Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Dec 27, 2023; 15(12): 2855-2865
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i12.2855
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i12.2855
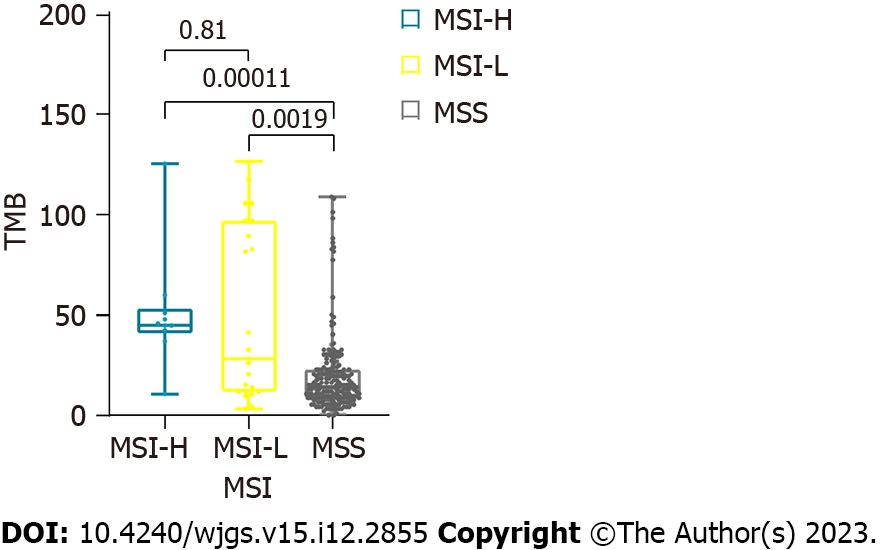
Figure 1 The distribution of tumor mutation burden in microsatellite instability-high, microsatellite instability-low, and microsatellite stable groups.
Tumor mutation burden (TMB) in both microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) and microsatellite instability-low (MSI-L) groups were higher than that in the microsatellite stable group (p < 0.01), whereas no difference was noted between the MSI-H and MSI-L groups. TMB: Tumor mutation burden; MSI-H: Microsatellite instability-high; MSI-L: Microsatellite instability-low; MSS: Microsatellite stable.
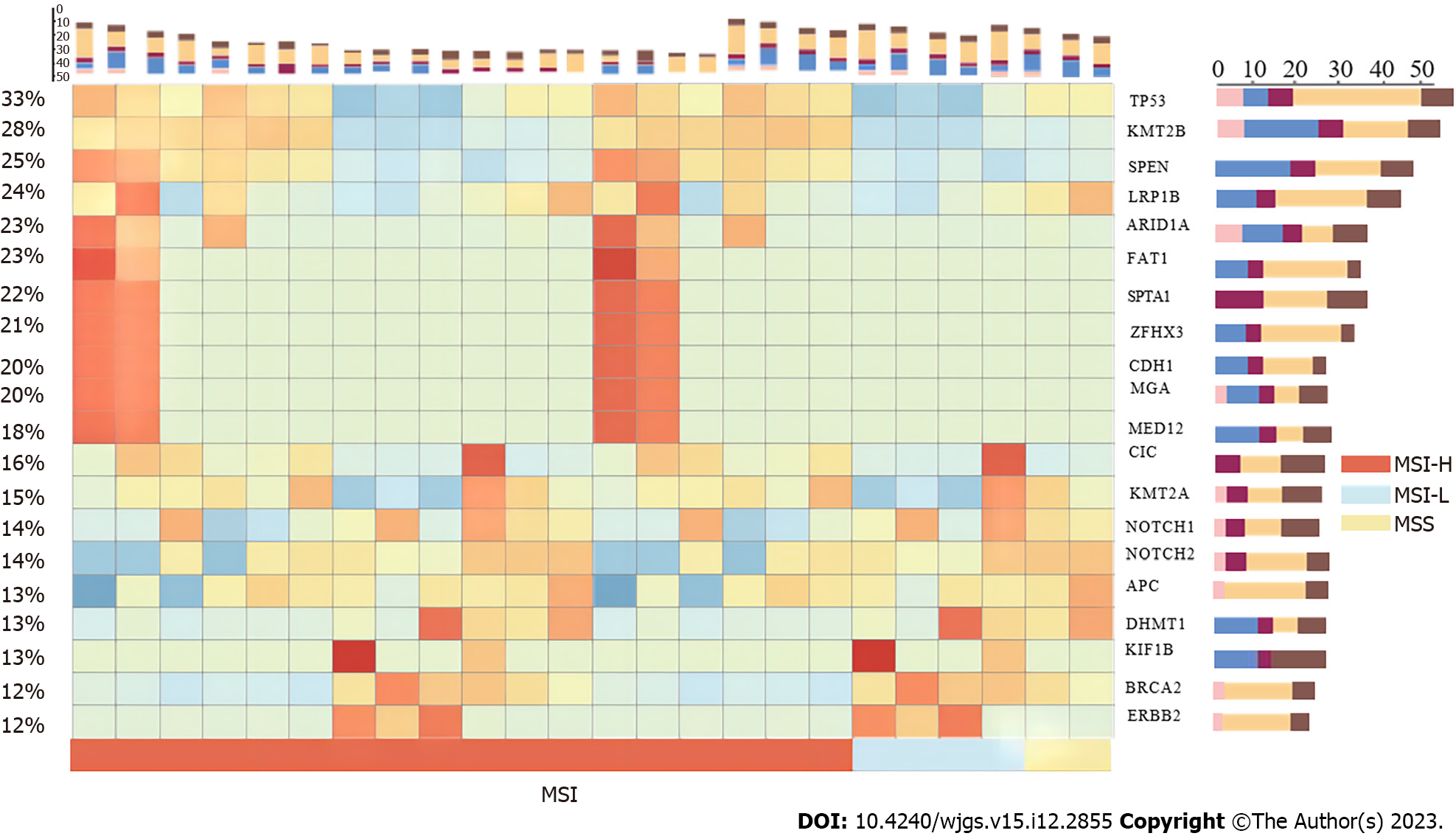
Figure 2 The mutation type and frequency of the top 20 mutated genes in samples clustered by microsatellite instability groups.
TP53 was the top mutated gene in gastric adenocarcinoma. MSI: Microsatellite instability; MSI-H: Microsatellite instability-high; MSI-L: Microsatellite instability-low; MSS: Microsatellite stable.
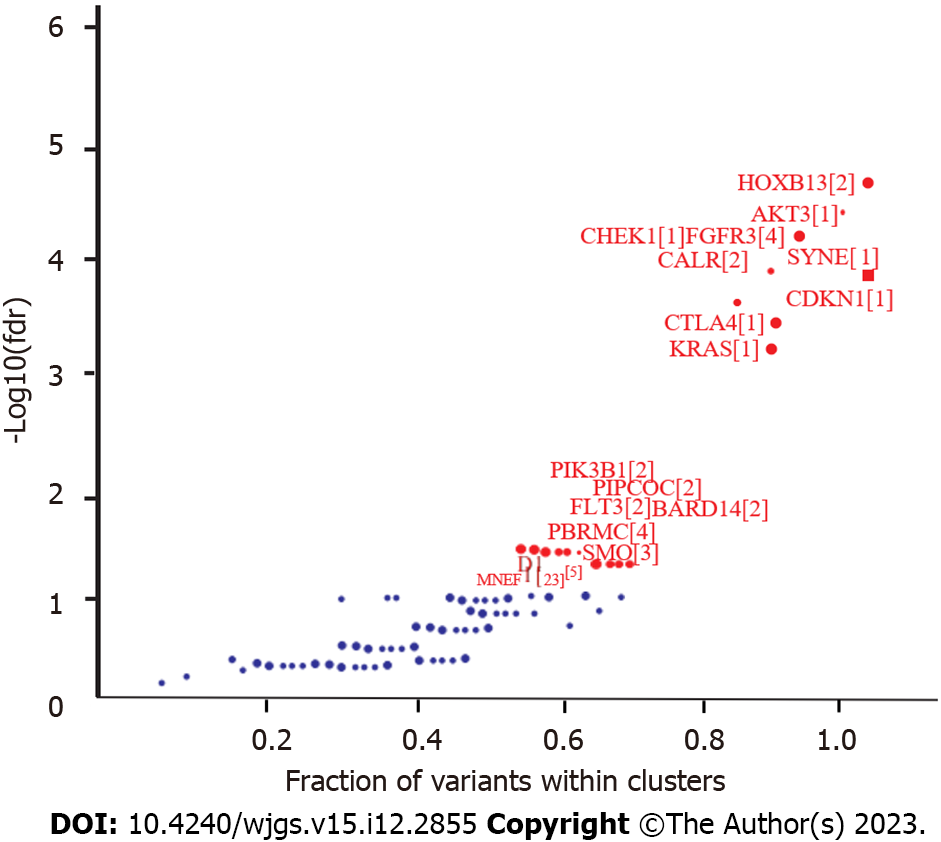
Figure 3
Driver genes identified by OncodriveCLUST in maftools.
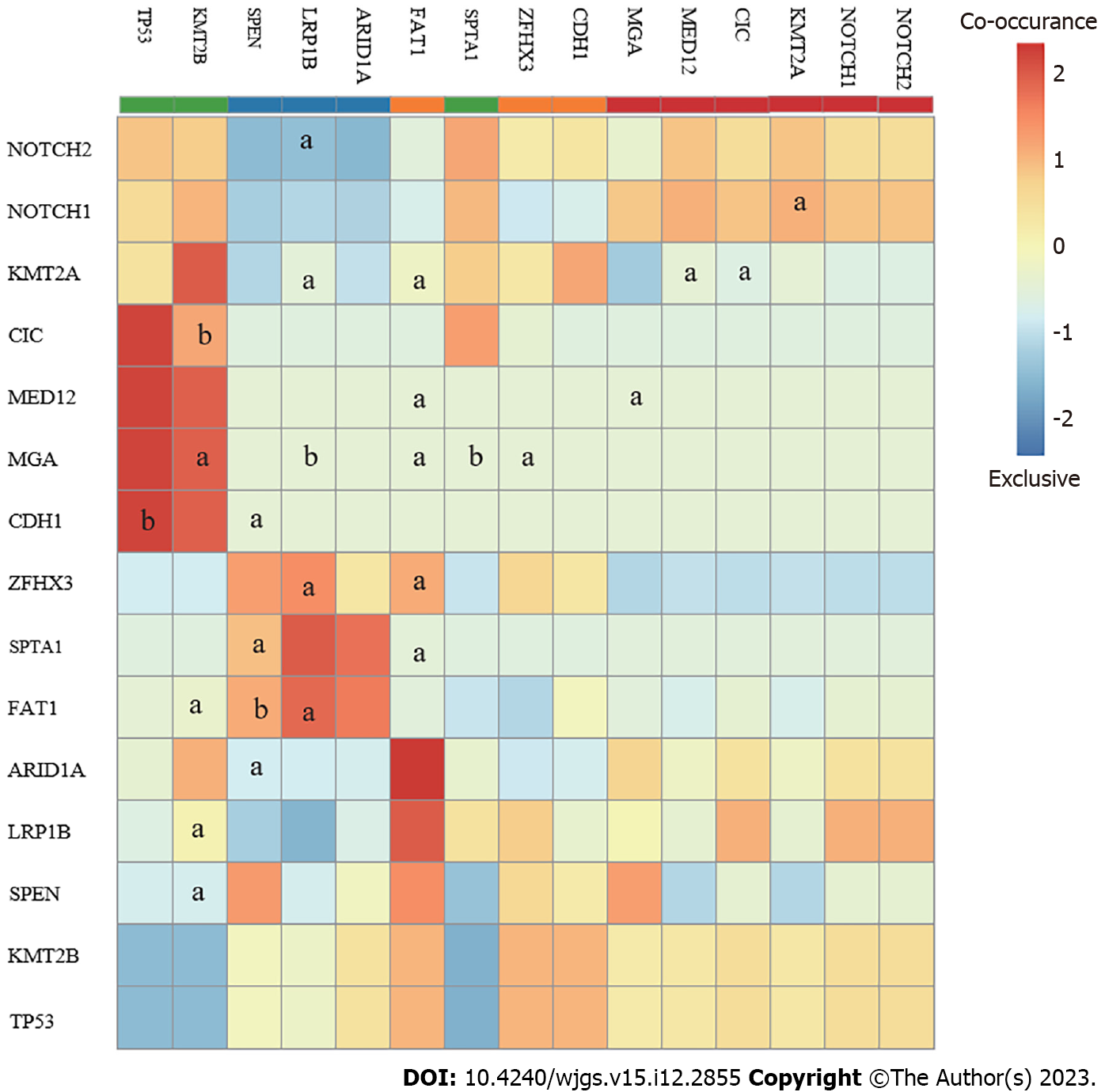
Figure 4 The co-occurrence and exclusion mutation relationships from the top 15 mutated genes in the samples.
TP53 and CDH1 were exclusively mutated with P < 0.1, suggesting two different patterns in the pathogenesis of gastric adenocarcinoma. aP 0.05; bP 0.1.
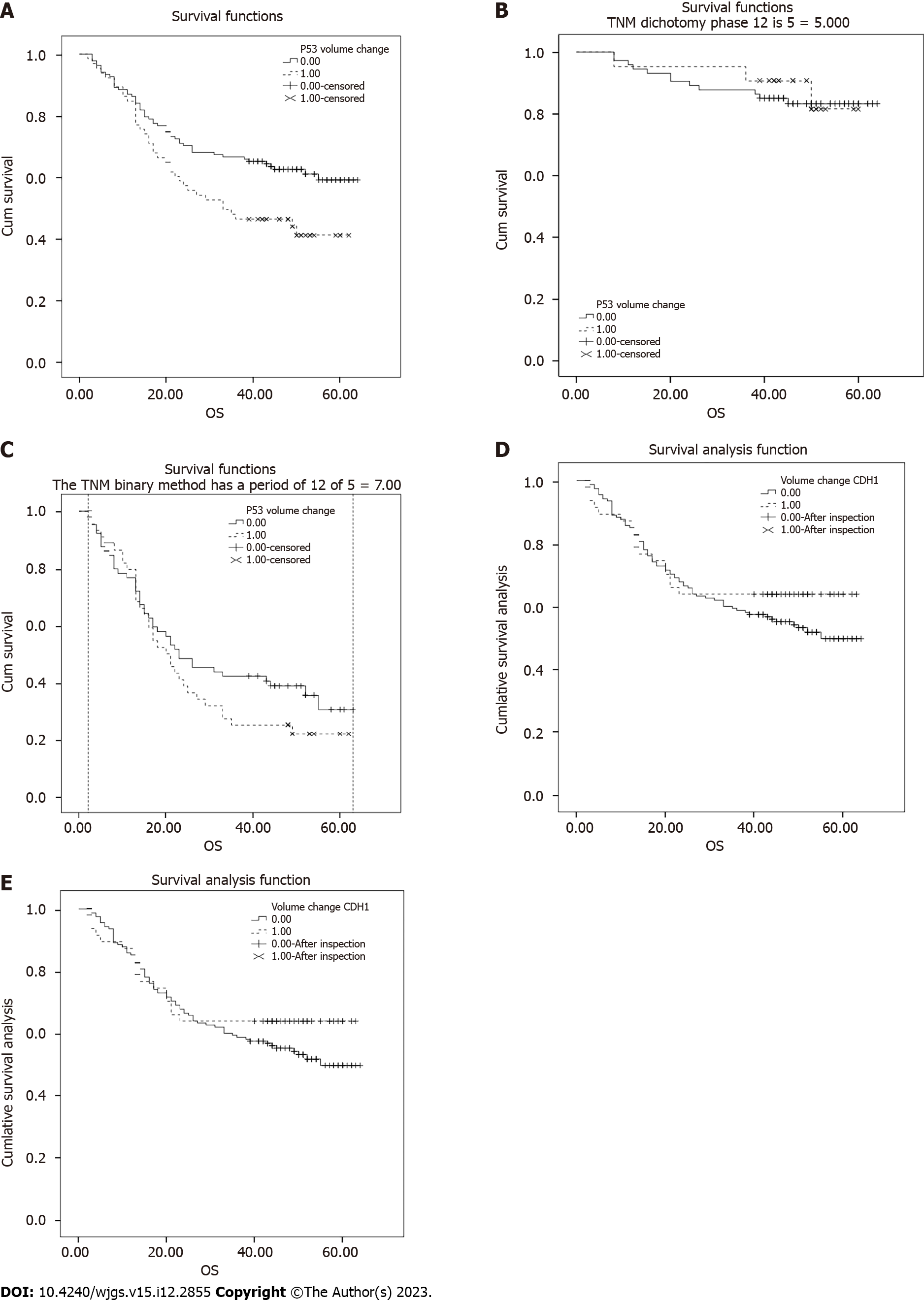
Figure 5 Survival analysis revealed that somatic mutations in TP53.
A: Patients carrying the TP53 somatic mutation had significantly lower 5-year overall survival (OS) than those without the mutation; B and C: TP53 did not affect the OS rate in the early (Ⅰ/Ⅱ, B) or middle-late (Ⅲ/Ⅳ, C) stages; D: CDH1 somatic mutation was not significantly related to the OS; E: Patients with both TP53 and CDH1 mutations had the worst 5-year OS rate. OS: Overall survival.
- Citation: Liu HL, Peng H, Huang CH, Zhou HY, Ge J. Mutational separation and clinical outcomes of TP53 and CDH1 in gastric cancer. World J Gastrointest Surg 2023; 15(12): 2855-2865
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v15/i12/2855.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v15.i12.2855