Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jul 27, 2023; 15(7): 1549-1558
Published online Jul 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i7.1549
Published online Jul 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i7.1549
Figure 1 Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography.
A: Coronal section shows a mass lesion (white arrow) protruding into the lumen of the splenic flexure with a slight contrast enhancement; B: Horizontal section shows a mass (white arrow) occupying 3/4 the circumference of the lumen.
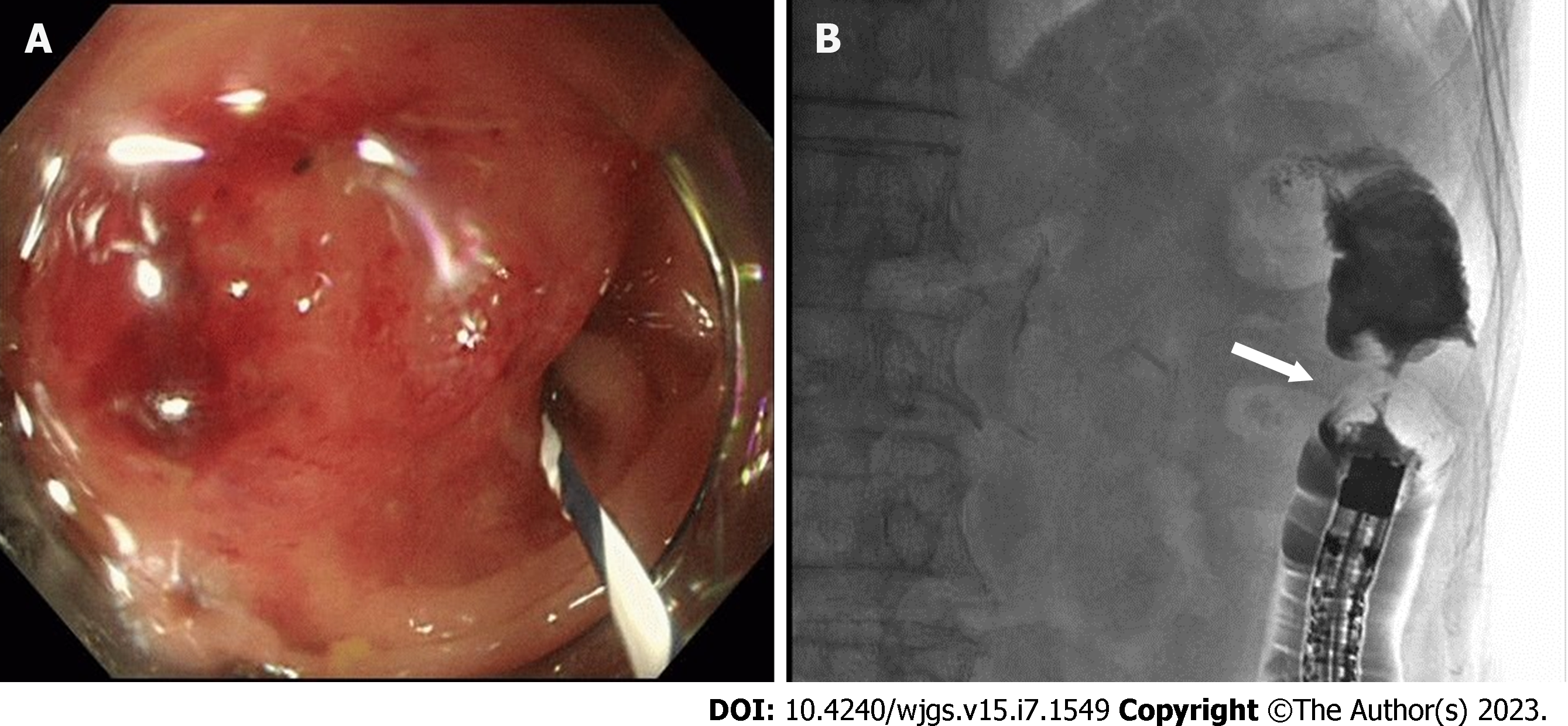
Figure 2 Colonoscopy and subsequent gastrografin enema.
A: Colonoscopy depicts a mass protruding into the lumen covered with smooth and reddish mucosa, the scope could not be advanced through the lesion; B: Gastrografin enema shows an apple core sign with luminal narrowing (white arrow), approximately 3 cm in length, in the descending colon.
Figure 3 Macroscopic and microscopic findings.
A: A circumferential protruding tumor in the descending colon with stent-induced mucosal changes; B: Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining (× 40), the tumor shows the appearance of squamous cell carcinoma, mainly confined to the submucosal layer; C-E: Immunohistochemical staining for CK5/6 (C, × 200), p40 (D, × 200), and CDX2 (E, × 400). The tumor cells are positive for CK5/6 and p40, and negative for CDX2; F: HE staining of the lung biopsy specimen of the patient (× 40). The patient was diagnosed with squamous cell lung cancer.
- Citation: Nakayama Y, Yamaguchi M, Inoue K, Hamaguchi S, Tajima Y. Successful resection of colonic metastasis of lung cancer after colonic stent placement: A case report and review of the literature. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(7): 1549-1558
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i7/1549.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i7.1549