Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2023; 15(12): 2938-2944
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i12.2938
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i12.2938
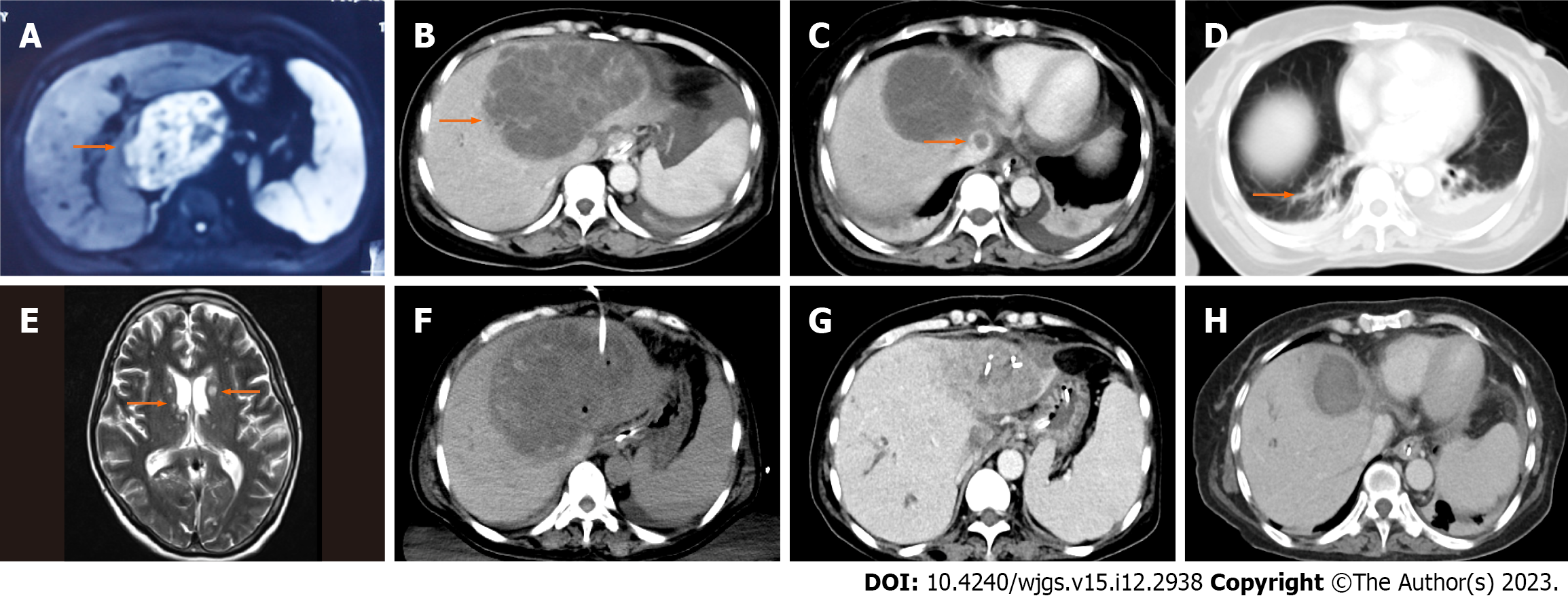
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography images of the patient.
A: A large heterogeneously cystic-solid mass was present in the left liver 1 mo prior to admission; B: An area of abnormal attenuation measuring 125 mm × 97 mm in the left lobe of the liver; C: Thrombus detected in the inferior vena cava by abdominal enhanced computed tomography (CT); D: Small patchy infiltrates identified in both lungs; E: Bilateral multiple T2 hyperintensities detected in the basal ganglia and subcortical white matter in the brain magnetic resonance imaging; F: Emergency ultrasound-guided percutaneous drainage of liver abscess was performed when the patient’s condition deteriorated; G: The size of liver abscess markedly decreased in the reexamination of abdominal CT; H: Inferior vena cava thrombus completely disappeared.
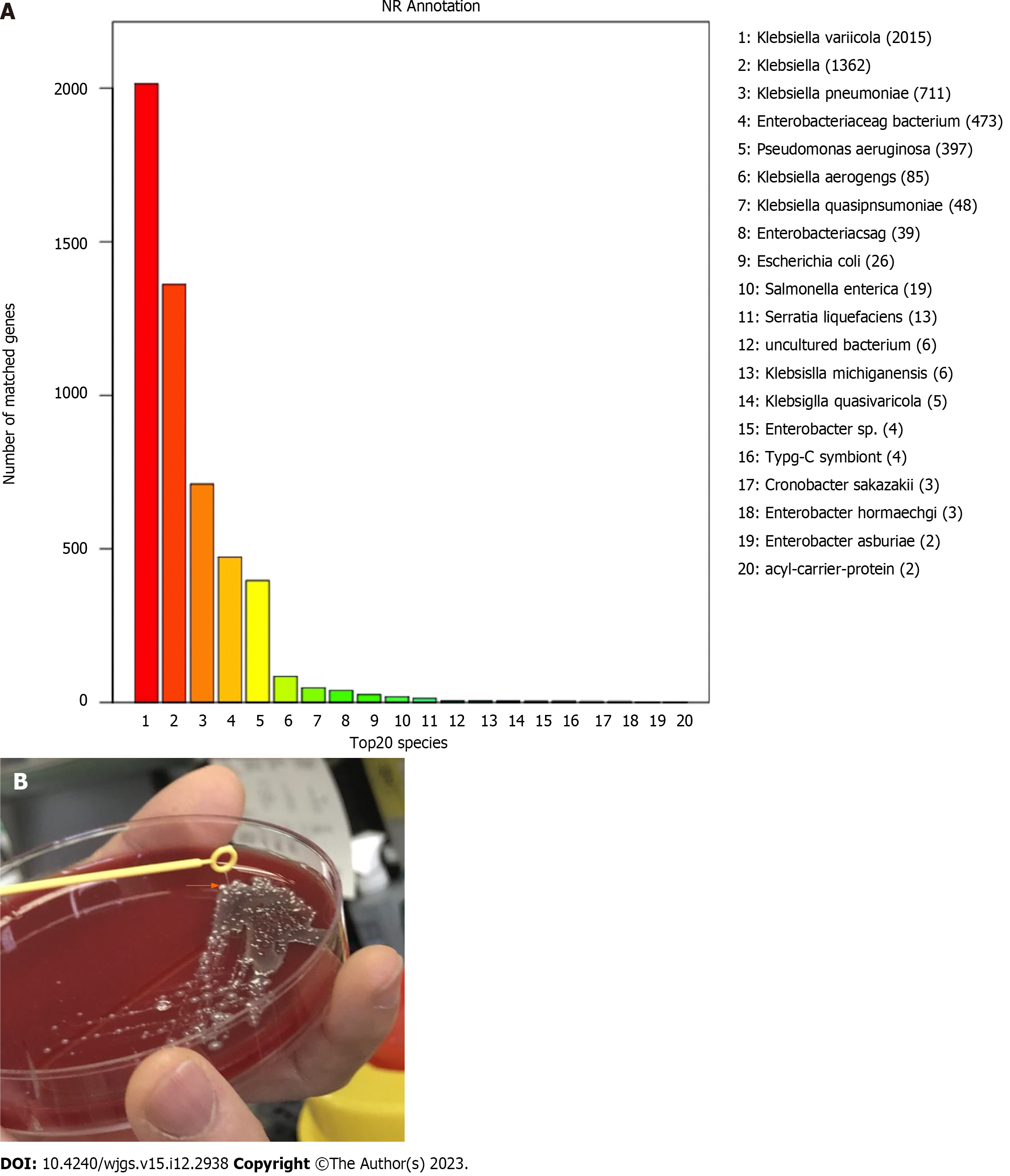
Figure 2 Identification of the pathogen.
A: Whole-genome sequencing results of pathogen identification; B: String test showing the hypermucoviscocous phenotype (orange arrow) of the strain Klebsiella variicola. The strain was grown on agar and the culture was touched with a disposable loop; the formation of a mucoid string greater than 5 mm indicates the formation of the hypermucoviscous phenotype.
- Citation: Zhang PJ, Lu ZH, Cao LJ, Chen H, Sun Y. Successful treatment of invasive liver abscess syndrome caused by Klebsiella variicola with intracranial infection and septic shock: A case report. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(12): 2938-2944
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i12/2938.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i12.2938