Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jan 27, 2024; 16(1): 248-256
Published online Jan 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i1.248
Published online Jan 27, 2024. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i1.248
Figure 1 Small bowel endoscopy and pathology images from case 1.
A: A circular ulcer with luminal narrowing and mucosal hyperplasia located in the middle segment of the ileum; B: Another circular ulcer with a narrowing located in the middle segment of the ileum; C: A longitudinal ulcer with mucosal hyperplasia located in the terminal segment of the ileum; D: Histopathological examination by hematoxylin-eosin (200 ×) staining demonstrated the formation of multiple granulomas.
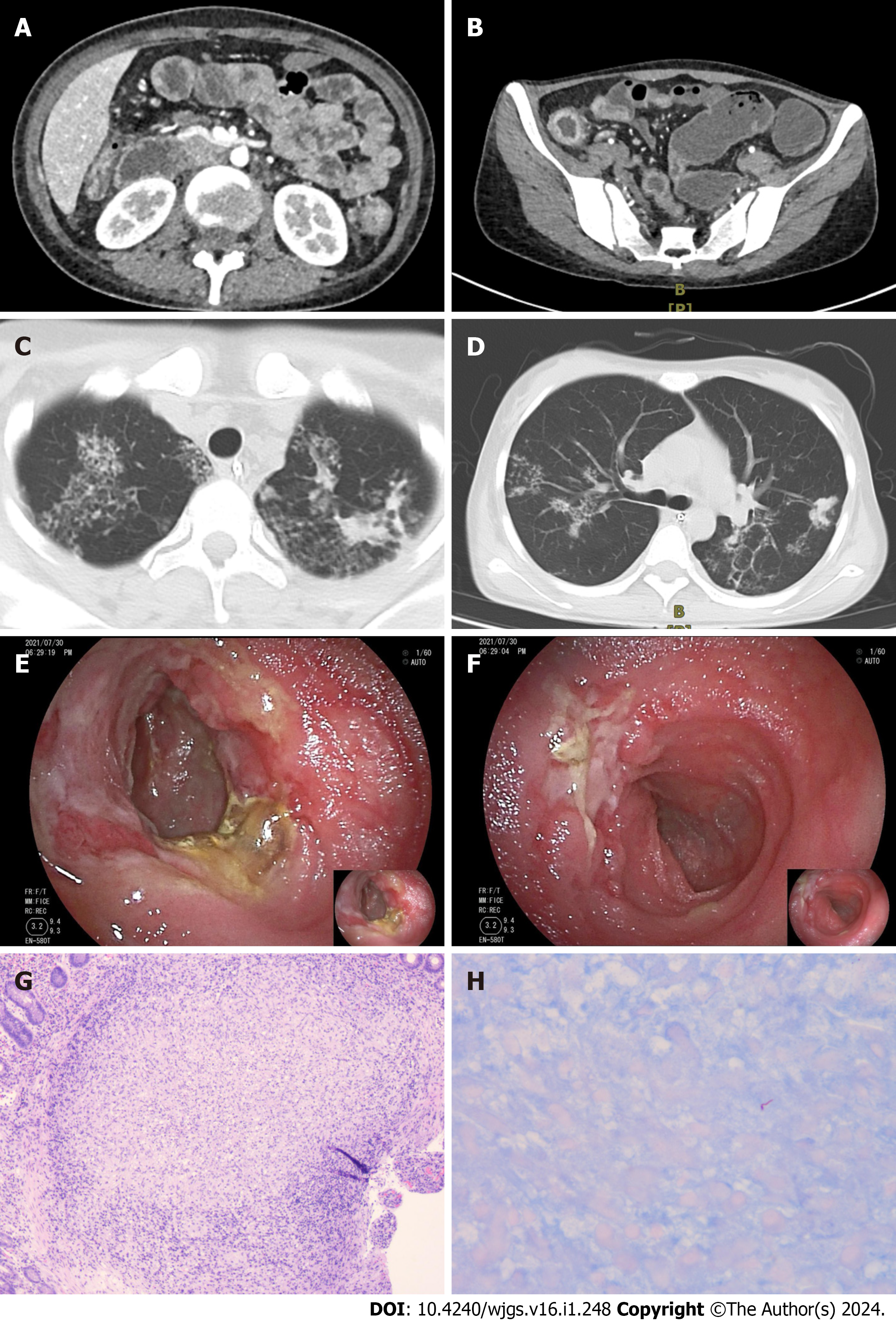
Figure 2 Computed tomography, small bowel endoscopy, and pathology images from case 2.
A: Computed tomography scan showing multiple strictures in the small intestine; B: CT scan showing multiple strictures and thickening of the colonic wall; C: CT scan showing multifocal patchy opacities in the upper lungs; D: CT scan showing multifocal patchy opacities in both lungs, predominantly in the right middle lobe and left lower lobe; E: An ulcer with purulent exudate and surrounding mucosal hyperplasia was observed at the terminal ileum; F: An ulcer with luminal involvement was observed at the terminal ileum; G: Histopathological examination via hematoxylin-eosin staining (100 ×) revealed the presence of multiple granulomas; H: Histopathological examination via acid-fast bacilli staining (400 ×) revealed positive bacteria.
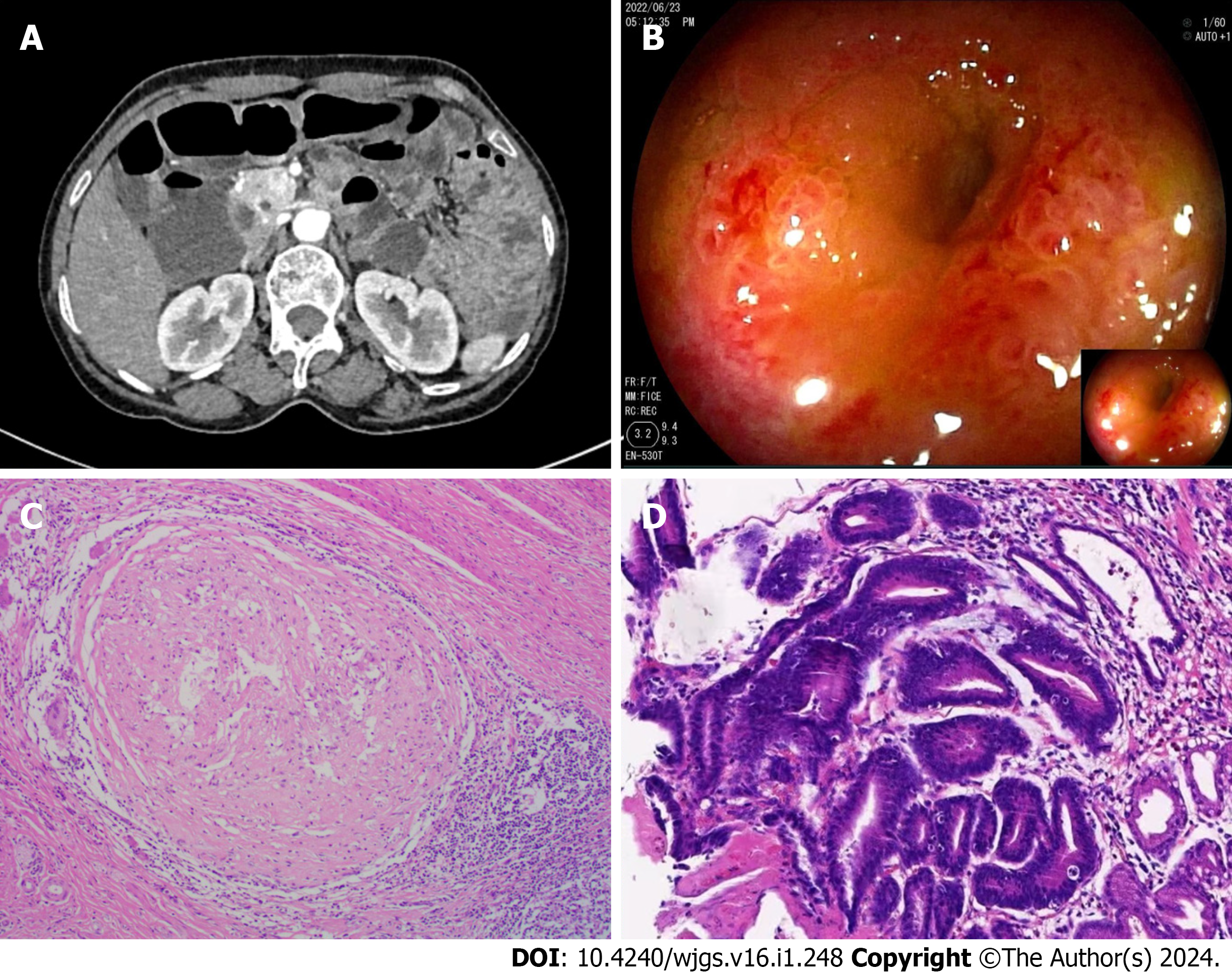
Figure 3 Computed tomography, small bowel endoscopy, and pathology images from case 3.
A: Computed tomography enterography revealed localized thickening of the small intestine with clustering in the lower left abdomen; B: Small bowel endoscopy revealing ileal stenosis; C: Histopathological examination by hematoxylin-eosin staining (100 ×) demonstrated the formation of granulomas; D: Histopathological examination by hematoxylin-eosin staining (200 ×) demonstrated advanced dysplasia in the gastric mucosa and focal carcinoma in situ.
- Citation: Huang G, Wu KK, Li XN, Kuai JH, Zhang AJ. Intestinal tuberculosis with small bowel stricture and hemorrhage as the predominant manifestation: Three case reports. World J Gastrointest Surg 2024; 16(1): 248-256
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v16/i1/248.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v16.i1.248