Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Feb 27, 2024; 16(2): 307-317
Published online Feb 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.307
Published online Feb 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.307
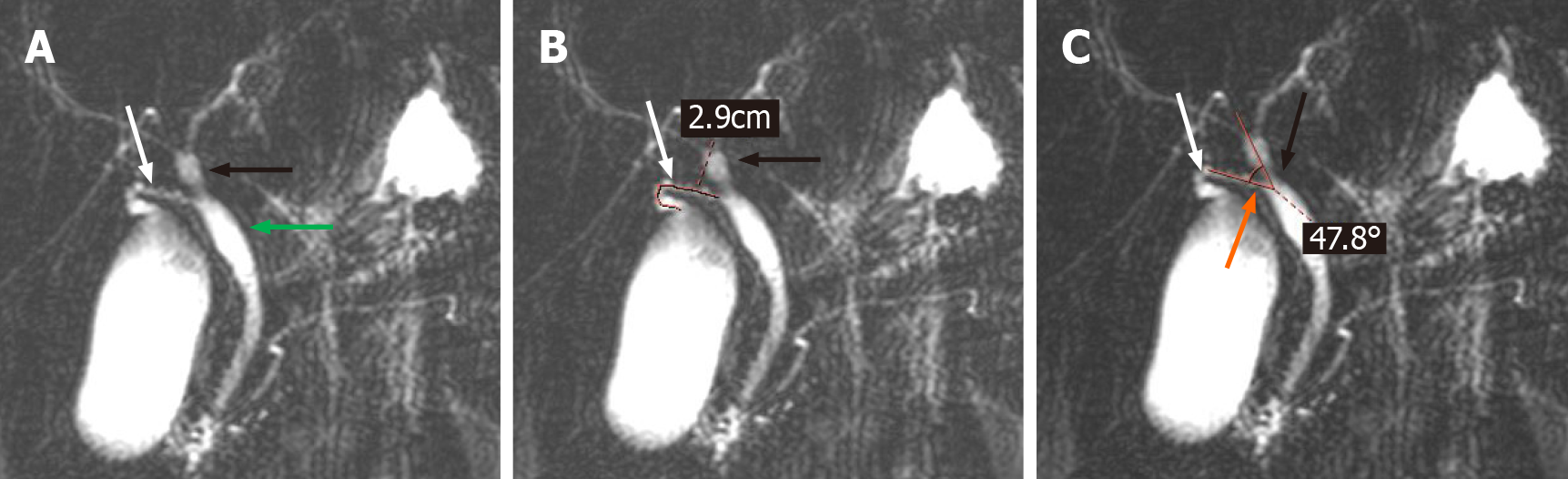
Figure 1 The length of cystic duct and < common hepatic duct were measured on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography images.
A: Measure relevant anatomy: Cystic duct (CD) (white arrow), common hepatic duct (CHD) (black arrow), common bile duct (green arrow); B: Length of CD: Measurements are taken from the beginning of the cystic duct and along the trajectory of the CD until it reaches the point of confluence of the CD (white arrow) into the CHD (black arrow); C: < CHD: The angle between the common hepatic duct (black arrow) and the cystic duct (white arrow).
Figure 2 The classification of intrahepatic bile duct anatomy.
A: Type A: The right posterior duct (RPD) (black arrow) converges into the right hepatic duct (yellow arrow); B: Type B: The RPD (black arrow) converges into the junction of the right and left hepatic ducts, and the three show a three-fork type; C: Type C: The RPD (black arrow) converges into the left hepatic duct (blue arrow); D: Type D: The RPD (black arrow) converges into the extrahepatic bile duct.
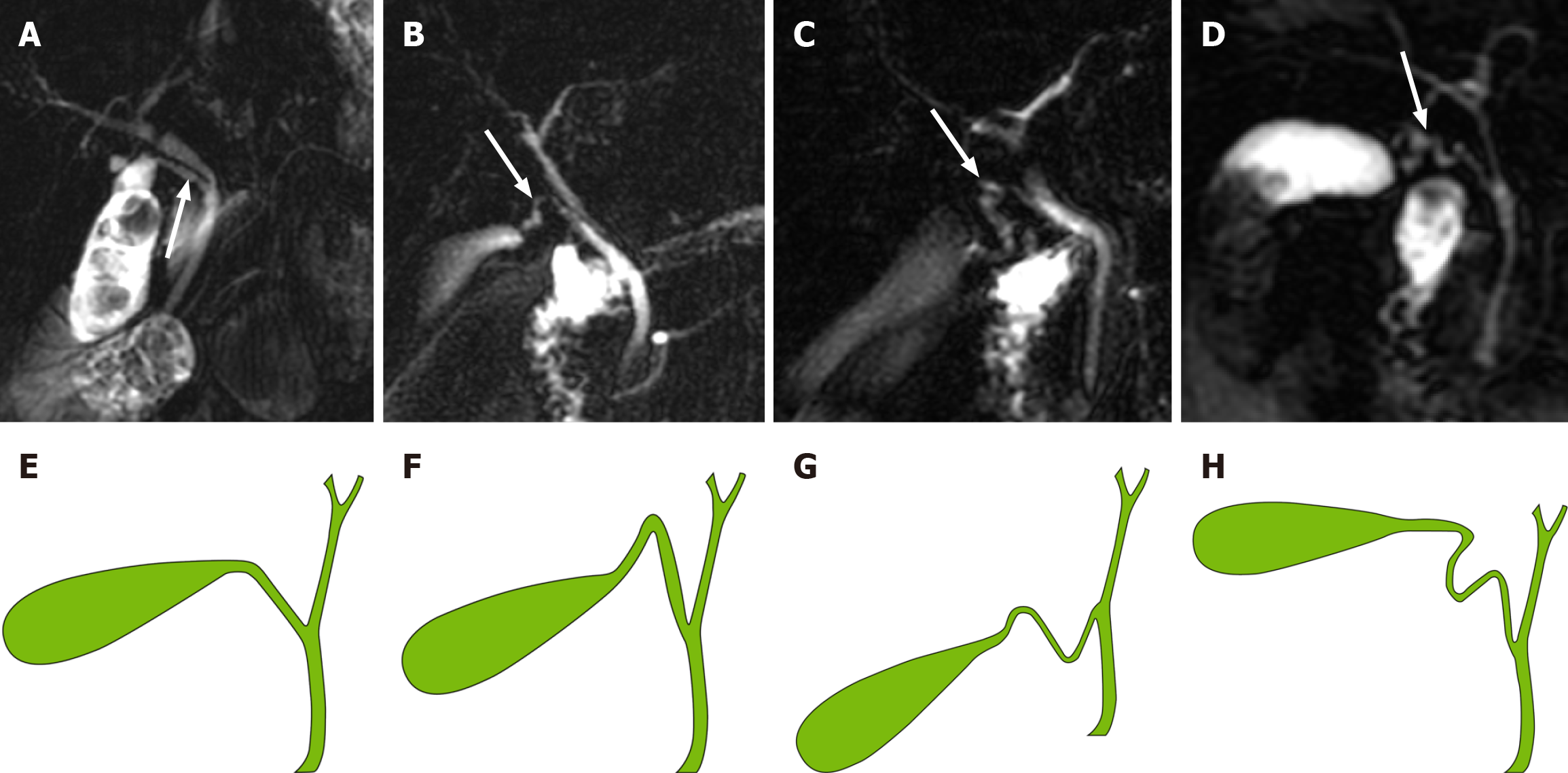
Figure 3 The classification of the morphology of cystic duct and model diagram.
A: Type I: Linear, cystic duct (CD) (white arrow) straight into extrahepatic bile duct (EHBD) with no tortuosity; B: Type II: n-shaped, CD (white arrow) has a bend in the shape of an n; C: Type III: S-shaped, CD (white arrow) converges in an S-shape into the EHBD; D: Type IV: W-shaped, CD (white arrow) converges into the EHBD in a W-shape; E: Type I: Linear; F: Type II: n-shaped; G: Type III: S-shaped; H: Type IV: W-shaped.
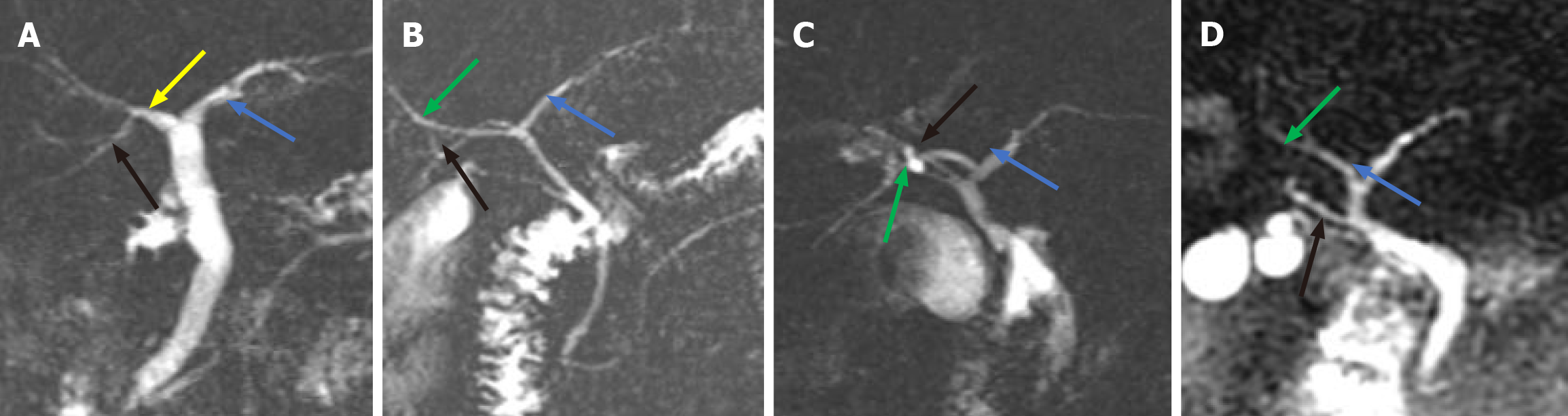
Figure 4 The cystic duct converges into the intrahepatic bile duct.
A: The cystic duct (CD) (white arrow) converges into the right hepatic duct (green arrow); B: The CD converges into the left hepatic duct (blue arrow); C: The CD converges into the confluence of the right and left hepatic ducts.
- Citation: Zhu JH, Zhao SL, Kang Q, Zhu Y, Liu LX, Zou H. Classification of anatomical morphology of cystic duct and its association with gallstone. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(2): 307-317
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i2/307.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i2.307