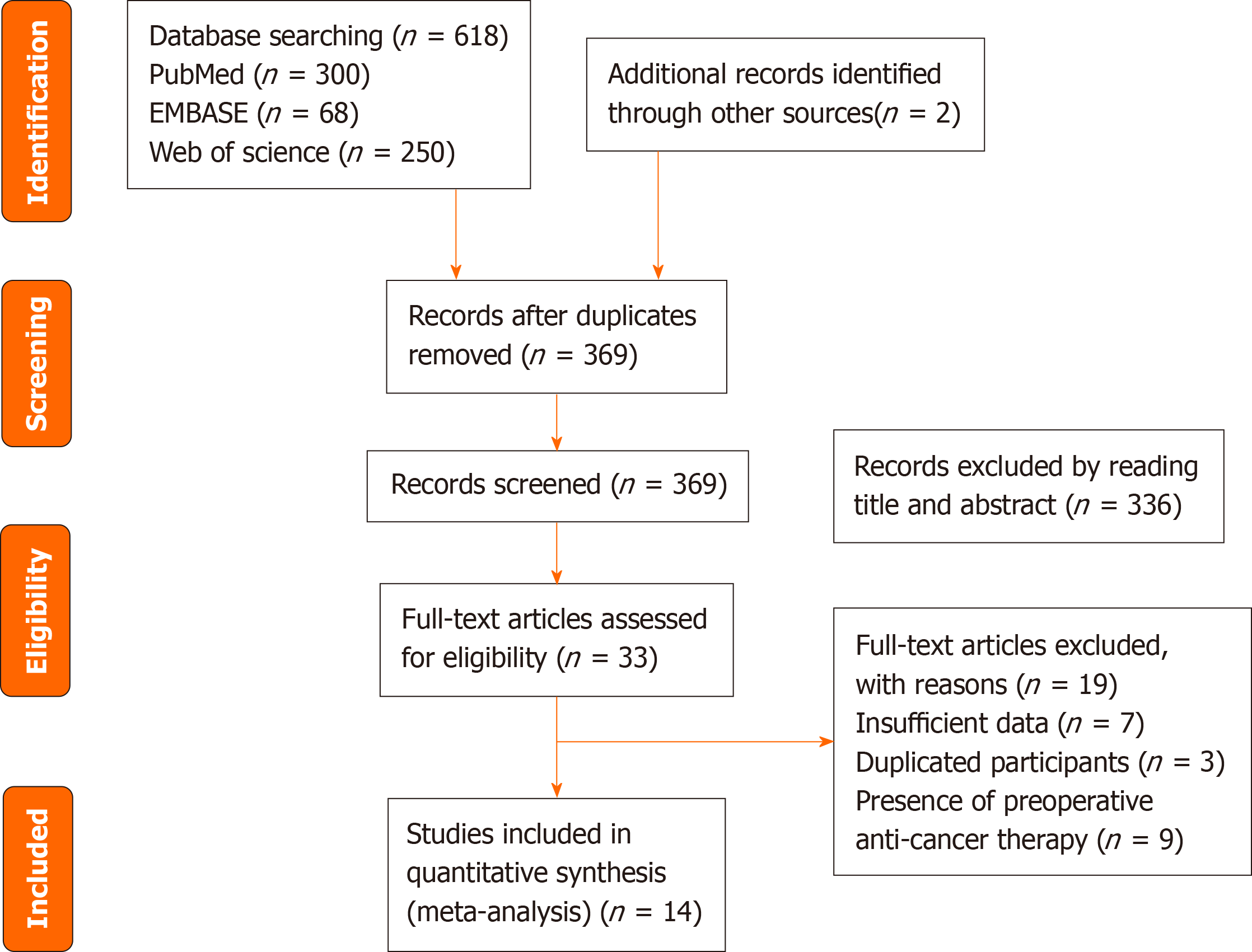
Figure 1 PRISMA flowchart for selection of the studies.
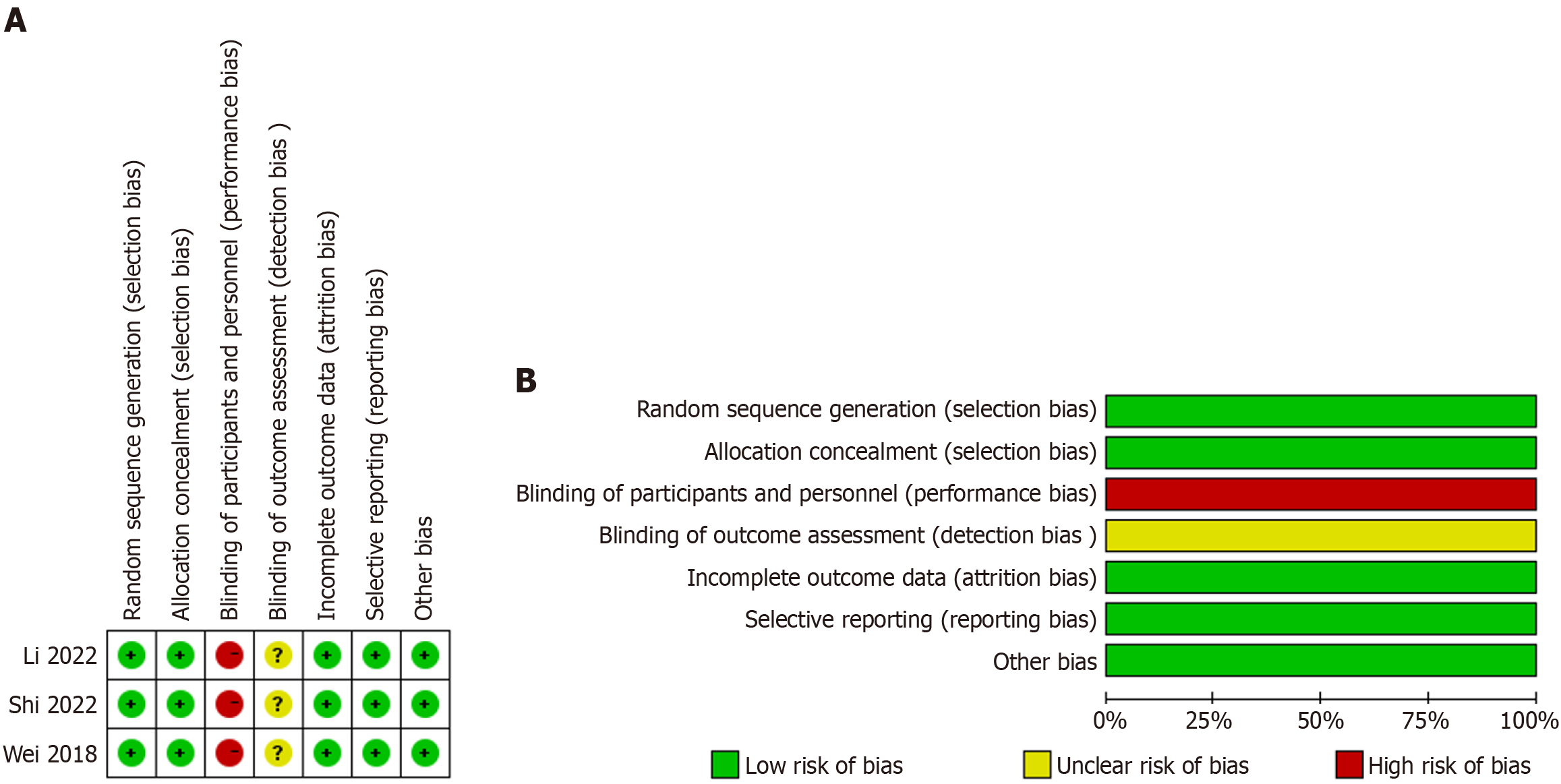
Figure 2 Risk-of-bias assessments for prospective clinical trials included in the meta-analysis.
A: Risk-of-bias summary; B: Risk-of-bias graph. +: Low risk of bias; ?: Unclear risk of bias; -: High risk of bias.
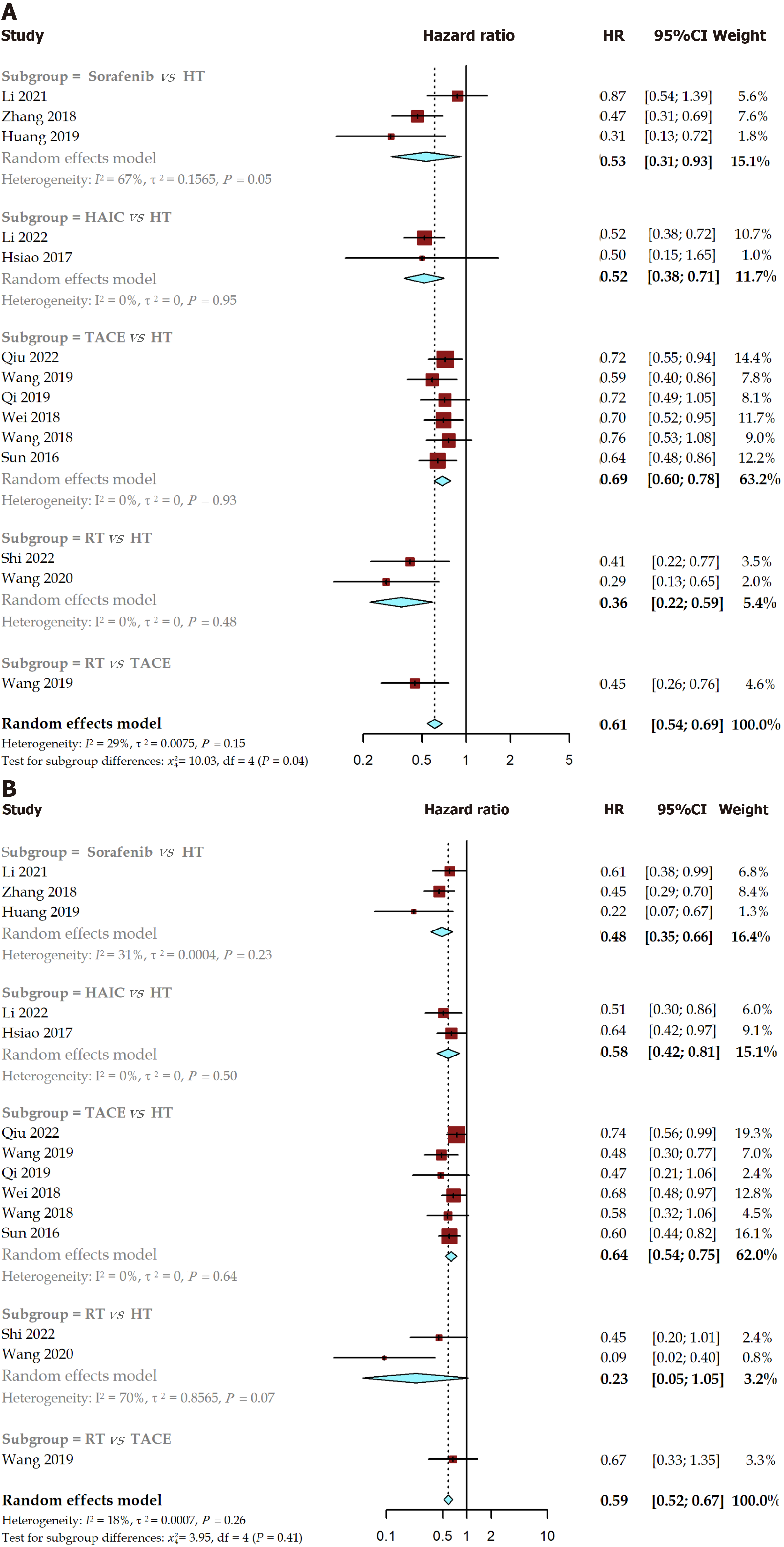
Figure 3 Forest plot of recurrence free survival and overall survival for pairwise meta-analysis.
A: Recurrence free survival; B: Overall survival. HT: Hepatectomy; HAIC: Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy; RT: Radiotherapy; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization; HR: Hazard ratio; CI: Confidence interval.
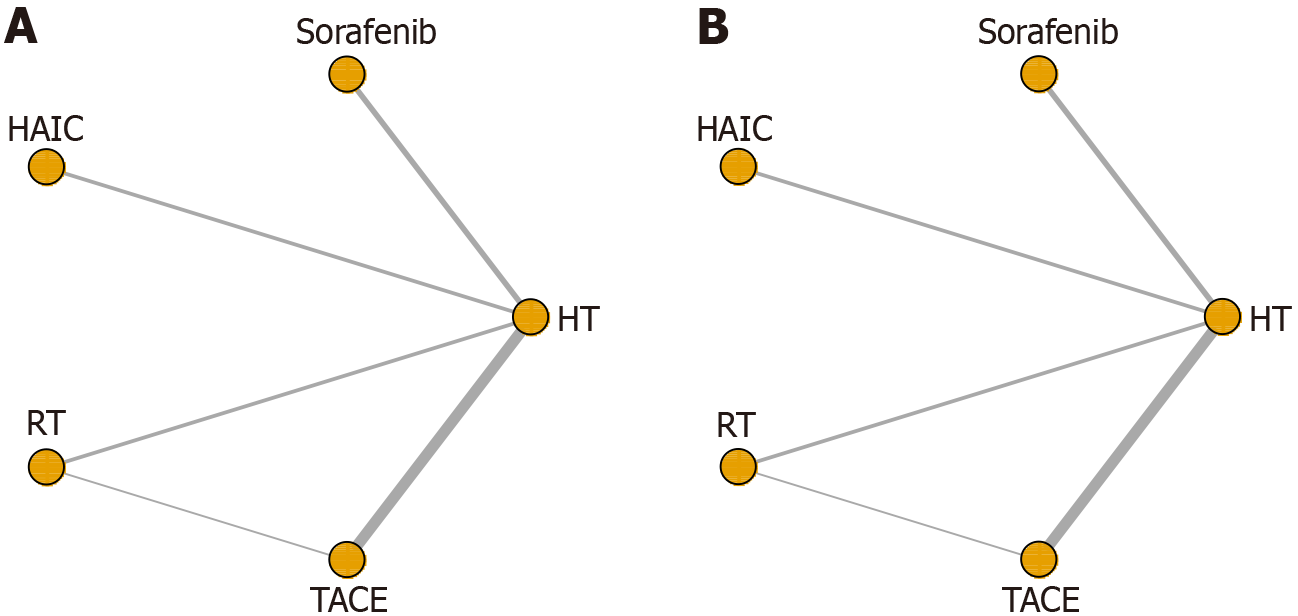
Figure 4 Network diagram of eligible comparisons for recurrence free survival and overall survival.
A: Recurrence free survival; B: Overall survival. HT: Hepatectomy; HAIC: Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy; RT: Radiotherapy; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization.
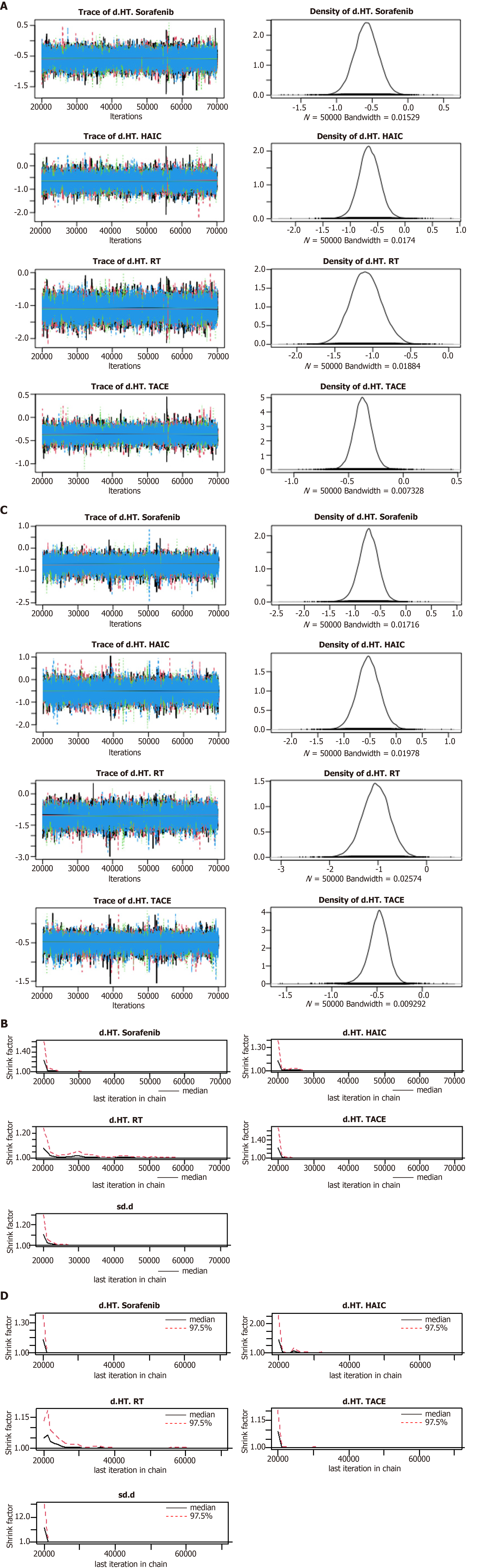
Figure 5 Convergence of the three chains established by trace and the Brooks-Gelman-Rubin diagnostic for recurrence free survival and overall survival.
A and B: Recurrence free survival; C and D: Overall survival. HT: Hepatectomy; HAIC: Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy; RT: Radiotherapy; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization.
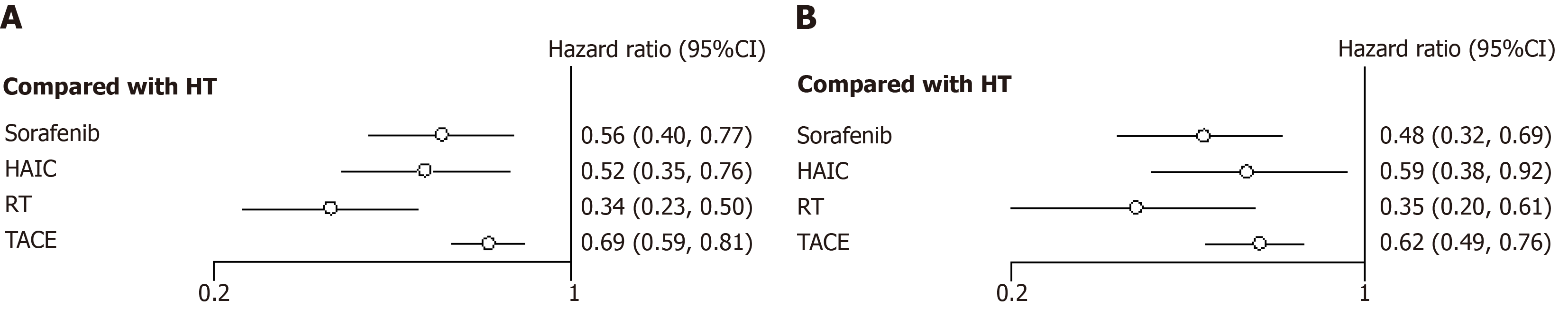
Figure 6 Hazard ratio along with 95% confidence interval for recurrence free survival and overall survival for each adjuvant therapy compared with hepatectomy.
A: Recurrence free survival; B: Overall survival. HT: Hepatectomy; HAIC: Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy; RT: Radiotherapy; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization; CI: Confidence interval.
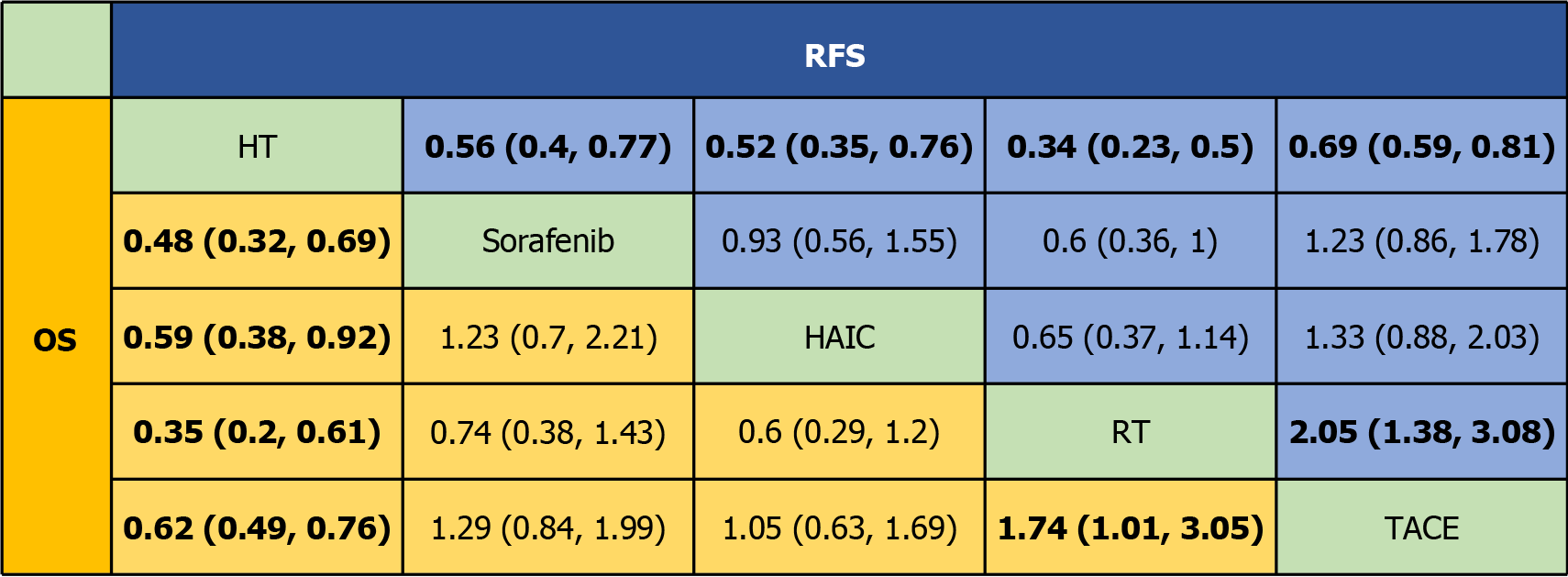
Figure 7 Pooled estimates of the network meta-analysis.
HT: Hepatectomy; HAIC: Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy; RT: Radiotherapy; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization; RFS: Recurrence free survival; OS: Overall survival.
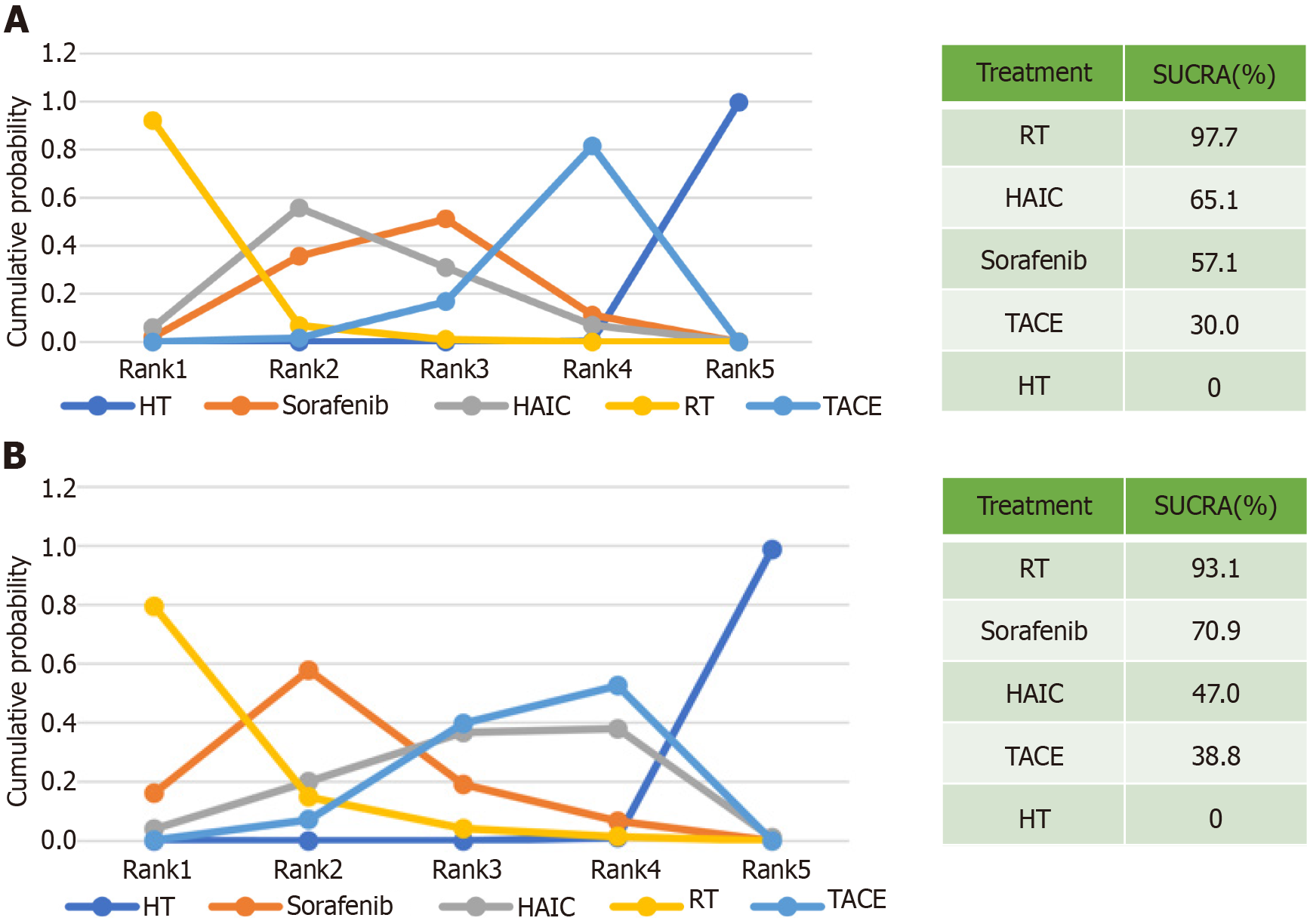
Figure 8 Cumulative ranking plot and surface under the cumulative ranking curve values for recurrence free survival and overall survival.
A: Recurrence free survival; B: Overall survival. HT: Hepatectomy; HAIC: Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy; RT: Radiotherapy; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization; SUCRA: Surface under the cumulative ranking curve.
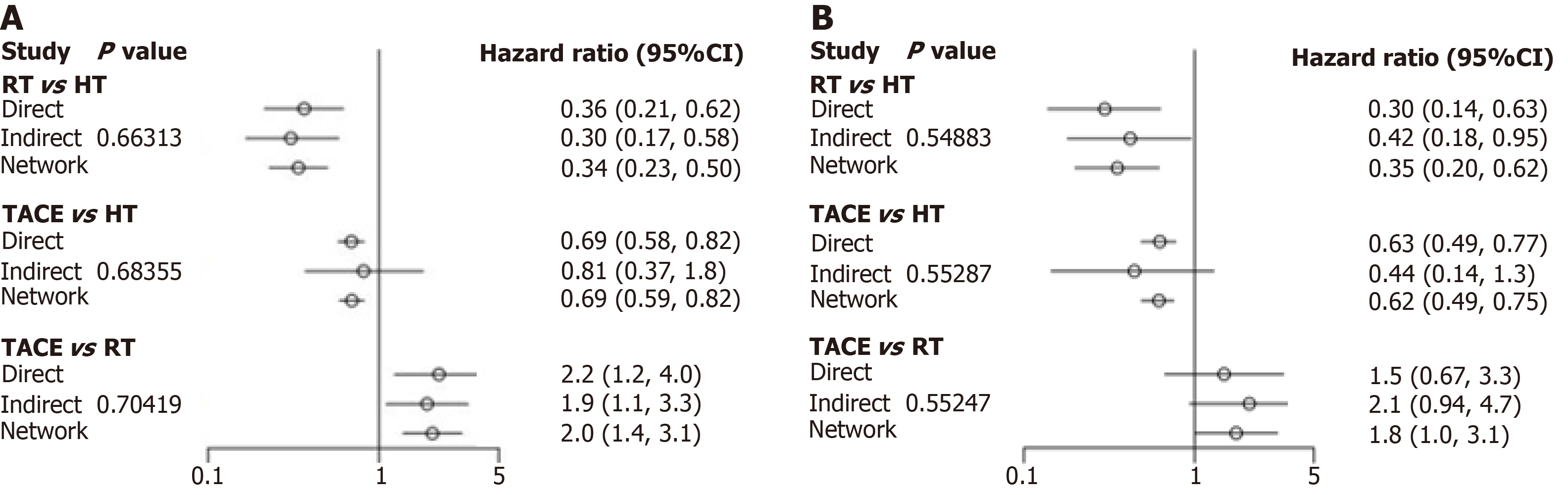
Figure 9 The node-splitting approach demonstrated consistency between the direct and indirect evidence for recurrence free survival and overall survival.
A: Recurrence free survival; B: Overall survival. HT: Hepatectomy; RT: Radiotherapy; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization; CI: Confidence interval.
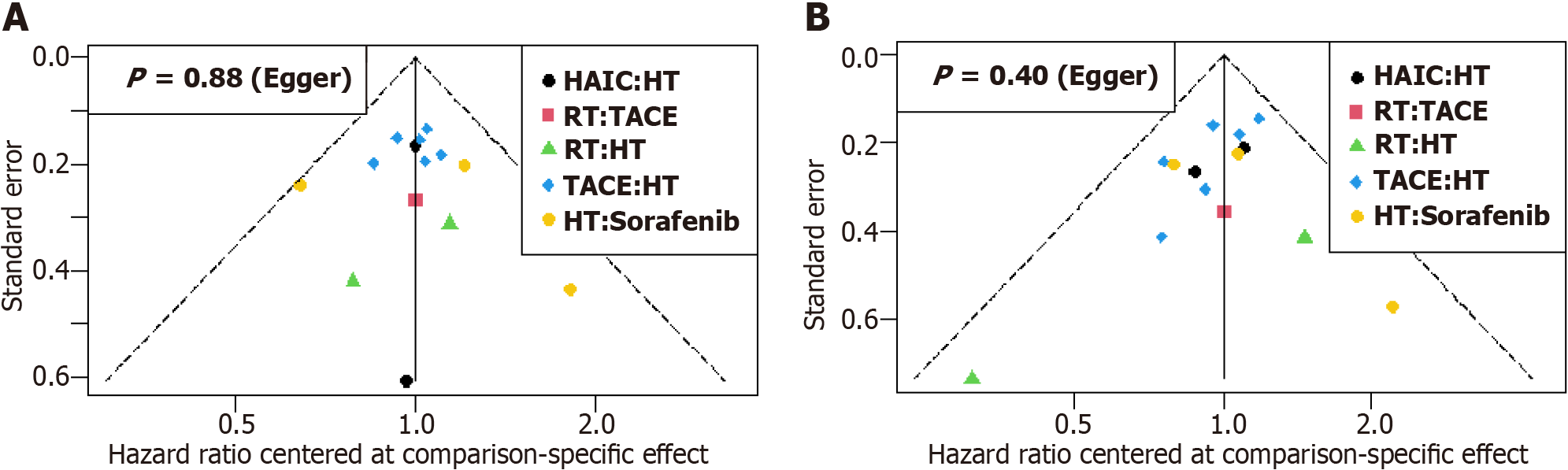
Figure 10 Funnel plot and Egger’s tests for the included studies in terms of recurrence free survival and overall survival.
A: Recurrence free survival; B: Overall survival. HT: Hepatectomy; HAIC: Hepatic artery infusion chemotherapy; RT: Radiotherapy; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization.
- Citation: Pei YX, Su CG, Liao Z, Li WW, Wang ZX, Liu JL. Comparative effectiveness of several adjuvant therapies after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(2): 554-570
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i2/554.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.554