Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2023; 15(12): 2890-2906
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i12.2890
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i12.2890
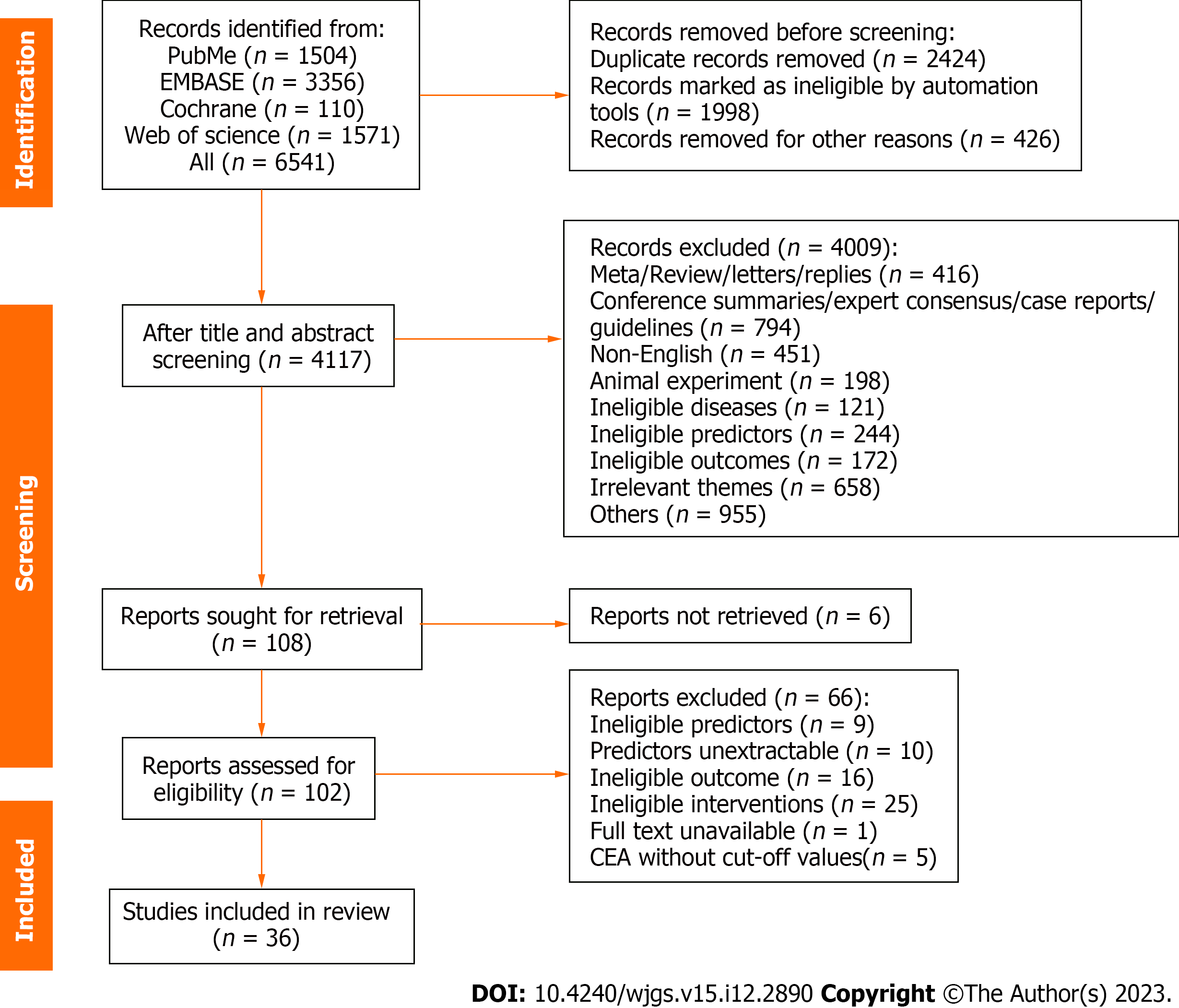
Figure 1 Literature screening process.
CEA: Carcinoembryonic antigen.
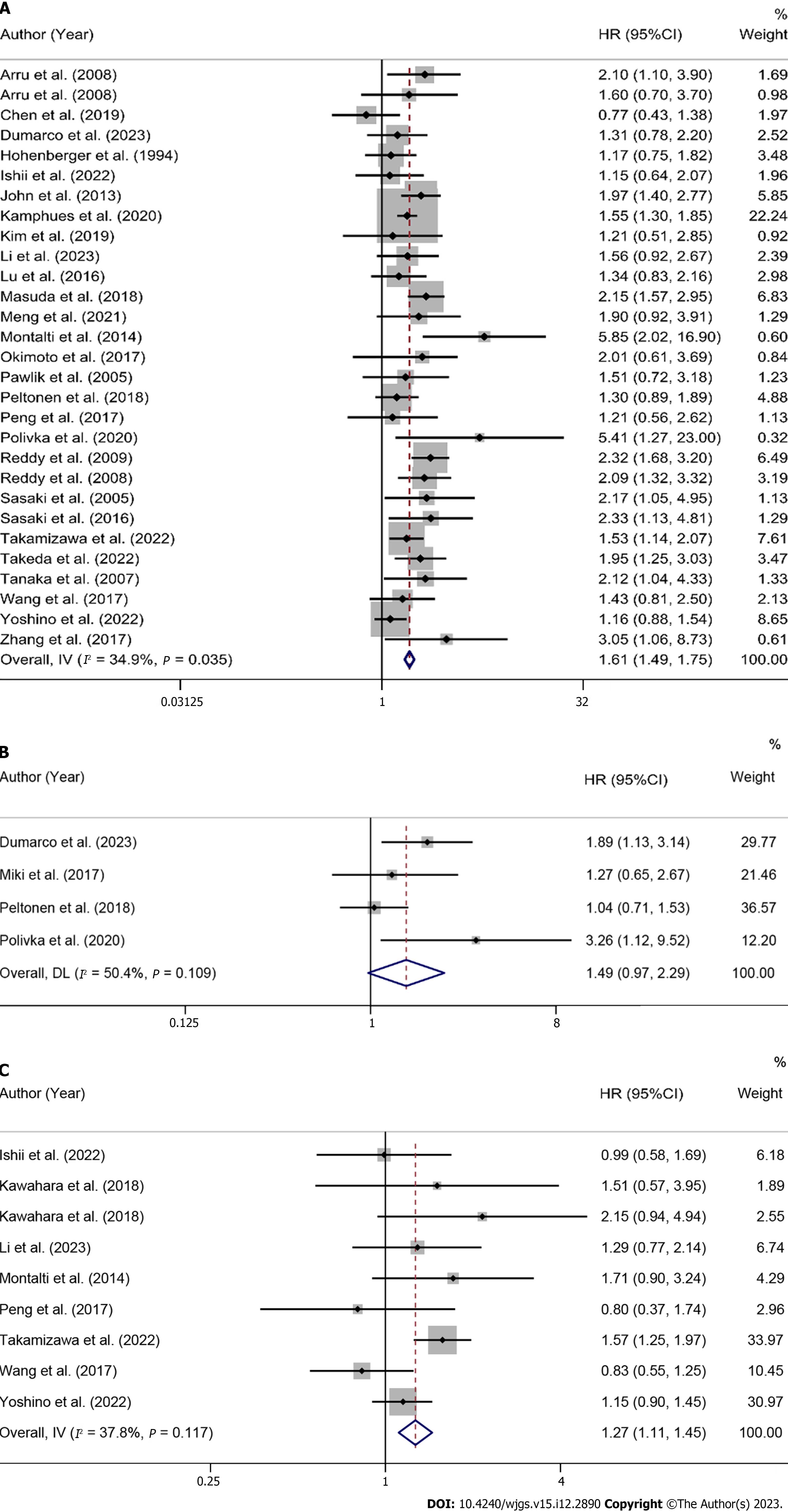
Figure 2 Forest plot of the correlation between high preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels and overall survival, disease-free survival, recurrence-free survival.
A: Forest plot of the correlation between high preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels and overall survival. In the study of Arru et al[65], the hazard ratio (HR) [95% confidence interval (CI)] for CEA levels > 5 ng/mL was 2.10 (1.10-3.90), and the HR (95%CI) for CEA levels < 5 ng/mL was 1.60 (0.70-3.70); B: Forest plot of the correlation between high preoperative serum CEA levels and disease-free survival; C: Forest plot of the correlation between high preoperative serum CEA levels and recurrence-free survival. In the study of Kawahara et al[36], the HR (95%CI) for CEA levels > 50 ng/mL was 2.15 (0.94-4.94), and the HR (95%CI) for CEA levels < 50 ng/mL was 1.51 (0.57-3.95). HR: Hazard ratio; CI: Confidence interval.
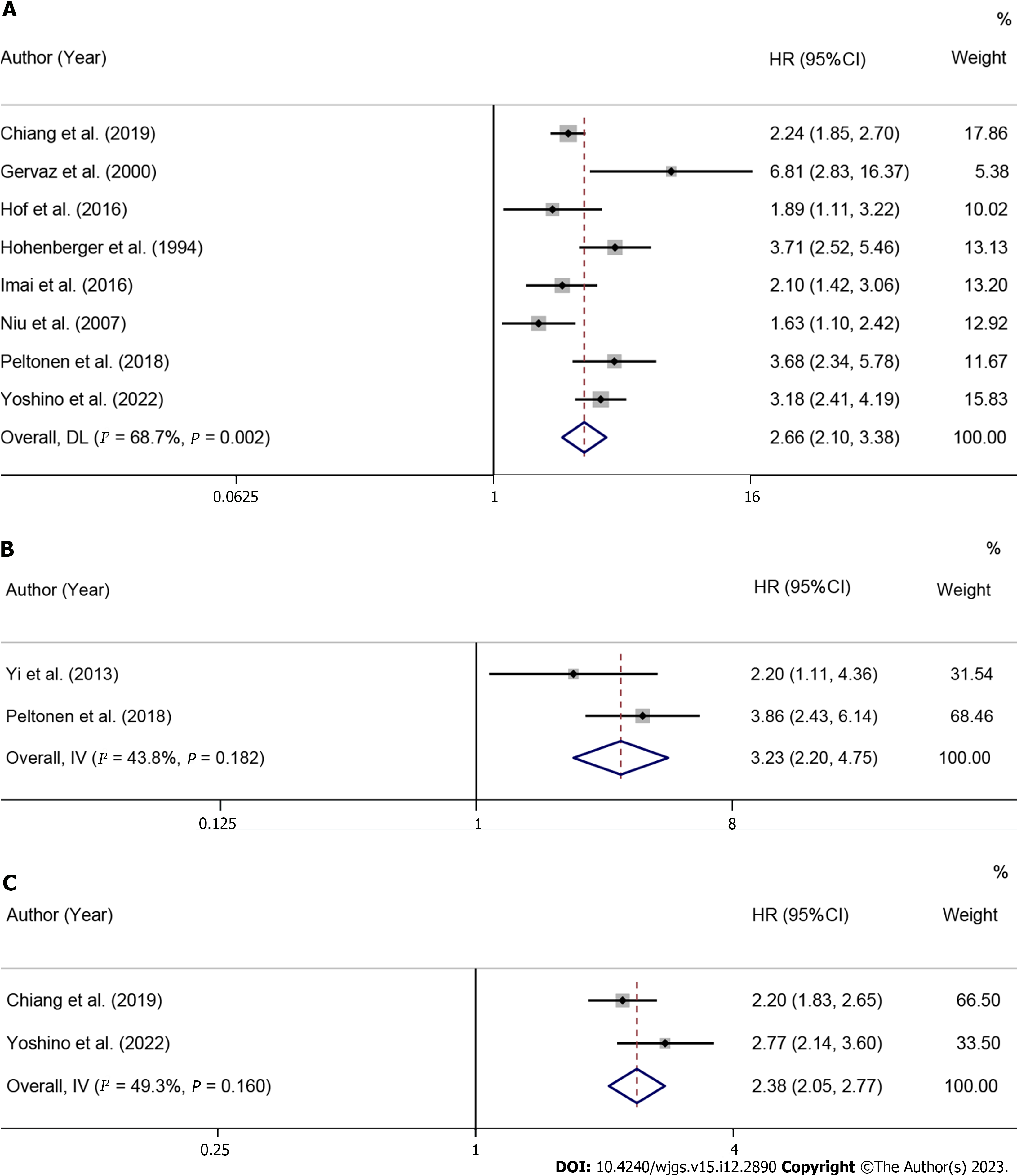
Figure 3 Forest plot of the correlation between high postoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels and overall survival, disease-free survival, recurrence-free survival.
A: Forest plot of the correlation between high postoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels and overall survival; B: Forest plot of the correlation between high postoperative serum CEA levels and disease-free survival; C: Forest plot of the correlation between high postoperative serum CEA levels and recurrence-free survival. HR: Hazard ratio; CI: Confidence interval.
- Citation: Tang F, Huang CW, Tang ZH, Lu SL, Bai T, Huang Q, Li XZ, Zhang B, Wu FX. Prognostic role of serum carcinoembryonic antigen in patients receiving liver resection for colorectal cancer liver metastasis: A meta-analysis. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(12): 2890-2906
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i12/2890.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i12.2890